Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Imagery
- "Nostalgia"
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):i. Published online March 17, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00213

- 1,335 View
- 274 Download
Editorial
- Appreciation to peer reviewers in 2023
- So-Young Park
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):1-3. Published online January 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01361
- 1,215 View
- 221 Download
Review articles
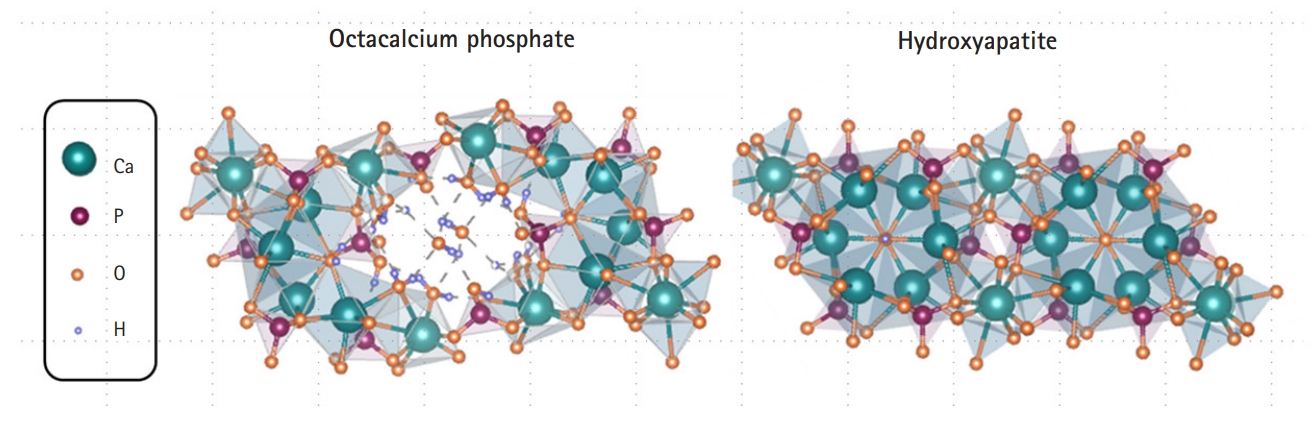
- Octacalcium phosphate, a promising bone substitute material: a narrative review
- Jooseong Kim, Sukyoung Kim, Inhwan Song
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):4-12. Published online May 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00010
- 2,730 View
- 156 Download
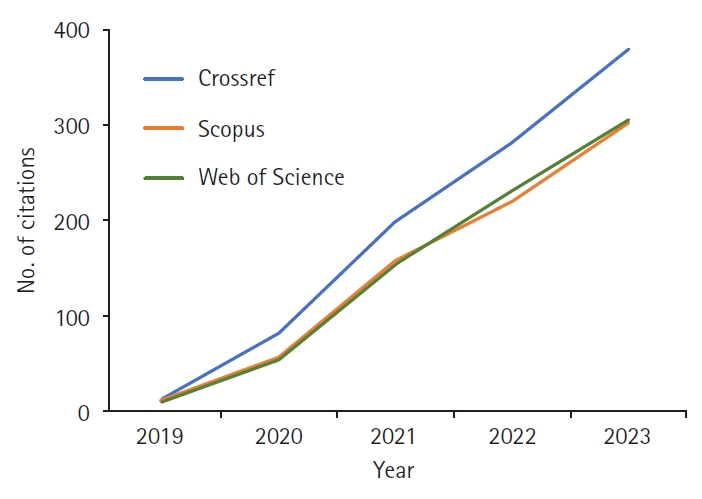
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Biomaterials have been used to supplement and restore function and structure by replacing or restoring parts of damaged tissues and organs. In ancient times, the medical use of biomaterials was limited owing to infection during surgery and poor surgical techniques. However, in modern times, the medical applications of biomaterials are diversifying owing to great developments in material science and medical technology. In this paper, we introduce biomaterials, focusing on calcium phosphate ceramics, including octacalcium phosphate, which has recently attracted attention as a bone graft material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Hydroxyapatite Coatings for Orthopaedic Implants from Colloidal Solutions: Part 1—Effect of Solution Concentration and Deposition Kinetics
Bríd Murphy, Mick A. Morris, Jhonattan Baez
Nanomaterials.2023; 13(18): 2577. CrossRef
- Development of Hydroxyapatite Coatings for Orthopaedic Implants from Colloidal Solutions: Part 1—Effect of Solution Concentration and Deposition Kinetics
- Role of gene therapy in treatment of cancer with craniofacial regeneration—current molecular strategies, future perspectives, and challenges: a narrative review
- Himanshu Singh
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):13-21. Published online May 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00073
- 1,376 View
- 63 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gene therapy involves the introduction of foreign genetic material into host tissue to alter the expression of genetic products. Gene therapy represents an opportunity to alter the course of various diseases. Hence, genetic products utilizing safe and reliable vectors with improved biotechnology will play a critical role in the treatment of various diseases in the future. This review summarizes various important vectors for gene therapy along with modern techniques for potential craniofacial regeneration using gene therapy. This review also explains current molecular approaches for the management and treatment of cancer using gene therapy. The existing literature was searched to find studies related to gene therapy and its role in craniofacial regeneration and cancer treatment. Various databases such as PubMed, Science Direct, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar were searched for English language articles using the keywords “gene therapy,” “gene therapy in present scenario,” “gene therapy in cancer,” “gene therapy and vector,” “gene therapy in diseases,” and “gene therapy and molecular strategies.”
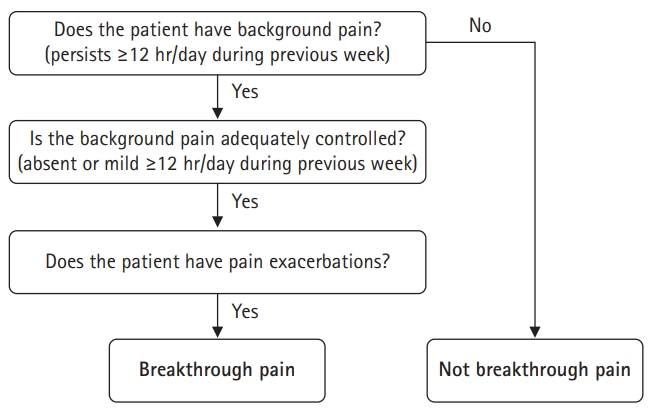
- Breakthrough pain and rapid-onset opioids in patients with cancer pain: a narrative review
- Jinseok Yeo
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):22-29. Published online June 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00367
- 5,449 View
- 230 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Breakthrough pain is transitory pain that occurs despite the use of opioids for background pain control. Breakthrough pain occurs in 40% to 80% of patients with cancer pain. Despite effective analgesic therapy, patients and their caregivers often feel that their pain is not sufficiently controlled. Therefore, an improved understanding of breakthrough pain and its management is essential for all physicians caring for patients with cancer. This article reviews the definition, clinical manifestations, accurate diagnostic strategies, and optimal treatment options for breakthrough pain in patients with cancer. This review focuses on the efficacy and safety of rapid-onset opioids, which are the primary rescue drugs for breakthrough pain.
Original articles
- The characteristics of elderly suicidal attempters in the emergency department in Korea: a retrospective study
- Ji-Seon Jang, Wan-Seok Seo, Bon-Hoon Koo, Hey-Geum Kim, Seok-Ho Yun, So-Hey Jo, Dae-Seok Bai, Young-Gyo Kim, Eun-Jin Cheon
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):30-38. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01004

- 1,079 View
- 58 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Although Korea ranks first in the suicide rate of elderly individuals, there is limited research on those who attempt suicide, with preventive measures largely based on population-based studies. We compared the demographic and clinical characteristics of elderly individuals who attempted suicide with those of younger adults who visited the emergency department after suicide attempts and identified the factors associated with lethality in the former group.
Methods
Individuals who visited the emergency department after a suicide attempt from April 1, 2017, to January 31, 2020, were included. Participants were classified into two groups according to age (elderly, ≥65 years; adult, 18–64 years). Among the 779 adult patients, 123 were elderly. We conducted a chi-square test to compare the demographic and clinical features between these groups and a logistic regression analysis to identify the risk factors for lethality in the elderly group.
Results
Most elderly participants were men, with no prior psychiatric history or suicide attempts, and had a higher prevalence of underlying medical conditions and attributed their attempts to physical illnesses. Being sober and planning suicide occurred more frequently in this group. In the elderly group, factors that increased the mortality rate were biological male sex (p<0.05), being accompanied by family members (p<0.05), and poisoning as a suicide method (p<0.01).
Conclusion
Suicide attempts in elderly individuals have different characteristics from those in younger adults and are associated with physical illness. Suicides in the former group are unpredictable, deliberate, and fatal. Therefore, tailored prevention and intervention strategies addressing the characteristics of those who are elderly and attempt suicide are required.
- Incidence and severity of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients with osteoporosis using data from a Korean nationwide sample cohort in 2002 to 2019: a retrospective study
- Su-Youn Ko, Tae-Yoon Hwang, Kiwook Baek, Chulyong Park
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):39-44. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01116

- 1,377 View
- 69 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is a significant concern, particularly among patients taking bisphosphonates (BPs), denosumab, and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) for osteoporosis. Despite the known risks, large-scale cohort studies examining the incidence and severity of MRONJ are lacking. We aimed to ascertain the incidence and risk of MRONJ among these patients, whom we stratified by age groups, medication types, and duration of use.
Methods
We utilized data from the National Health Insurance Service’s sample cohort database, focusing on patients aged 40 years and above diagnosed with osteoporosis. The patients were divided into three groups: those prescribed BPs only, those prescribed SERMs only, and those prescribed both.
Results
The overall incidence rate of MRONJ was 0.17%. A significantly higher incidence rate was observed among those taking osteoporosis medications, particularly among females with a relative risk of 4.99 (95% confidence interval, 3.21–7.74). The SERM group also had an incidence rate comparable to that of the BP group. Severity was assessed based on the invasiveness of the treatment methods, with 71.3% undergoing invasive treatment in the medication group.
Conclusion
This study provides valuable insights into the incidence and severity of MRONJ among a large cohort of patients with osteoporosis. It underscores the need for comprehensive guidance on MRONJ risks across different medication groups and sets the stage for future research focusing on specific populations and treatment outcomes.
Case reports
- Sciatic neurotmesis and periostitis ossificans progressiva due to a traumatic/unexpected glass injury: a case report
- Berkay Yalçınkaya, Hasan Ocak, Ahmet Furkan Çolak, Levent Özçakar
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):45-47. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01018

- 837 View
- 62 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Peripheral nerves may be affected or injured for several reasons. Peripheral nerve damage can result from trauma, surgery, anatomical abnormalities, entrapment, systemic diseases, or iatrogenic injuries. Trauma and iatrogenic injuries are the most common causes. The ulnar, median, and radial nerves are the most injured nerves in the upper extremities, while the sciatic and peroneal nerves are the most injured nerves in the lower extremities. The clinical symptoms of peripheral nerve damage include pain, weakness, numbness/tingling, and paresthesia. Therefore, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of peripheral nerve injuries are crucial. If a peripheral nerve injury is left untreated, it can lead to severe complications and significant morbidity. The sciatic nerve is one of the most affected nerves. This nerve is generally injured by trauma and iatrogenic causes. Children are more susceptible to trauma than adults. Therefore, sciatic nerve injuries are observed in pediatric patients. When the sciatic nerve is damaged, pain, weakness, sensory loss, and gait disturbances can occur. Therefore, the diagnosis and treatment of sciatic nerve injuries are important to avoid unexpected consequences. Ultrasound can play an important role in the diagnosis of peripheral nerve injury and the follow-up of patients. The aim of this case report is twofold. First, we aimed to emphasize the critical role of ultrasonographic evaluation in the diagnosis of peripheral nerve injuries and pathologies. Second, we aimed to present this case, which has distinguishing features, such as the existence of periostitis ossificans progressiva with sciatic neurotmesis due to a traumatic glass injury.
- DaVinci SP-based simultaneous bilateral partial nephrectomy from the midline transperitoneal approach: a case report
- Young Hwii Ko, Jong Gyun Ha, Jae Yoon Jang, Yeung Uk Kim
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):48-52. Published online January 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01032

- 809 View
- 37 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - While simultaneous bilateral partial nephrectomy with a conventional multiport robot has been consistently reported since the 2010s, the introduction of the DaVinci SP system (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) could provide a novel way to perform surgery on bilateral kidneys while innovatively reducing the number of incisions. In our first report worldwide, the patient with bilateral small renal mass (2.0 cm for the left and 1.5 cm for the right side) and preoperative normal renal function was placed in the lateral decubitus position on an inverted bed. After tilting the bed to be as horizontal as possible, a 4-cm incision was made in the lower part of the umbilicus for the floating trocar technique. The partial nephrectomy was performed reliably as with the conventional transperitoneal approach, and then the patient could be repositioned to the contralateral side for the same procedure, maintaining all trocars. Total operation time (skin to skin), total console time, and the left- and right-side warm ischemic times were 260, 164, 27, and 23 minutes, respectively, without applying the early declamping technique. The estimated blood loss was 200 mL. The serum creatinine right after the operation, on the first day, 3 days, and 90 days after surgery were 0.92, 0.77, 0.79, and 0.81 mg/dL, respectively. For 90 days after the procedure, no complications or radiologic recurrence were observed. Further clinical studies will reveal the advantages of using the DaVinci SP device for this procedure over traditional multiport surgery, maximizing the benefit of a single port-based approach.
Communications
- The applicability of noncontact sensors in the field of rehabilitation medicine
- Yoo Jin Choo, Jun Sung Moon, Gun Woo Lee, Wook-Tae Park, Min Cheol Chang
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):53-55. Published online December 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01144

- 947 View
- 49 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A noncontact sensor field is an innovative device that can detect, measure, or monitor physical properties or conditions without direct physical contact with the subject or object under examination. These sensors use a variety of methods, including electromagnetic, optical, and acoustic technique, to collect information about the target without physical interaction. Noncontact sensors find wide-ranging applications in various fields such as manufacturing, robotics, automobiles, security, environmental monitoring, space industry, agriculture, and entertainment. In particular, they are used in the medical field, where they provide continuous monitoring of patient conditions and offer opportunities in rehabilitation medicine. This article introduces the potential of noncontact sensors in the field of rehabilitation medicine.
Image vignette
- Dynamic ultrasound examination of the median nerve during follow-up after wrist fracture/surgery
- Ahmet Furkan Çolak, Ayşe İrem Yeşiloğlu, Alpaslan Fatih Kaynar, Bayram Kaymak, Levent Özçakar
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):56-57. Published online January 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01291

- 545 View
- 36 Download
Resident fellow section: Teaching images
- Ultrasound assessment of a supraclavicular lipoma entrapping the brachial plexus: a diagnostic insight
- Wei-Ting Wu, Ke-Vin Chang, Kamal Mezian, Vincenzo Ricci, Levent Özçakar
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024;41(1):58-60. Published online December 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01284

- 1,055 View
- 46 Download

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



