Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Review articles
- Gallbladder polyps: evolving approach to the diagnosis and management
- Kook Hyun Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):1-9. Published online May 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00213

- 23,597 View
- 485 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Gallbladder (GB) polyp is a mucosal projection into the GB lumen. With increasing health awareness, GB polyps are frequently found using ultrasonography during health screening. The prevalence of GB polyps ranges between 1.3% and 9.5%. Most patients are asymptomatic and have benign characteristics. Of the nonneoplastic polyps, cholesterol polyps are most common, accounting for 60%–70% of lesions. However, a few polyps have malignant potential. Currently, the guidelines recommend laparoscopic cholecystectomy for polyps larger than 1 cm in diameter due to their malignan potential. The treatment algorithm can be influenced by the size, shape, and numbers of polyps, old age (>50 years), the presence of primary sclerosing cholangitis, and gallstones. This review summarizes the commonly recognized concepts on GB polyps from diagnosis to an algorithm of treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder endoscopic mucosal resection: a pilot porcine study
Huifang Pang, Quan Man, Li Min, Zheng Zhang, Shengtao Zhu, Shuyue Yang, Yao Xu, Haijun Hou, Shutian Zhang, Peng Li
Minimally Invasive Therapy & Allied Technologies.2023; 32(1): 24. CrossRef - The link between Helicobacter pylori infection and gallbladder and biliary tract diseases: A review
Klay Puay Khim Lim, Aaron Jia Loong Lee, Xiuting Jiang, Thomas Zheng Jie Teng, Vishal G. Shelat
Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery.2023; 27(3): 241. CrossRef - The gallbladder: what’s new in 2022?
Rachel Runde, Edward D. Auyang, Raye Ng, Kaysey Llorente, Hina Arif Tiwari, Shana Elman, William M. Thompson
Abdominal Radiology.2022; 48(1): 2. CrossRef - Gallbladder polyps: diagnosis and treatment tactics (literature review)
S. N. Perekhodov, D. V. Nikolaev, S. S. Saidov
Bulletin of the Medical Institute "REAVIZ" (REHABILITATION, DOCTOR AND HEALTH).2021; 11(4): 88. CrossRef - Is there a role for growth status in distinguishing gallbladder adenomas from cholesterol polyps? – A retrospective study based on 520 cholecystectomy patients
Wenqing Bao, Anan Xu, Shubin Ni, Bo Wang, Humaira Urmi, Bin Zhao, Yongmei You, Hai Hu
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 56(12): 1450. CrossRef - Polyps and cancer of the biliary system (lecture for medical practitioners)
G. V. Shavkuta
South Russian Journal of Therapeutic Practice.2020; 1(2): 78. CrossRef
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder endoscopic mucosal resection: a pilot porcine study
- Classification of endometriosis
- Soo-Young Lee, Yu-Jin Koo, Dae-Hyung Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):10-18. Published online August 7, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00444

- 24,339 View
- 769 Download
- 54 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Endometriosis is a chronic disease associated with pelvic pain and infertility. Several classification systems for the severity of endometriosis have been proposed. Of these, the revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification is the most well-known. The ENZIAN classification was developed to classify deep infiltrating endometriosis and focused on the retroperitoneal structures. The endometriosis fertility index was developed to predict the fertility outcomes in patients who underwent surgery for endometriosis. Finally, the American Association of Gynecological Laparoscopists classification is currently being developed, for which 30 endometriosis experts are analyzing and researching data by assigning scores to categories considered important; however, it has not yet been fully validated and published. Currently, none of the classification systems are considered the gold standard. In this article, we review the classification systems, identify their pros and cons, and discuss what improvements need to be made to each system in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Epidemiology of infertility in women with endometriosis
Umberto Leone Roberti Maggiore, Valentina Chiappa, Marcello Ceccaroni, Giovanni Roviglione, Luca Savelli, Simone Ferrero, Francesco Raspagliesi, Ludovica Spanò Bascio
Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology.2024; 92: 102454. CrossRef - Analysis of VEGF, IGF1/2 and the Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) H19 Expression in Polish Women with Endometriosis
Beata Smolarz, Tomasz Szaflik, Hanna Romanowicz, Magdalena Bryś, Ewa Forma, Krzysztof Szyłło
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(10): 5271. CrossRef - Acupuncture for pain and pain-related disability in deep infiltrating endometriosis
Giulia Chiarle, Gianni Allais, Silvia Sinigaglia, Gisella Airola, Sara Rolando, Fabiola Bergandi, Salvatore Micalef, Chiara Benedetto
Frontiers in Pain Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inguinal hernia following the use of fluid anti-adhesive agents in laparoscopic surgery: a literature review and case report
Man-Jung Chu, Pei-Shen Huang
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(3): 1805. CrossRef - Horizons in Endometriosis: Proceedings of the Montreux Reproductive Summit, 14-15 July 2023
A Vallée, E Saridogan, F Petraglia, J Keckstein, N Polyzos, C Wyns, L Gianaroli, B Tarlatzis, J.M. Ayoubi, A Feki
Facts, Views and Vision in ObGyn.2024; 16(Supplement): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of factors affecting pregnancy rate after laparoscopic surgery for infertility associated with endometriosis
Jinna Zhang, Ningzi Lian, Sang Guo, Xi Xie
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2024; 297: 214. CrossRef - Beyond the surface: Does stage I-II endometriosis impact fertility? Exploring the challenges of mild disease
Begum Aydogan Mathyk, Esra Cetin, Youssef Youssef, Anthony N. Imudia, Diana Encalada Soto, Emad Mikhail, Gaby Moawad
Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology.2024; : 102501. CrossRef - Nerve Bundle Density and Expression of NGF and IL-1β Are Intra-Individually Heterogenous in Subtypes of Endometriosis
Mahfuza Sreya, Dwayne R. Tucker, Jennifer Yi, Fahad T. Alotaibi, Anna F. Lee, Heather Noga, Paul J. Yong
Biomolecules.2024; 14(5): 583. CrossRef - The Known, the Unknown and the Future of the Pathophysiology of Endometriosis
Maria Ariadna Ochoa Bernal, Asgerally T. Fazleabas
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(11): 5815. CrossRef - Changes in the number and activity of natural killer cells and its clinical association with endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis
Getnet Gedefaw Azeze, Ling Wu, Bekalu Kassie Alemu, Chi Chiu Wang, Tao Zhang
F&S Reviews.2024; 5(2): 100072. CrossRef - Resveratrol ameliorates mitochondrial biogenesis and reproductive outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome undergoing assisted reproduction: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Negar Ajabi Ardehjani, Marzieh Agha-Hosseini, Maryam Shabani Nashtaei, Mahshad Khodarahmian, Maryam Shabani, Masoome Jabarpour, Farzane Fereidouni, Tayebeh Rastegar, Fardin Amidi
Journal of Ovarian Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of the Ferroptosis Regulators: Glutathione Peroxidase 4, Acyl-Coenzyme A Synthetase Long-Chain Family Member 4, and Transferrin Receptor 1 in Patient-Derived Endometriosis Tissue
Lidia A. Mielke Cabello, Gabriela Meresman, Dogus Darici, Noelia Carnovale, Birthe Heitkötter, Miriam Schulte, Nancy A. Espinoza-Sánchez, Quang-Khoi Le, Ludwig Kiesel, Sebastian D. Schäfer, Martin Götte
Biomolecules.2024; 14(7): 876. CrossRef - Ultrasound Characteristics and Scanning Techniques of Uterosacral Ligaments for the Diagnosis of Endometriosis
Shae Maple, K Jane Chalmers, Eva Bezak, Katelyn Henry, Nayana Parange
Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.2023; 42(6): 1193. CrossRef - The Influence of Lactoferrin in Plasma and Peritoneal Fluid on Iron Metabolism in Women with Endometriosis
Ewa Skarżyńska, Monika Wróbel, Hanna Zborowska, Mateusz Franciszek Kołek, Grzegorz Mańka, Mariusz Kiecka, Michał Lipa, Damian Warzecha, Robert Spaczyński, Piotr Piekarski, Beata Banaszewska, Artur Jakimiuk, Tadeusz Issat, Wojciech Rokita, Jakub Młodawski,
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1619. CrossRef - Long Non-Coding RNA SNHG4 Expression in Women with Endometriosis: A Pilot Study
Tomasz Szaflik, Hanna Romanowicz, Krzysztof Szyłło, Beata Smolarz
Genes.2023; 14(1): 152. CrossRef - Epidemiological and Immune Profile Analysis of Italian Subjects with Endometriosis and Multiple Sclerosis
Brunella Zizolfi, Virginia Foreste, Simona Bonavita, Valentina Rubino, Giuseppina Ruggiero, Vincenzo Brescia Morra, Roberta Lanzillo, Antonio Carotenuto, Francesca Boscia, Maurizio Taglialatela, Maurizio Guida
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(5): 2043. CrossRef - Rectal endometriosis imaging: A case based pictorial essay
Garvit D. Khatri, Deepashri Basavalingu, Nitin Chaubal, Manjiri Dighe
WFUMB Ultrasound Open.2023; 1(1): 100002. CrossRef - KRAS mutations and endometriosis burden of disease
Natasha L Orr, Arianne Albert, Yang Doris Liu, Amy Lum, JooYoon Hong, Catalina L Ionescu, Janine Senz, Tayyebeh M Nazeran, Anna F Lee, Heather Noga, Kate Lawrenson, Catherine Allaire, Christina Williams, Mohamed A Bedaiwy, Michael S Anglesio, Paul J Yong
The Journal of Pathology: Clinical Research.2023; 9(4): 302. CrossRef - The Clinical Presentation of Endometriosis and Its Association to Current Surgical Staging
Matilda Shaked Ashkenazi, Ole Linvåg Huseby, Gard Kroken, Marcela Trocha, Aurora Henriksson, Hanna Jasiak, Karen Cuartas, Alessandra Loschiavo, Isabella Kuhn, Dina Støve, Hanna Grindahl, Emilia Latour, Mathias Melbø, Katrine Holstad, Sebastian Kwiatkowski
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(7): 2688. CrossRef - Evaluation and management of endometriosis
T. Yoldemir
Climacteric.2023; 26(3): 248. CrossRef - COX isozymes and non-uniform neoangiogenesis: What is their role in endometriosis?
Andrea Caruana, Charles Savona-Ventura, Jean Calleja-Agius
Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators.2023; 167: 106734. CrossRef - Time to move beyond surgical classification systems for endometriosis
María Isabel Hernández Cardona, Christana Ajewole, Hannah Lewis, Jorge F. Carrillo, Mario E. Castellanos, Stefanie Barish, Juan Diego Villegas Echeverri, Georgine Lamvu
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2023; 163(1): 58. CrossRef - Antimüllerian hormone (AMH) and age as predictors of preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies (PGT-A) cycle outcomes and blastocyst quality on day 5 in women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF)
A. Arnanz, A. Bayram, I. Elkhatib, A. Abdala, A. El-Damen, R. Patel, B. Lawrenz, L. Melado, H. Fatemi, N. De Munck
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics.2023; 40(6): 1467. CrossRef - Association between polymorphisms of cytokine genes and endometriosis: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis
Shulin Zhong, Yuzhen Liang, Zhixi Wu, Li Wei
Journal of Reproductive Immunology.2023; 158: 103969. CrossRef - Psychological hallmarks of endometriosis with emphasis on sexual dysfunction, stress, anxiety and depressive symptoms
Ludek Fiala, Jiri Lenz, Zdenek Adamik, Rachel Sajdlova, Daniela Kestlerova, Vaclav Vetvicka
International Clinical Pathology Journal.2023; 10(1): 45. CrossRef - Detection of Endometriosis Lesions Using Gd-Based Collagen I Targeting Probe in Murine Models of Endometriosis
Nazanin Talebloo, Maria Ariadna Ochoa Bernal, Elizabeth Kenyon, Christiane L. Mallett, Asgerally Fazleabas, Anna Moore
Molecular Imaging and Biology.2023; 25(5): 833. CrossRef - Exosomal microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs: as novel biomarkers for endometriosis
Elahe Soltani-Fard, Marzieh Asadi, Sina Taghvimi, Asma Vafadar, Parisa Vosough, Amir Tajbakhsh, Amir Savardashtaki
Cell and Tissue Research.2023; 394(1): 55. CrossRef - Use of the Free Endometriosis Risk Advisor App as a Non-Invasive Screening Test for Endometriosis in Patients with Chronic Pelvic Pain and/or Unexplained Infertility
Camran Nezhat, Ellie Armani, Hsuan-Chih Carolina Chen, Zahra Najmi, Steven R. Lindheim, Ceana Nezhat
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(16): 5234. CrossRef - Endometriosis: Classification, pathophysiology, and treatment options
Elma Pašalić, Murtaza M. Tambuwala, Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić
Pathology - Research and Practice.2023; 251: 154847. CrossRef - Endometriosis Grade 4 in In Vitro Fertilisation and Its Management: A Case Report
Abhijeet Raj, Kshiti P Deshpande, Neema Acharya
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging of Urinary Bladder and Ureteral Endometriosis with Emphasis on Diagnosis and Technique
Anuradha S. Shenoy-Bhangle, Izabela Pires Franco, Lauren J. Ray, Jinjin Cao, Aoife Kilcoyne, Natally Horvat, Luciana Pardini Chamie
Academic Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence, Surgical, and Medical Management of Patients with Endometriosis amongst Indian Women
Roya Rozati, Wajeeda Tabasum, Mohammed Sarosh Ahmed, Aleem Ahmed Khan, Talia Nazeer Ahmed, Sumaiya Nayela, Salwa Sahar Azimi
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences.2023; 5(6): 101. CrossRef - Endometriosis: An Overview
Tanvir Agnihotri, Abheek Ghosh, Ashley Lamba, Charles E. Ray
Seminars in Interventional Radiology.2023; 40(06): 544. CrossRef - Comparison of Clinical and Reproductive Outcomes between Adenomyomectomy and Myomectomy
Kristyna Hlinecka, Michal Mara, Barbora Boudova, Zdenka Lisa, Adela Richtarova, David Kuzel
Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology.2022; 29(3): 392. CrossRef - Evaluating Surgical Complexity of Endoscopic Hysterectomy: An Inter-rater and Intra-rater Agreement Study of Novel Scoring Tool
Meenal Misal, Marlene Girardo, Sadikah Behbehani, Vimee Bindra, Mark R. Hoffman, Wei How Lim, Courtney Martin, Sukrant K. Mehta, Alysha Nensi, Thiers Soares, Deborah Taylor, Steve Wagner, Kelly N. Wright, Megan N. Wasson
Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology.2022; 29(5): 683. CrossRef - MRI in the Diagnosis of Endometriosis and Related Diseases
Aki Kido, Yuki Himoto, Yusaku Moribata, Yasuhisa Kurata, Yuji Nakamoto
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(4): 426. CrossRef - Role of Robotic Surgery in Benign Gynecology
Mireille D. Truong, Lauren N. Tholemeier
Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America.2022; 49(2): 273. CrossRef - NLRP3 activated macrophages promote endometrial stromal cells migration in endometriosis
Feng Zhou, Fanxuan Zhao, Qianmeng Huang, Xiang Lin, Songying Zhang, Yongdong Dai
Journal of Reproductive Immunology.2022; 152: 103649. CrossRef - Endometriosis: A Disease with Few Direct Treatment Options
Patricia Ribeiro de Carvalho França, Anna Carolina Pereira Lontra, Patricia Dias Fernandes
Molecules.2022; 27(13): 4034. CrossRef - The Role of the Immune System in the Development of Endometriosis
Monika Abramiuk, Ewelina Grywalska, Paulina Małkowska, Olga Sierawska, Rafał Hrynkiewicz, Paulina Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej
Cells.2022; 11(13): 2028. CrossRef - Transvaginal Ultrasound vs. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Value in Endometriosis Diagnosis
Alexandra Baușic, Ciprian Coroleucă, Cătălin Coroleucă, Diana Comandașu, Roxana Matasariu, Andrei Manu, Francesca Frîncu, Claudia Mehedințu, Elvira Brătilă
Diagnostics.2022; 12(7): 1767. CrossRef - History of Endometriosis Is Independently Associated with an Increased Risk of Ovarian Cancer
Antonio Sarría-Santamera, Zaukiya Khamitova, Arnur Gusmanov, Milan Terzic, Mar Polo-Santos, Miguel A. Ortega, Angel Asúnsolo
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(8): 1337. CrossRef - Surgical Classification of Endometriosis
João Nogueira Neto, Mauricio Simões Abrão, Eduardo Schor, Julio Cesar Rosa-e-Silva
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia / RBGO Gynecology and Obstetrics.2022; 44(08): 737. CrossRef - Analysis of Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) UCA1, MALAT1, TC0101441, and H19 Expression in Endometriosis
Tomasz Szaflik, Hanna Romanowicz, Krzysztof Szyłło, Radosław Kołaciński, Magdalena M. Michalska, Dariusz Samulak, Beata Smolarz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11583. CrossRef - Colorectal infiltrating deep endometriosis: Laparoscopic treatment. A case report
Giuseppe Di Buono, Matilde Micheli, Gaia Russo, Roberta Vella, Giuseppe Amato, Girolamo Geraci, Antonino Agrusa
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Aged garlic extract as a potential prophylactic to reduce the progression of endometriosis and associated pain burden
Emily Redwood, Virginie Lam, Ryusuke Takechi, Deborah Anne Kerr, Connie Jackaman, Arazu Sharif, John Charles Louis Mamo
Frontiers in Pain Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Histotyping and grading of endometriosis and its association with clinico-pathological parameters
Jyothika Litson, Rini Agnes, Gayatri Ravikumar
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2022; 42(8): 3628. CrossRef - Plasma and Peritoneal Fluid Fibronectin and Collagen IV Levels as Potential Biomarkers of Endometriosis
Damian Warzecha, Julia Załęcka, Grzegorz Mańka, Mariusz Kiecka, Michał Lipa, Robert Spaczyński, Piotr Piekarski, Beata Banaszewska, Artur Jakimiuk, Tadeusz Issat, Wojciech Rokita, Jakub Młodawski, Maria Szubert, Piotr Sieroszewski, Grzegorz Raba, Kamil Sz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15669. CrossRef - Progestins in the symptomatic management of endometriosis: a meta-analysis on their effectiveness and safety
Jon-Benay Mitchell, Sarentha Chetty, Fatima Kathrada
BMC Women's Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of CDKN2B-AS1 on cellular proliferation, invasion and AKT3 expression are attenuated by miR-424-5p in a model of ovarian endometriosis
Sixue Wang, Mingyu Yi, Xinyue Zhang, Tingting Zhang, Li Jiang, Le Cao, Yuxin Zhou, Xiaoling Fang
Reproductive BioMedicine Online.2021; 42(6): 1057. CrossRef - Structured report for dynamic ultrasonography in patients with suspected or known endometriosis: Recommendations of the International Society for Gynecologic Endoscopy (ISGE)
Dusan Djokovic, Patrícia Pinto, Bruno J. van Herendael, Antonio Simone Laganà, Viju Thomas, Jörg Keckstein
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2021; 263: 252. CrossRef - Stigma and Endometriosis: A Brief Overview and Recommendations to Improve Psychosocial Well-Being and Diagnostic Delay
Omar T. Sims, Jhumka Gupta, Stacey A. Missmer, Irene O. Aninye
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(15): 8210. CrossRef - AAGL 2021 Endometriosis Classification: An Anatomy-based Surgical Complexity Score
Mauricio S. Abrao, Marina Paula Andres, Charles E. Miller, Julian A. Gingold, Mariona Rius, Joao Siufi Neto, Francisco Carmona
Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology.2021; 28(11): 1941. CrossRef - Involvement of bradykinin and bradykinin B1 receptor in patients with endometriosis
Xin Meng, Ying Li, Qingxue Li, Jian Yang, Mingli An, Xinping Fu, Shuancheng Zhang, Jingwei Chen
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Epidemiology of infertility in women with endometriosis
- Updates on the treatment of adhesive capsulitis with hydraulic distension
- Jang Hyuk Cho
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):19-26. Published online August 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00535
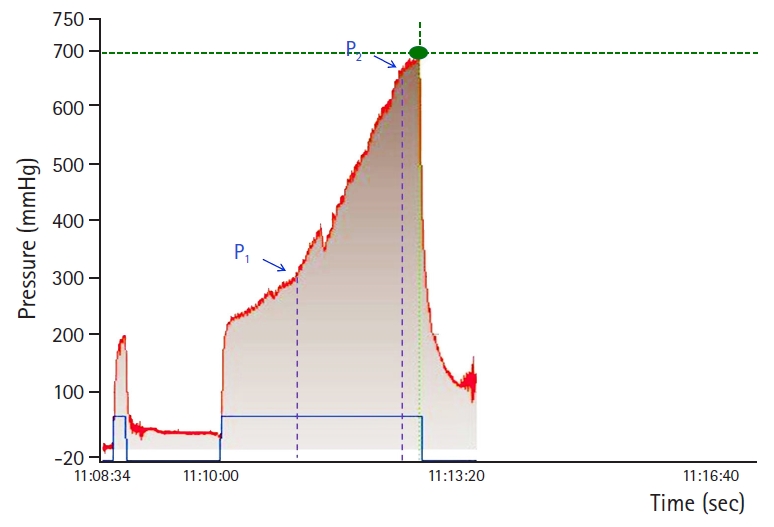
- 9,373 View
- 237 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder joint is a common disease characterized by pain at the insertional area of the deltoid muscle and decreased range of motion. The pathophysiological process involves fibrous inflammation of the capsule and intraarticular adhesion of synovial folds leading to capsular thickening and contracture. Regarding the multidirectional limitation of motion, a limitation in external rotation is especially prominent, which is related to not only global fibrosis but also to a localized tightness of the anterior capsule. Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging studies can be applied to rule out other structural lesions in the diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis. Hydraulic distension of the shoulder joint capsule provides pain relief and an immediate improvement in range of motion by directly expanding the capsule along with the infusion of steroids. However, the optimal technique for hydraulic distension is still a matter of controversy, with regards to the infusion volume and rupture of the capsule. By monitoring the real-time pressure-volume profile during hydraulic distension, the largest possible fluid volume can be infused without rupturing the capsule. The improvement in clinical outcomes is shown to be greater in capsule-preserved hydraulic distension than in capsule-ruptured distension. Moreover, repeated distension is possible, which provides additional clinical improvement. Capsule-preserved hydraulic distension with maximal volume is suggested to be an efficacious treatment option for persistent adhesive capsulitis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rotator Interval vs Posterior Approach Ultrasound-guided Corticosteroid Injections in Primary Frozen Shoulder: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Francisco Javier Arrambide-Garza, Juventino Tadeo Guerrero-Zertuche, Neri Alejandro Alvarez-Villalobos, Alejandro Quiroga-Garza, Abraham Espinosa-Uribe, Felix Vilchez-Cavazos, Yolanda Salinas-Alvarez, Juan Antonio Rivera-Perez, Rodrigo Enrique Elizondo-Om
Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.2024; 105(4): 760. CrossRef - A prospective, randomized, blinded study on the efficacy of using corticosteroids in hydrodilatation as a treatment for adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder
Joan Tomàs Gebellí-Jové, Antonio Buñuel-Viñau, Marta Canela-Capdevila, Jordi Camps, Fàtima Sabench, Petrea Iftimie-Iftimie
Shoulder & Elbow.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Frozen Shoulder: Diagnosis and Management
Sean R. Wise, Paul Seales, Alex P. Houser, Chase B. Weber
Current Sports Medicine Reports.2023; 22(9): 307. CrossRef - Ultrasound-guided hydrodilatation of glenohumeral joint combined with acupotomy for treatment of frozen shoulder
Huajun Xu, Yingchun Zhang, Caishan Wang
Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation.2022; 35(5): 1153. CrossRef - Impact of capsular preservation on patient-reported outcomes and complication rates in total hip arthroplasty using the direct anterior approach
Vincent A. Stadelmann, Hannes A. Rüdiger, Selina Nauer, Michael Leunig
The Bone & Joint Journal.2022; 104-B(7): 826. CrossRef - Management of Patients with Adhesive Capsulitis via Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodilatation without Concomitant Intra-Articular Lidocaine Infusion: A Single-Center Experience
Yung-Chieh Chen, Shu-Huei Shen, Hong-Jen Chiou, Yung-Liang Wan
Life.2022; 12(9): 1293. CrossRef - Role of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Adhesive Capsulitis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Syed Imran Haider, Muhammad Zarak Awais, Muhammad Tahir Iqbal
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Musculoskeletal complications in patients with diabetes mellitus
Jong Han Choi, Hae-Rim Kim, Kee-Ho Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(6): 1099. CrossRef - Comparison of the spread pattern of medial-to-lateral and lateral-to-medial rotator interval injections: A cadaveric study
Benjamin J. Kozlowski, John Tran, Philip W.H. Peng, Anne M.R. Agur, Nimish Mittal
Interventional Pain Medicine.2022; 1(4): 100164. CrossRef - Updates on Intra-articular Corticosteroid Injection for the Treatment of Adhesive Capsulitis
Ju Heon Oh, In Ho Jung, Eun Woo Park, Jang Hyuk Cho
Keimyung Medical Journal.2022; 41(2): 51. CrossRef
- Rotator Interval vs Posterior Approach Ultrasound-guided Corticosteroid Injections in Primary Frozen Shoulder: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Pathophysiology and protective approaches of gut injury in critical illness
- Chang Yeon Jung, Jung Min Bae
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):27-33. Published online September 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00703
- 7,591 View
- 205 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The gut is a complex organ that has played an important role in digestion, absorption, endocrine functions, and immunity. The gut mucosal barriers consist of the immunologic barrier and nonimmunologic barrier. During critical illnesses, the gut is susceptible to injury due to the induction of intestinal hyperpermeability. Gut hyperpermeability and barrier dysfunction may lead to systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Additionally, gut microbiota are altered during critical illnesses. The etiology of such microbiome alterations in critical illnesses is multifactorial. The interaction or systemic host defense modulation between distant organs and the gut microbiome is increasingly studied in disease research. No treatment modality exists to significantly enhance the gut epithelial integrity, permeability, or mucus layer in critically ill patients. However, multiple helpful approaches including clinical and preclinical strategies exist. Enteral nutrition is associated with an increased mucosal barrier in animal and human studies. The trophic effects of enteral nutrition might help to maintain the intestinal physiology, prevent atrophy of gut villi, reduce intestinal permeability, and protect against ischemia-reperfusion injury. The microbiome approach such as the use of probiotics, fecal microbial transplantation, and selective decontamination of the digestive tract has been suggested. However, its evidence does not have a high quality. To promote rapid hypertrophy of the small bowel, various factors have been reported, including the epidermal growth factor, membrane permeant inhibitor of myosin light chain kinase, mucus surrogate, pharmacologic vagus nerve agonist, immune-enhancing diet, and glucagon-like peptide-2 as preclinical strategies. However, the evidence remains unclear.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Limonene Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect on LPS-Induced Jejunal Injury in Mice by Inhibiting NF-κB/AP-1 Pathway
Sarmed H. Kathem, Yasameen Sh. Nasrawi, Shihab H. Mutlag, Surya M. Nauli
Biomolecules.2024; 14(3): 334. CrossRef - Bacillus licheniformis reverses the environmental ceftriaxone sodium-induced gut microbial dysbiosis and intestinal inflammation in mice
Zhibo Zeng, Wen Yue, Cermon Kined, PengPeng Wang, Ran Liu, Jing Liu, Xinzhu Chen
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2023; 257: 114890. CrossRef - Severe gastrointestinal injury associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Thrombosis or Inflammation?: A retrospective case series study
Henry Robayo-Amortegui, Alex Forero-Delgadillo, Michel Pérez-Garzón, Claudia Poveda-Henao, Conny Muñoz-Claros, Andrea Bayona-Solano, Carlos Orozco, Ricardo Buitrago-Bernal
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31188. CrossRef - The Gut-Liver Axis in Cholestatic Liver Diseases
Andreas Blesl, Vanessa Stadlbauer
Nutrients.2021; 13(3): 1018. CrossRef - The Role of DAMPS in Burns and Hemorrhagic Shock Immune Response: Pathophysiology and Clinical Issues. Review
Desirè Pantalone, Carlo Bergamini, Jacopo Martellucci, Giovanni Alemanno, Alessandro Bruscino, Gherardo Maltinti, Maximilian Sheiterle, Riccardo Viligiardi, Roberto Panconesi, Tommaso Guagni, Paolo Prosperi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(13): 7020. CrossRef - Safety of Using Enteral Nutrition Formulations Containing Dietary Fiber in Hospitalized Critical Care Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis
Kelly Copeland Cara, Andrew R. Beauchesne, Taylor C. Wallace, Mei Chung
Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition.2021; 45(5): 882. CrossRef
- Limonene Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect on LPS-Induced Jejunal Injury in Mice by Inhibiting NF-κB/AP-1 Pathway
Original articles
- Association between gestational age at delivery and lymphocyte-monocyte ratio in the routine second trimester complete blood cell count
- Hyun-Hwa Cha, Jong Mi Kim, Hyun Mi Kim, Mi Ju Kim, Gun Oh Chong, Won Joon Seong
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):34-38. Published online June 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00234

- 6,012 View
- 103 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
We aimed to determine whether routine second trimester complete blood cell (CBC) count parameters, including neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte-monocyte ratio (LMR), and platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), could predict obstetric outcomes.
Methods
We included singleton pregnancies for which the 50-g oral glucose tolerance test and CBC were routinely performed between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation in our outpatient clinic from January 2015 to December 2017. The subjects were divided into three groups according to their pregnancy outcomes as follows: group 1, spontaneous preterm births, including preterm labor and preterm premature rupture of membranes; group 2, indicated preterm birth due to maternal, fetal, or placental causes (hypertensive disorder, fetal growth restriction, or placental abruption); and group 3, term deliveries, regardless of the indication of delivery. We compared the CBC parameters using a bivariate correlation test.
Results
The study included 356 pregnancies. Twenty-eight subjects were in group 1, 20 in group 2, and 308 in group 3. There were no significant differences between the three groups in neutrophil, monocyte, lymphocyte, and platelet counts. Although there was no significant difference in NLR, LMR, and PLR between the three groups, LMR showed a negative correlation with gestational age at delivery (r=−0.126, p=0.016).
Conclusion
We found that a higher LMR in the second trimester was associated with decreased gestational age at delivery. CBC parameters in the second trimester of pregnancy could be used to predict adverse obstetric outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation of maternal platelet to lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C- reactive protein with gestational age at delivery and fetal outcome - A prospective observational study from tertiary care centre
Mrinalini Kannan, Sajeetha Kumari R, Vinodhini Shanmugham
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2024; 28: 101687. CrossRef - Relationship between Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio with Spontaneous Preterm Birth: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Liang Peng, Baodi Cao, Fangpeng Hou, Baolin Xu, Hong Zhou, Luyi Liang, Yu Jiang, Xiaohui Wang, Jingjian Zhou, Lingzhang Meng
Journal of Immunology Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - High Apoptotic Index in Amniotic Membrane of Pregnant Women is A Risk Factor for Preterm Labor
Anak Agung Gede Putra Wiradnyana, Anak Agung Ngurah Jaya Kusuma, Anak Agung Ngurah Anantasika, I Made Darmayasa, Ryan Saktika Mulyana, Gde Bagus Rizky Kornia
European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences.2023; 5(3): 79. CrossRef - Evaluation of Complete Blood Cell Count Parameters in the Diagnosis of Threatened Preterm Labor and Premature Rupture of Membranes
Jule Eriç Horasanlı, Elifsena Canan Alp, Ramazan Bülbül
Dubai Medical Journal.2022; 5(3): 157. CrossRef - The Association of Inflammatory Biomarker of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Spontaneous Preterm Delivery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sina Vakili, Parham Torabinavid, Reza Tabrizi, Alireza Shojazadeh, Nasrin Asadi, Kamran Hessami, Oleh Andrukhov
Mediators of Inflammation.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Correlation of maternal platelet to lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C- reactive protein with gestational age at delivery and fetal outcome - A prospective observational study from tertiary care centre
- Pelvic floor muscle exercise with biofeedback helps regain urinary continence after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy
- Yeong Uk Kim, Dong Gyu Lee, Young Hwii Ko
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):39-46. Published online June 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00276
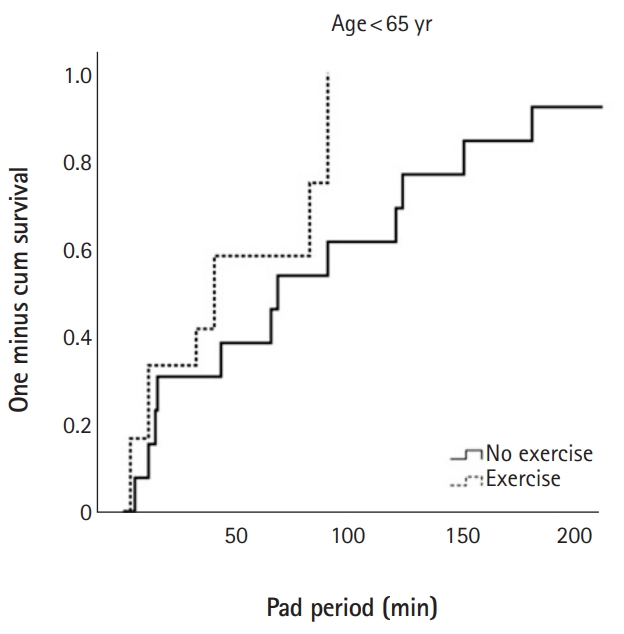
- 7,118 View
- 168 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
To determine the benefit of pelvic floor muscle exercise with visual biofeedback on promoting patient recovery from incontinence, we investigated variables associated with the early restoration of continence for patients who underwent robot-assisted radical prostatectomy.
Methods
Of the 83 patients enrolled, 41 consecutive patients completed pelvic floor muscle exercise (the exercise group), and the other 42 consecutive patients just before the pelvic floor muscle exercise program commenced (the control group). The primary outcome was whether pelvic floor muscle exercise engagement was associated with zero pad continence restoration within 3 months of surgery.
Results
Continence restoration percentages (defined as zero pads used per day) at 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery were 49.4%, 77.1%, and 94.0%, respectively. The exercise group achieved significantly higher recovery rates at 1 month (p=0.037), 3 months (p<0.001), and 6 months (p=0.023). Cox regression analysis demonstrated that a lower Gleason score (<8; hazard ratio, 2.167), lower prostate specific antigen (<20 ng/dL; hazard ratio, 2.909), and engagement in pelvic floor muscle exercise (hazard ratio, 3.731) were independent predictors of early recovery from postprostatectomy incontinence. Stratification by age showed that those younger than 65 years did not benefit significantly from exercise (log-rank test, p=0.08), but that their elderly counterparts, aged 65–70 years (p=0.007) and >70 years old (p=0.002) benefited significantly.
Conclusion
This study suggests that postoperative engagement in pelvic floor muscle exercise with biofeedback speeds up the recovery of continence in elderly patients (≥65 years old) that undergo robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Urinary incontinence rehabilitation of after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Kai Yu, Fan Bu, Tengteng Jian, Zejun Liu, Rui Hu, Sunmeng Chen, Ji Lu
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing engagement in pelvic floor muscle exercise following radical prostatectomy: A scoping review
Yousef Qan'ir, Lixin Song, Kathleen Knafl, Paschal Sheeran, Hung‐Jui Tan, Mohammed Shahait, Ahmad AL‐Sagarat
International Journal of Urological Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Kegel exercises on the prevention of urinary and fecal incontinence in patients with prostate cancer undergoing radiotherapy
A.E. Urvaylıoğlu, S. Kutlutürkan, D. Kılıç
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 51: 101913. CrossRef
- Urinary incontinence rehabilitation of after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- Evaluation of craniofacial morphology in short-statured children: growth hormone deficiency versus idiopathic short stature
- Ki Bong Kim, Eun-Kyong Kim, Kyung Mi Jang, Min Seon Kim, Eun Young Park
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):47-52. Published online July 7, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00325
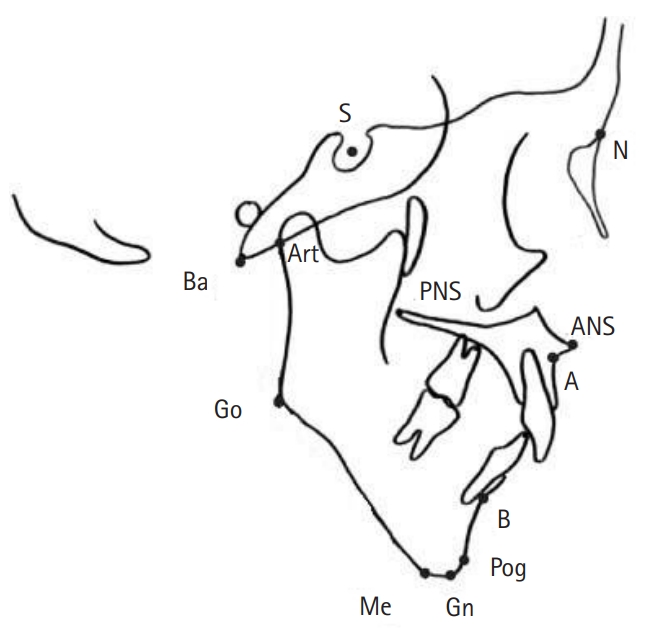
- 5,923 View
- 89 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Short stature is defined as a height below the 3rd percentile or more than two standard deviations below the mean for a given age, sex, and population. There have been inconsistent results regarding craniofacial morphology in short-statured children. This study aimed to analyze the differences between short-statured children with growth hormone deficiency, idiopathic short-statured children, and normal children.
Methods
Thirty-one short-statured children with growth hormone deficiency, 32 idiopathic short-statured children, and 32 healthy children were enrolled in this study. The measurements of their craniofacial structures from lateral cephalograms were evaluated.
Results
There were statistically significant differences among the three groups seven variables (anterior cranial base length, posterior cranial base length, total cranial base length, upper posterior facial height, posterior total facial height, mandibular ramus length, and overall mandibular length) in the linear measurement and five variables (saddle angle, gonial angle, mandibular plane angle, position of mandible, and maxilla versus mandible) in the angular measurement.
Conclusion
Compared to the control group, many linear and angular measurements of the craniofacial structures were significantly different in the two short-statured groups (p<0.05). Treatment plans by orthodontists should include these craniofacial structure characteristics. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dental arches in inherited severe isolated growth hormone deficiency
Rafaela S. Girão, Manuel H. Aguiar-Oliveira, Bruna M.R. Andrade, Marcos A.V. Bittencourt, Roberto Salvatori, Evânio V. Silva, André L.M. Santos, Matheus M. Cunha, Wilton M. Takeshita, Alaíde H.A. Oliveira, Eugênia H.O. Valença, Alécia A. Oliveira-Santos,
Growth Hormone & IGF Research.2022; 62: 101444. CrossRef - Sella turcica dimensions and maxillary growth in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate
Gregory S. Antonarakis, Luis Huanca Ghislanzoni, David M. Fisher
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 123(6): e916. CrossRef - Clinical Implications of Growth Hormone Deficiency for Oral Health in Children: A Systematic Review
Natalia Torlińska-Walkowiak, Katarzyna Anna Majewska, Andrzej Kędzia, Justyna Opydo-Szymaczek
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(16): 3733. CrossRef - A Clinical Study on the Treatment of Children’s Short Stature with Auxiliary Comprehensive Management Combined with Growth Patch
Haiying Feng, Weizhu Zhao, Huijun Yu, Guanfu Wang, Qunhong Wang, Songwen Tan
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Dental arches in inherited severe isolated growth hormone deficiency
- Effect of in vitro testicular spermatozoa culture on pregnancy outcomes: an experience at a single university hospital
- Jisun Lee, Jung Hyeon Yoo, Jae Hun Lee, Hyun Soo Ahn, Kyung Joo Hwang, Miran Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):53-59. Published online December 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00773
- 5,362 View
- 73 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
There are no guidelines for the optimal incubation time or temperature to improve pregnancy outcomes in testicular sperm extraction-intracytoplasmic sperm injection (TESE-ICSI) cycles. We aimed to evaluate whether a 24-hour in vitro culture of testicular spermatozoa affects pregnancy outcomes in TESE-ICSI cycles.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of 83 TESE-ICSI cycles using testicular spermatozoa in 46 couples with male partners suffering from nonobstructive or obstructive azoospermia. Sperm retrieval was performed either on the oocyte retrieval (OR) day (65 cycles in 33 couples; group A) or on the day before OR (18 cycles in 13 couples; group B) followed by in vitro culture for 24 hours. The clinical characteristics and pregnancy outcomes, including the number of retrieved oocytes, fertilization rates, embryo transfer rates, implantation and clinical pregnancy rates, were compared between the two groups.
Results
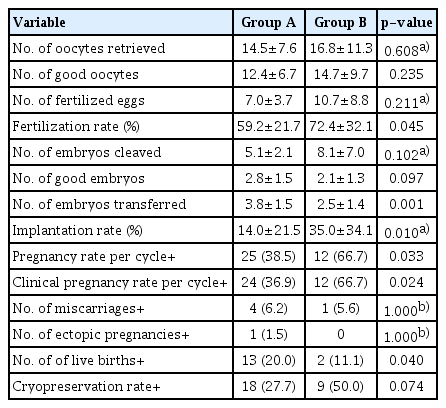
There were no differences in terms of clinical characteristics except for the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) in males. Group B had higher LH levels than group A (4.56±1.24 IU/L vs. 3.67±1.07 IU/L, p=0.017). Group B showed higher fertilization rate (72.4±32.1% vs. 59.2±21.7%, p=0.045), implantation rate (35.0±34.1% vs. 14.0±21.5%, p=010), pregnancy rate per cycle (80% vs. 39%, p=0.033), and clinical pregnancy rate per cycle (80% vs. 37.5%, p=0.024) than those of group A.
Conclusion
Testicular sperm retrieval performed on the day before OR followed by in vitro culture can potentially improve pregnancy outcomes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intelligent Medicine on the Regulation Effect of Weekend Catch-Up Sleep on the Relationship Between Hypertension and All-Cause Mortality
Hui Li, Min Yang, Yanchun Bao
International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Extend the Survival of Human Sperm In Vitro in Non-Freezing Conditions: Damage Mechanisms, Preservation Technologies, and Clinical Applications
Qingyuan Cheng, Liman Li, Min Jiang, Bo Liu, Yang Xian, Shasha Liu, Xiao Liu, Wenrui Zhao, Fuping Li
Cells.2022; 11(18): 2845. CrossRef
- Intelligent Medicine on the Regulation Effect of Weekend Catch-Up Sleep on the Relationship Between Hypertension and All-Cause Mortality
Case reports
- Cushing syndrome in pregnancy, diagnosed after delivery
- Han Byul Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, El Kim, Keun Soo Ahn, Hye Soon Kim, Nam Kyung Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):60-64. Published online May 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00290

- 5,769 View
- 114 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cushing syndrome (CS) is rare in pregnancy, and few cases have been reported to date. Women with untreated CS rarely become pregnant because of the ovulatory dysfunction induced by hypercortisolism. It is difficult to diagnose CS in pregnancy because of its very low incidence, the overlap between the clinical signs of hypercortisolism and the physiological changes that occur during pregnancy and the changes in hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis activity that occur during pregnancy and limit the value of standard diagnostic testing. However, CS in pregnancy is associated with poor maternal and fetal outcomes; therefore, its early diagnosis and treatment are important. Here, we report two patients with CS that was not diagnosed during pregnancy, in whom maternal and fetal morbidity developed because of hypercortisolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endogenous Cushing’s syndrome during pregnancy
Nada Younes, Matthieu St-Jean, Isabelle Bourdeau, André Lacroix
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2023; 24(1): 23. CrossRef - Cushing Syndrome in Pregnancy: A Case Presentation and Review of Literature
HamidReza Samimagham, Ava Ziaei, Mohammad Tamaddondar, Mitra Kazemi Jahromi
Journal of Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Endogenous Cushing’s syndrome during pregnancy
- Development of donepezil-induced hypokalemia following treatment of cognitive impairment
- Dongryul Kim, Hye Eun Yoon, Hoon Suk Park, Seok Joon Shin, Bum Soon Choi, Byung Soo Kim, Tae Hyun Ban
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):65-69. Published online June 1, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00269
- 6,104 View
- 134 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Donepezil is a cholinesterase inhibitor used extensively to treat Alzheimer disease. The increased cholinergic activity is associated with adverse effects, therefore gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, are common. Hypokalemia is a rare adverse event that occurs in less than 1% of donepezil-treated patients. Although hypokalemia of mild and moderate grade does not present serious signs and symptoms, severe hypokalemia often results in prolonged hospitalization and mortality. Herein, we report a case of hypokalemia developed after the initiation of donepezil therapy for cognitive impairment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil Protects Zebrafish against Cognitive Dysfunction by Regulating Cholinergic and Antioxidants Systems
Luminita Capatina, Elena Todirascu-Ciornea, Edoardo Marco Napoli, Giuseppe Ruberto, Lucian Hritcu, Gabriela Dumitru
Antioxidants.2020; 9(11): 1083. CrossRef
- Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil Protects Zebrafish against Cognitive Dysfunction by Regulating Cholinergic and Antioxidants Systems
- Co-existence of relapsing polychondritis and Crohn disease treated successfully with infliximab
- Hye-In Jung, Hyun Jung Kim, Ji-Min Kim, Ju Yup Lee, Kyung Sik Park, Kwang Bum Cho, Yoo Jin Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):70-73. Published online June 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00304

- 5,385 View
- 90 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Relapsing polychondritis (RP) is a rare, progressive immune-mediated systemic inflammatory disease of unknown etiology, characterized by recurrent inflammation of cartilaginous structures. Approximately 30% of RP cases are associated with other autoimmune diseases. However, the co-occurrence of RP and Crohn disease (CD) has rarely been reported. Herein, we present a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with RP and CD, who was refractory to initial conventional medications, including azathioprine and glucocorticoid, but who subsequently responded to infliximab (IFX). For both diseases, remission was sustained with IFX. There has been no previous report regarding the successful treatment of co-existing RP and CD with IFX.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relapsing Polychondritis in a Patient With Auricular Chondritis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case Report With Literature Review
David D Bickford, Thomas Ritter, Pinky Jha, Hari R Paudel
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Relapsing Polychondritis in a Patient With Auricular Chondritis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case Report With Literature Review
- Transpedal lymphatic embolization for lymphorrhea at the graft harvest site after coronary artery bypass grafting
- Jung Guen Cha, Sang Yub Lee, Jihoon Hong, Hun Kyu Ryeom, Gab Chul Kim, Young Woo Do
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):74-77. Published online July 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00297
- 4,824 View
- 64 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
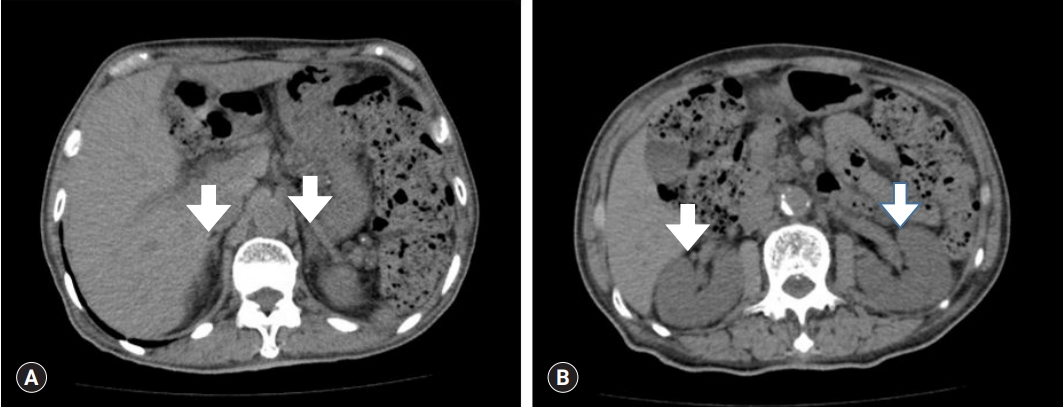
PDF - Lymphorrhea is a rare but potentially severe complication that occurs after various surgical procedures. Untreated lymphorrhea may lead to wound dehiscence, infection, and prolonged hospital stay. Currently, there is no standard effective treatment. Early management usually includes leg elevation, drainage, and pressure dressing. However, these methods are associated with prolonged recovery and high recurrence rates. We report a case of lymphorrhea from a calf wound after endoscopic great saphenous vein (GSV) harvesting for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). The patient presented with intractable oozing from the postoperative wound on the right calf. Lymphorrhea perGsisted for 6 weeks despite negative-pressure wound therapy with a long-acting somatostatin. We performed unilateral pedal lymphangiography that confirmed wound lymphorrhea, followed by glue embolization. No recurrence was observed after 8 months of follow-up. This case report demonstrates the successful use of lymphangiography with glue embolization in the control of lymphorrhea after GSV harvesting for CABG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Free Chimeric Anterolateral Thigh Flap with Vastus Lateralis Muscle Transfer for the Treatment of Intractable Upper Arm Lymphorrhea due to Large Upper Body Lymphangioma
Sei Yoshida, Hideki Kadota, Kentaro Anan, Nobuaki Hatakeyama
International Journal of Surgical Wound Care.2024; 5(2): 46. CrossRef - Supermicrosurgical lymphatic venous anastomosis for intractable lymphocele after great saphenous vein harvesting graft
Hirofumi Imai, Shuhei Yoshida, Toshiro Mese, Solji Roh, Isao Koshima
Journal of Vascular Surgery Cases, Innovations and Techniques.2022; 8(1): 45. CrossRef - Update February 2021
Francine Blei
Lymphatic Research and Biology.2021; 19(1): 96. CrossRef - Lymphatic complications after harvesting venous conduits in coronary artery bypass grafting surgery
D. V. Manvelyan, Yu. Y. Vechersky, V. V. Zatolokin, M. S. Kuznetsov, B. N. Kozlov
The Siberian Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2021; 36(3): 27. CrossRef
- Free Chimeric Anterolateral Thigh Flap with Vastus Lateralis Muscle Transfer for the Treatment of Intractable Upper Arm Lymphorrhea due to Large Upper Body Lymphangioma
- Pancreatic metastasis from malignant phyllodes tumor of the breast
- Seung Eun Lee, Young Kyung Bae, Joon Hyuk Choi
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(1):78-82. Published online November 27, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00759

- 4,795 View
- 67 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pancreatic metastasis from malignant phyllodes tumor (PT) of the breast is rare, and only a few cases have been reported in the literature. Here, we report a case of pancreatic metastasis from malignant PT of the breast in a 48-year-old woman. She had had three episodes of recurrence of malignant PT in her right breast. She presented with epigastric pain for 2 months. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging revealed a 6 cm-sized, well-defined, heterogeneous mass with peripheral enhancement in the body of the pancreas. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration was performed, and the pathologic report suggested spindle cell mesenchymal neoplasm. Subsequently, surgical excision was performed, and the mass was confirmed as a metastatic malignant PT. The imaging findings are discussed and the literature is briefly reviewed in this report.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrating single‐cell and spatial transcriptomes reveals COL4A1/2 facilitates the spatial organisation of stromal cells differentiation in breast phyllodes tumours
Xia Li, Xuewen Yu, Jiaxin Bi, Xu Jiang, Lu Zhang, Zhixin Li, Mumin Shao
Clinical and Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: Osteosarcomatous differentiation in the lung metastasis of a malignant phyllodes tumor
Ruijing Liu, Jingli Xue, Wen Liu, Beibei Jiang, Fuyun Shi, Zhenzheng Wang, Peifeng Li
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic approach to fibroepithelial tumors of the breast
Frances Tresserra, María Angeles Martinez-Lanao, Melissa Fernandez-Acevedo, Cristina Castellet, Sonia Baulies
Revista de Senología y Patología Mamaria.2022; 35: S22. CrossRef
- Integrating single‐cell and spatial transcriptomes reveals COL4A1/2 facilitates the spatial organisation of stromal cells differentiation in breast phyllodes tumours

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



