Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Ahead-of print
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Ahead-of print
Articles in E-pub version are posted online ahead of regular printed publication.
Original article
- Outcomes in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest according to prehospital advanced airway management timing: a retrospective observational study
- Sang-Hun Lee, Hyun Wook Ryoo
- Received April 1, 2024 Accepted May 9, 2024 Published online July 18, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2024.00332 [Epub ahead of print]

- 173 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), guidelines recommend advanced airway (AA) management at the advanced cardiovascular life support stage; however, the ideal timing remains controversial. Therefore, we evaluated the prognosis according to the timing of AA in patients with OHCA.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective observational study of patients with OHCA at six major hospitals in Daegu Metropolitan City, South Korea, from August 2019 to June 2022. We compared groups with early and late AA and evaluated prognosis, including recovery of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), survival to discharge, and neurological evaluation, according to AA timing.
Results
Of 2,087 patients with OHCA, 945 underwent early AA management and 1,142 underwent late AA management. The timing of AA management did not influence ROSC in the emergency department (5–6 minutes: adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.97; p=0.914; 7–9 minutes: aOR, 1.37; p=0.223; ≥10 minutes: aOR, 1.32; p=0.345). The timing of AA management also did not influence survival to discharge (5–6 minutes: aOR, 0.79; p=0.680; 7–9 minutes: aOR, 1.04; p=0.944; ≥10 minutes: aOR, 1.86; p=0.320) or good neurological outcomes (5–6 minutes: aOR, 1.72; p=0.512; 7–9 minutes: aOR, 0.48; p=0.471; ≥10 minutes: aOR, 0.96; p=0.892).
Conclusion
AA timing in patients with OHCA was not associated with ROSC, survival to hospital discharge, or neurological outcomes.
Review article
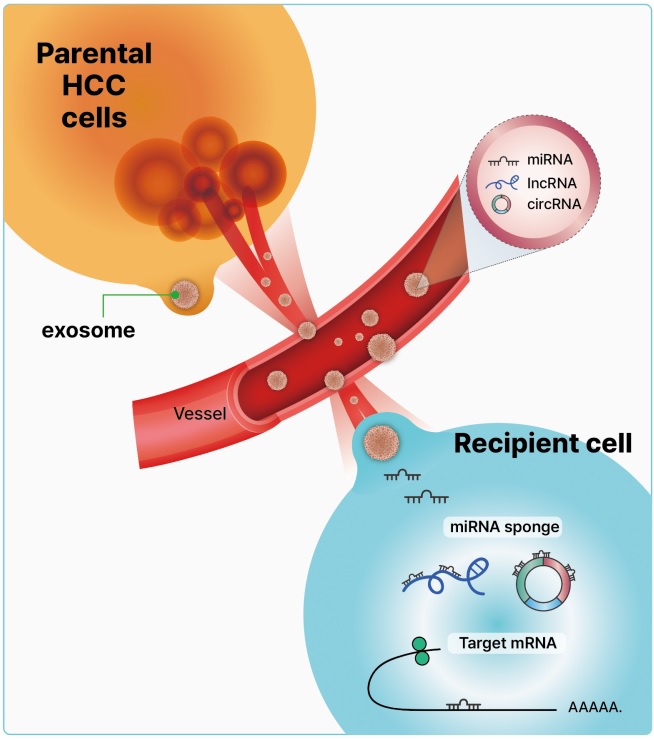
- Clinical significance of exosomal noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: a narrative review
- Jae Sung Yoo, Min Kyu Kang
- Received October 30, 2023 Accepted December 30, 2023 Published online February 8, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.01186 [Epub ahead of print]
- 1,117 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal malignancies worldwide, with poor prognosis owing to its high frequency of recurrence and metastasis. Moreover, most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage owing to a lack of early detection markers. Exosomes, which are characterized by their cargos of stable intracellular messengers, such as DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids, play a crucial role in regulating cell differentiation and HCC development. Recently, exosomal noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs), including microRNAs, long ncRNAs, and circular RNAs, have become increasingly important diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive markers of HCC. Herein, we discuss the clinical implications of exosomal ncRNAs, specifically those within the HCC regulatory network.
Imagery
- Cosmos in full autumn
- Published online January 24, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2024.00052 [Epub ahead of print]

- 496 View
- 3 Download

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine First
First Prev
Prev



