Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Editorial
- Advances in the science and treatment of respiratory diseases
- Jin Hong Chung
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):251-252. Published online September 2, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00661
- 4,245 View
- 104 Download
Review articles
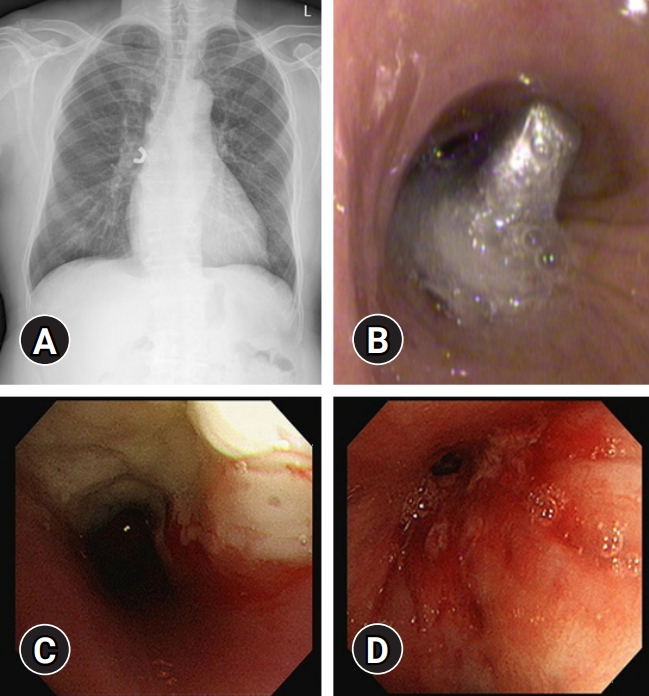
- An update on the role of bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary disease
- June Hong Ahn
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):253-261. Published online August 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00584
- 9,193 View
- 243 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bronchoscopy has evolved over the past few decades and has been used by respiratory physicians to diagnose various airway and lung diseases. With the popularization of medical check-ups and growing interest in health, early diagnosis of lung diseases is essential. With the development of endobronchial ultrasound, ultrathin bronchoscopy, and electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy, bronchoscopy has been able to widen its scope in diagnosing pulmonary diseases. In this review, we have described the brief history, role, and complications of bronchoscopy used in diagnosing pulmonary lesions, from simple flexible bronchoscopy to bronchoscopy combined with several up-to-date technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Disposable Versus Reusable Bronchoscopes: A Narrative Review of Cost-effectiveness, Risk of Cross-contamination and Environmental Impact
Illaa Smesseim, Johannes M.A. Daniels, Jouke Annema, Peter I. Bonta, Dirk-Jan Slebos
Archivos de Bronconeumología.2024; 60(4): 250. CrossRef - Flexible bronchoscopy indications and outcomes between indigenous and non‐indigenous patients in the Northern Territory of Australia
Mohammad M. Seyedshahabedin, Timothy P. Howarth, Lin Mo, Edwina Biancardi, Subash S. Heraganahally
Internal Medicine Journal.2023; 53(9): 1634. CrossRef - Endobronchial ultrasound‐guided re‐biopsy of non–small cell lung cancer with acquired resistance after EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment
Kyung Soo Hong, Jinmo Cho, Jong Geol Jang, Min Hye Jang, June Hong Ahn
Thoracic Cancer.2023; 14(4): 363. CrossRef - Observational findings of transbronchial lung biopsy in patients with interstitial lung disease: a retrospective study in Aleppo University Hospital
Fateh Kashkash, Abdullah Khorri
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(2): 146. CrossRef - Invasive Diagnostic Procedures from Bronchoscopy to Surgical Biopsy—Optimization of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Samples for Molecular Testing
Nensi Lalić, Aleksandra Lovrenski, Miroslav Ilić, Olivera Ivanov, Marko Bojović, Ivica Lalić, Spasoje Popević, Mihailo Stjepanović, Nataša Janjić
Medicina.2023; 59(10): 1723. CrossRef - Utility of Radial Probe Endobronchial Ultrasound Guided Transbronchial Lung Biopsy in Bronchus Sign Negative Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions
Kyung Soo Hong, Kwan Ho Lee, Jin Hong Chung, Kyeong-Cheol Shin, Hyun Jung Jin, Jong Geol Jang, June Hong Ahn
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Radial Probe Endobronchial Ultrasound Using Guide Sheath-Guided Transbronchial Lung Biopsy in Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions without Fluoroscopy
Kyung Soo Hong, Heeyun Ahn, Kwan Ho Lee, Jin Hong Chung, Kyeong-Cheol Shin, Hyun Jung Jin, Jong Geol Jang, Seok Soo Lee, Min Hye Jang, June Hong Ahn
Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases.2021; 84(4): 282. CrossRef - Advances in the science and treatment of respiratory diseases
Jin Hong Chung
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2020; 37(4): 251. CrossRef
- Disposable Versus Reusable Bronchoscopes: A Narrative Review of Cost-effectiveness, Risk of Cross-contamination and Environmental Impact
- Biological treatments for severe asthma
- Hyun Jung Jin
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):262-268. Published online September 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00647

- 6,632 View
- 176 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Severe asthma patients comprise about 3% to 13% of all asthma patients, but they have higher hospital utilization rates and higher medical costs than those of nonsevere asthma patients. Treatment methods for severe asthma patients are still lacking; however, the recent development of biologics is expected to have a positive effect. The biological therapies developed so far are mainly aimed at treating asthma patients with type 2 inflammation. These biologics have been found to reduce symptoms of asthma, improve lung function, reduce the use of oral corticosteroids, and improve quality of life of patients. This article reviews the mechanism of action and indications for approved biologics and discusses what should be considered when choosing biologics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current and Novel Biologic Therapies for Patients with Asthma and Nasal Polyps
Hanna K. Mandl, Jessa E. Miller, Daniel M. Beswick
Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America.2024; 57(2): 225. CrossRef - Moderate-High Blood Eosinophilia Is Associated with Increased Hospitalization and Other Asthma Comorbidities
Sara Naharro-González, Clara Lorente-Sorolla, José Manuel Rodrigo-Muñoz, Marcela Valverde-Monge, Erwin Javier Pinillos-Robles, Diana Betancor, Mar Fernández-Nieto, Diana Sánchez-Mellado, Marta Gil-Martínez, Jessica Mireya Santillán-Coello, José Miguel Vil
Biomolecules.2024; 14(1): 126. CrossRef - Incremental net monetary benefit of biologic therapies in moderate to severe asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of economic evaluation studies
Sajesh K. Veettil, Vanessa Vincent, Taylor Shufelt, Emma Behan, M. Sakil Syeed, Ammarin Thakkinstian, David C. Young, Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk
Journal of Asthma.2023; 60(9): 1702. CrossRef - Tackling the cytokine storm using advanced drug delivery in allergic airway disease
Vyoma K. Patel, Sukriti Vishwas, Rajan Kumar, Gabriele De Rubis, Shakti D. Shukla, Keshav Raj Paudel, Bikash Manandhar, Thakur Gurjeet Singh, Dinesh Kumar Chellappan, Monica Gulati, Indu Pal Kaur, Venkata Sita Rama Raju Allam, Philip M. Hansbro, Brian G.
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2023; 82: 104366. CrossRef - The evolving landscape of immunotherapy for the treatment of allergic conditions
Aarti Pandya, Esosa Adah, Bridgette Jones, Rachel Chevalier
Clinical and Translational Science.2023; 16(8): 1294. CrossRef - Effect of Dupilumab in Korean Patients With Uncontrolled Moderate-to-Severe Asthma: A LIBERTY ASTHMA QUEST Sub-analysis
Chin Kook Rhee, Jung-Won Park, Heung-Woo Park, You Sook Cho
Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Research.2022; 14(2): 182. CrossRef - The role of peripheral eosinophilia in diagnosing lung disorders: experience from a single pneumonological center
Justyna Fijołek, Elzbieta Wiatr, Dorota Piotrowska-Kownacka, Kazimierz Roszkowski-Sliz
Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in the science and treatment of respiratory diseases
Jin Hong Chung
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2020; 37(4): 251. CrossRef
- Current and Novel Biologic Therapies for Patients with Asthma and Nasal Polyps
- Therapeutic potential of targeting kinase inhibition in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Suji Kim, Jae Hyang Lim, Chang-Hoon Woo
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):269-276. Published online July 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00458

- 8,921 View
- 243 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Fibrosis is characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components. The fibrotic process ultimately leads to organ dysfunction and failure in chronic inflammatory and metabolic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, advanced kidney disease, and liver cirrhosis. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a common form of progressive and chronic interstitial lung disease of unknown etiology. Pathophysiologically, the parenchyma of the lung alveoli, interstitium, and capillary endothelium becomes scarred and stiff, which makes breathing difficult because the lungs have to work harder to transfer oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveolar space and bloodstream. The transforming growth factor beta (TGF-) signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis and scarring of the lung tissue. Recent clinical trials focused on the development of pharmacological agents that either directly or indirectly target kinases for the treatment of IPF. Therefore, to develop therapeutic targets for pulmonary fibrosis, it is essential to understand the key factors involved in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis and the underlying signaling pathway. The objective of this review is to discuss the role of kinase signaling cascades in the regulation of either TGF--dependent or other signaling pathways, including Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase, c-jun N-terminal kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5, and p90 ribosomal S6 kinase pathways, and potential therapeutic targets in IPF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeting Growth Factor and Cytokine Pathways to Treat Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Hongbo Ma, Shengming Liu, Shanrui Li, Yong Xia
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D3 alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by regulating the MAPK pathway via targeting PSAT1 expression in vivo and in vitro
Wenxiang Zhu, Qi Ding, Lu Wang, Gonghao Xu, Yirui Diao, Sihao Qu, Sheng Chen, Yuanyuan Shi
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 101: 108212. CrossRef - Advances in the science and treatment of respiratory diseases
Jin Hong Chung
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2020; 37(4): 251. CrossRef - Effects of Pirfenidone and Nintedanib on Markers of Systemic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Preliminary Report
Alessandro G. Fois, Elisabetta Sotgiu, Valentina Scano, Silvia Negri, Sabrina Mellino, Elisabetta Zinellu, Pietro Pirina, Gianfranco Pintus, Ciriaco Carru, Arduino A. Mangoni, Angelo Zinellu
Antioxidants.2020; 9(11): 1064. CrossRef
- Targeting Growth Factor and Cytokine Pathways to Treat Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Diagnosis and treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
- Jong Geol Jang, Jin Hong Chung
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):277-285. Published online September 4, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00626

- 16,187 View
- 532 Download
- 43 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tuberculosis (TB) is still a major health problem worldwide. Especially, multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB), which is defined as TB that shows resistance to both isoniazid and rifampicin, is a barrier in the treatment of TB. Globally, approximately 3.4% of new TB patients and 20% of the patients with a history of previous treatment for TB were diagnosed with MDR-TB. The treatment of MDR-TB requires medications for a long duration (up to 20–24 months) with less effective and toxic second-line drugs and has unfavorable outcomes. However, treatment outcomes are expected to improve due to the introduction of a new agent (bedaquiline), repurposed drugs (linezolid, clofazimine, and cycloserine), and technological advancement in rapid drug sensitivity testing. The World Health Organization (WHO) released a rapid communication in 2018, followed by consolidated guidelines for the treatment of MDR-TB in 2019 based on clinical trials and an individual patient data meta-analysis. In these guidelines, the WHO suggested reclassification of second-line anti-TB drugs and recommended oral treatment regimens that included the new and repurposed agents. The aims of this article are to review the treatment strategies of MDR-TB based on the 2019 WHO guidelines regarding the management of MDR-TB and the diagnostic techniques for detecting resistance, including phenotypic and molecular drug sensitivity tests.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Computational insights into potential marine natural products as selective inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis InhA: A structure-based virtual screening study
Manikandan Jayaraman, Vijayakumar Gosu, Rajalakshmi Kumar, Jeyakanthan Jeyaraman
Computational Biology and Chemistry.2024; 108: 107991. CrossRef - Targeting of essential mycobacterial replication enzyme DnaG primase revealed Mitoxantrone and Vapreotide as novel mycobacterial growth inhibitors**
Waseem Ali, Salma Jamal, Rishabh Gangwar, Faraz Ahmed, Rahul Sharma, Meetu Agarwal, Javaid Ahmad Sheikh, Abhinav Grover, Sonam Grover
Molecular Informatics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comprehensive Review on Long vs. Short Regimens in Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB) Under Programmatic Management of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (PMDT)
Ashwin Karnan, Ulhas Jadhav, Babaji Ghewade, Anjana Ledwani, Poorna Shivashankar
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel pyrido-[2,3-d]-pyrimidin-2-amine analogues as antimycobacterial agents
Boddupalli Venkata Siva Kumar, Yogesh Mahadu Khetmalis, Kosana Sai Chaitanya, Ala Chandu, Gauri Shetye, Rui Ma, Sankaranarayanan Murugesan, Scott G. Franzblau, Kondapalli Venkata Gowri Chandra Sekhar
Journal of Molecular Structure.2024; 1303: 137600. CrossRef - Direct TAMRA-dUTP labeling of M. tuberculosis genes using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)
Basma Altattan, Jasmin Ullrich, Emily Mattig, Aline Poppe, Renata Martins, Frank F. Bier
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial peptides as new-generation antibiotics against Mycobacterium
Parisa Eslami, Adnan Khosravi
Journal of Preventive, Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies in Medicine.2024; 3(1): 6. CrossRef - A Case of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in an Active Duty Military Health Care Worker
Amanda E Saunders, Kevin M Shanahan, John W Downs
Military Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Non-Adherence to Treatment Among Migrants with MDR-TB in Wuhan, China: A Cross-Sectional Study
Kunhe Lin, Li Xiang
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2024; Volume 17: 727. CrossRef - Development of a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system to deliver delamanid via a pressurized metered dose inhaler for treatment of multi-drug resistant pulmonary tuberculosis
Himanshu Paliwal, Titpawan Nakpheng, Pijush Kumar Paul, K. Prem Ananth, Teerapol Srichana
International Journal of Pharmaceutics.2024; 655: 124031. CrossRef - Drug Targets, Current and Future Therapeutics for the Treatment of
Multi Drug Resistant Tuberculosis with their Clinical Applications: A
Critical Review
Deepshikha Singh, Vikram Singh, Subhankar P. Mandal, Karen Dsouza, B.R. Prashantha Kumar, Sheshagiri R. Dixit
Current Drug Therapy.2024; 19(3): 317. CrossRef - Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationship of 2,6-Disubstituted Thiosemicarbazone Derivatives of Pyridine as Potential Antituberculosis Agents
Dagmara Ziembicka, Katarzyna Gobis, Małgorzata Szczesio, Andrzej Olczak, Ewa Augustynowicz-Kopeć, Agnieszka Głogowska, Izabela Korona-Głowniak, Krzysztof Bojanowski
Materials.2023; 16(1): 448. CrossRef - Multidrug-Resistant TB (MDR-TB) and Extensively Drug-Resistant TB (XDR-TB) Among Children: Where We Stand Now
Kona Chowdhury, Rahnuma Ahmad, Susmita Sinha, Siddhartha Dutta, Mainul Haque
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety and depression level of patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) in two hospitals in Banten province, Indonesia
Tirta Darmawan Susanto, Allen Widysanto, Darien Alfa Cipta, Arron Tanara, Ghivarell Rizkie Wirawan, Adeline Bercadina Kosim, Christabella Maria Djoni, Ervinna Tantri, Chandni Kumar, Chelsie Angelius
Dialogues in Health.2023; 2: 100115. CrossRef - Characteristics of Previous Tuberculosis Treatment History in Patients with Treatment Failure and the Impact on Acquired Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
Soedarsono Soedarsono, Ni Made Mertaniasih, Tutik Kusmiati, Ariani Permatasari, Wiwik Kurnia Ilahi, Amelia Tantri Anggraeni
Antibiotics.2023; 12(3): 598. CrossRef - Evolution of tuberculosis diagnostics: From molecular strategies to nanodiagnostics
Srestha Mukherjee, Summaya Perveen, Anjali Negi, Rashmi Sharma
Tuberculosis.2023; 140: 102340. CrossRef - Assessment of the Diagnostic Utility of GeneXpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/Rifampicin (MTB/RIF) Assay in the Suspected Cases of Tuberculous Meningitis
Sakshi Patel, Malti Dadheech, Anand K Maurya, Jitendra Singh, Shashank Purwar, Nirendra Rai, Radha Sarawagi, Ankur Joshi, Sagar Khadanga
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tandem LC-MS Identification of Antitubercular Compounds in Zones of Growth Inhibition Produced by South African Filamentous Actinobacteria
Daniel J. Watson, Lubbe Wiesner, Tlhalefo Matimela, Denzil Beukes, Paul R. Meyers
Molecules.2023; 28(11): 4276. CrossRef - Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Stigma Among HealthCare Workers Toward the Development of a Stigma-Reduction Strategy: A Scoping Review
Lolita Liboon Aranas, Khorshed Alam, Prajwal Gyawali, Rashidul Mahumud Alam
INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality Mindset: The Missing Ingredient in Tuberculosis Care and Control in Togo
Kossivi Agbélénko Afanvi, Mohammed Fall Dogo, Koffi Atsu Aziagbé, Komi Séraphin Adjoh, Koumavi Kristoli Didier Ekouévi
European Journal of Theoretical and Applied Sciences.2023; 1(4): 36. CrossRef - Machine Learning of the Whole Genome Sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A Scoping PRISMA-Based Review
Ricardo Perea-Jacobo, Guillermo René Paredes-Gutiérrez, Miguel Ángel Guerrero-Chevannier, Dora-Luz Flores, Raquel Muñiz-Salazar
Microorganisms.2023; 11(8): 1872. CrossRef - Cotreatment With Clofazimine and Rapamycin Eliminates Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis by Inducing Polyfunctional Central Memory T-Cell Responses
Dhiraj Kumar Singh, Ashima Bhaskar, Isha Pahuja, Aishwarya Shaji, Barnani Moitra, Yufang Shi, Ved Prakash Dwivedi, Gobardhan Das
The Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 228(9): 1166. CrossRef - Treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis in children and young adolescents in Brazil
Fernanda Bruzadelli Paulino da Costa, Thaís Zamboni Berra, Jaqueline Garcia de Almeida Ballestero, Patricia Bartholomay Oliveira, Daniele Maria Pelissari, Yan Mathias Alves, Antônio Carlos Vieira Ramos, Juliana Queiroz Rocha de Paiva, Titilade Kehinde Aya
Journal of Clinical Tuberculosis and Other Mycobacterial Diseases.2023; 33: 100388. CrossRef - Tackling Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis: New Challenges from the Old Pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Giuseppe Mancuso, Angelina Midiri, Silvia De Gaetano, Elena Ponzo, Carmelo Biondo
Microorganisms.2023; 11(9): 2277. CrossRef - Drug-resistant Monoarticular Wrist Joint Tuberculosis in Renal Transplant Recipient with Literature Review
Jasmine Sethi, Vignesh Subramani, Rajender Kumar, Shivakumar Patil, Ashish Sharma
Indian Journal of Transplantation.2023; 17(3): 371. CrossRef - Predictive capabilities of baseline radiological findings for early and late disease outcomes within sensitive and multi-drug resistant tuberculosis cases
Gabriel Rosenfeld, Andrei Gabrielian, Darrell Hurt, Alex Rosenthal
European Journal of Radiology Open.2023; 11: 100518. CrossRef - Nanocarriers in Tuberculosis Treatment: Challenges and Delivery Strategies
Mahesh Kumar, Tarun Virmani, Girish Kumar, Rohitas Deshmukh, Ashwani Sharma, Sofia Duarte, Pedro Brandão, Pedro Fonte
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(10): 1360. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis on the correlation between HIV infection and multidrug-resistance tuberculosis
Yulong Song, Qian Jin, Jihai Qiu, Dan Ye
Heliyon.2023; 9(11): e21956. CrossRef - Current Insights into Diagnosing and Treating Neurotuberculosis in Adults
Sofiati Dian, Ahmad Rizal Ganiem, Lindsey HM te Brake, Arjan van Laarhoven
CNS Drugs.2023; 37(11): 957. CrossRef - Economic burden of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis on patients and households: a global systematic review and meta-analysis
Temesgen Yihunie Akalu, Archie C. A. Clements, Haileab Fekadu Wolde, Kefyalew Addis Alene
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nano vs Resistant Tuberculosis: Taking the Lung Route
Deepika Sharma, Pooja, Sunita Nirban, Smriti Ojha, Tarun Kumar, Neha Jain, Najwa Mohamad, Pradeep Kumar, Manisha Pandey
AAPS PharmSciTech.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi-Drug Resistance Tuberculosis (MDR-TB) Challenges in India: A Review
Deepak Vishwakarma, Abhay Gaidhane, Sweta Sahu, Ashwini S Rathod
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis and its Implication with COVID-19
Jasmine Arya, Sweety Dahiya, Anil Kumar Chhillar
Coronaviruses.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tuberculosis drug discovery: Progression and future interventions in the wake of emerging resistance
Summaya Perveen, Diksha Kumari, Kuljit Singh, Rashmi Sharma
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 229: 114066. CrossRef - Abdominal Tuberculosis Mimicking Ovarian Cancer: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Ikhwan Rinaldi, Abdul Muthalib, Djaja Gosal, Teguh Wijayadi, Barlian Sutedja, Tjondro Setiawan, Andika Gunawan, Nelly Susanto, Lingga Magdalena, Diah Rini Handjari, Fetisari Kurniawan, Aisyah Rifani, Kevin Winston
International Medical Case Reports Journal.2022; Volume 15: 169. CrossRef - Pediatric Tuberculosis Management: A Global Challenge or Breakthrough?
Lehlogonolo N. F. Maphalle, Bozena B. Michniak-Kohn, Modupe O. Ogunrombi, Oluwatoyin A. Adeleke
Children.2022; 9(8): 1120. CrossRef - Various approaches to improving adherence of patients with tuberculosis. Prospects for the use of additive technologies in TB practice
A. G. Naumov, A. S. Shprykov
PULMONOLOGIYA.2022; 34(1): 80. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Peptides as Potential Anti-Tubercular Leads: A Concise Review
Gabriel S. Oliveira, Raquel P. Costa, Paula Gomes, Maria Salomé Gomes, Tânia Silva, Cátia Teixeira
Pharmaceuticals.2021; 14(4): 323. CrossRef - Treatment of Human Babesiosis: Then and Now
Isaline Renard, Choukri Ben Mamoun
Pathogens.2021; 10(9): 1120. CrossRef - Novel mutations detected from drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated from North East of Thailand
Ei Phoo Thwe, Wises Namwat, Porntip Pinlaor, Kulrattana Rueangsak, Arunnee Sangka
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - On the Mechanism of Development of Autoimmune Diseases Following Exposure to Inactivated Mycobacterium tuberculosis
SV Skupnevskiy, GM Trukhina, EG Pukhaeva, AK Badtiev, FK Rurua, FE Batagova, ZhG Farnieva
ЗДОРОВЬЕ НАСЕЛЕНИЯ И СРЕДА ОБИТАНИЯ - ЗНиСО / PUBLIC HEALTH AND LIFE ENVIRONMENT.2021; : 76. CrossRef - Oral regimen for multi-drug-resistant TB can promote patient-centred and community-based treatment
Suman Saurabh, Pankaj Bhardwaj
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(12): 4607. CrossRef - Adverse effects induced by second-line antituberculosis drugs: an update based on last WHO treatment recommendations for drug-resistant tuberculosis
Ionela-Alina Grosu-Creangă, Antigona Carmen Trofor, Radu Adrian Crișan-Dabija, Daniela Robu-Popa, Cristina Mihaela Ghiciuc, Elena Cătălina Lupușoru
Pneumologia.2021; 70(3): 117. CrossRef - Advances in the science and treatment of respiratory diseases
Jin Hong Chung
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2020; 37(4): 251. CrossRef
- Computational insights into potential marine natural products as selective inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis InhA: A structure-based virtual screening study
- Novel respiratory infectious diseases in Korea
- Hyun Jung Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):286-295. Published online September 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00633
- 6,654 View
- 77 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Respiratory infections are very common and highly contagious. Respiratory infectious diseases affect not only the person infected but also the family members and the society. As medical sciences advance, several diseases have been conquered; however, the impact of novel infectious diseases on the society is enormous. As the clinical presentation of respiratory infections is similar regardless of the pathogen, the causative agent is not distinguishable by symptoms alone. Moreover, it is difficult to develop a cure because of the various viral mutations. Various respiratory infectious diseases ranging from influenza, which threaten the health of mankind globally, to the coronavirus disease 2019, which resulted in a pandemic, exist. Contrary to human expectations that development in health care and improvement in hygiene will conquer infectious diseases, humankind’s health and social systems are threatened by novel infectious diseases. Owing to the development of transport and trading activity, the rate of spread of new infectious diseases is increasing. As respiratory infections can threaten the members of the global community at any time, investigations on preventing the transmission of these diseases as well as development of effective antivirals and vaccines are of utmost importance and require a worldwide effort.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Barriers to and facilitators of populational adherence to prevention and control measures of COVID-19 and other respiratory infectious diseases: a qualitative evidence synthesis
Tácito Zaildo, Thayla Amorim Santino, Gabriela Chaves, Baldomero Antonio Kato da Silva, João Carlos Alchieri, Cecilia M. Patino, Sarah Leite, Kleber Giovanni Luz, Ricardo Oliveira Guerra, Tito Hugo Soares da Penha, Gabriel Rodrigues da Silva, Ada Cristina
European Respiratory Review.2023; 32(168): 220238. CrossRef - Diarylpentanoids, the privileged scaffolds in antimalarial and anti‐infectives drug discovery: A review
Amirah H. Ramli, Siti M. Mohd Faudzi
Archiv der Pharmazie.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Infectious Respiratory Diseases Decreased during the COVID-19 Pandemic in South Korea
Da Hae Kim, Thi Mai Nguyen, Jin Hee Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 6008. CrossRef - Advances in the science and treatment of respiratory diseases
Jin Hong Chung
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2020; 37(4): 251. CrossRef
- Barriers to and facilitators of populational adherence to prevention and control measures of COVID-19 and other respiratory infectious diseases: a qualitative evidence synthesis
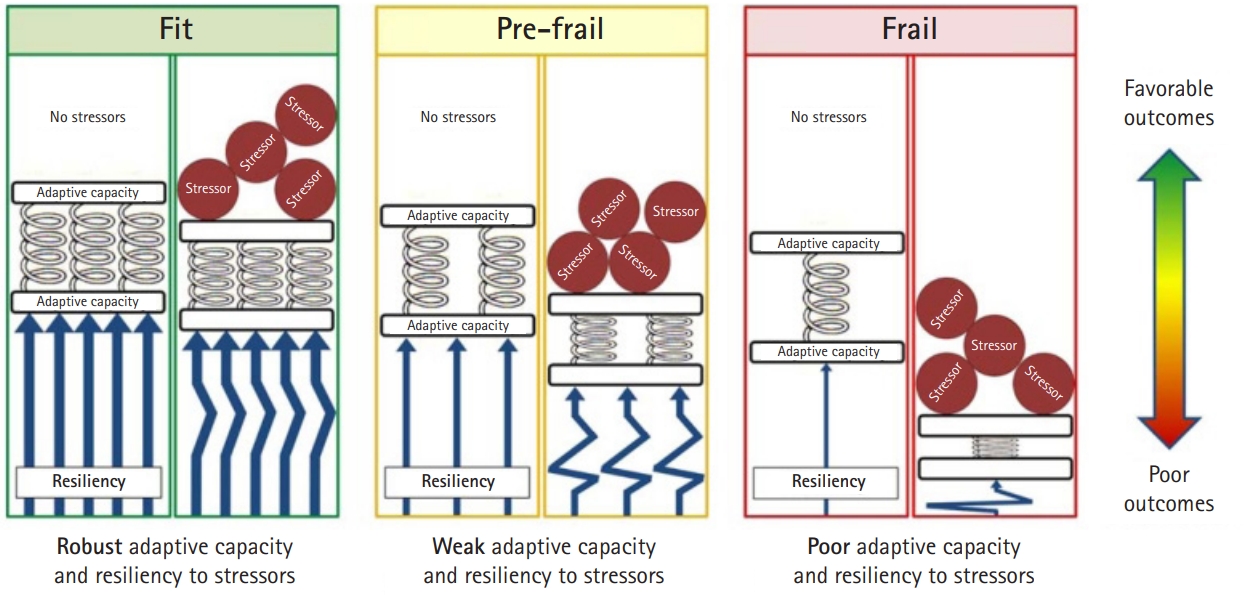
- Frailty and elderly in urology: implications for postoperative complications
- Phil Hyun Song
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):296-301. Published online October 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00752
- 5,044 View
- 57 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The geriatric population is at a greater risk of postoperative complications than young adults. This risk is associated with the physiologic decline seen in this population known as frailty. Unlike fitter patients, frail patients who undergo operative treatment have a greater likelihood of developing postoperative complications and endure prolonged hospital stays. This circumstance is comparable to the urological status. Therefore, tolerable measurement of frailty as a domain of preoperative health status has been suggested to ascertain vulnerability in elderly patients. In this review, we will elaborate on the concept of frailty and examine its importance with respect to surgical complications, focusing on the urological status.
Original articles
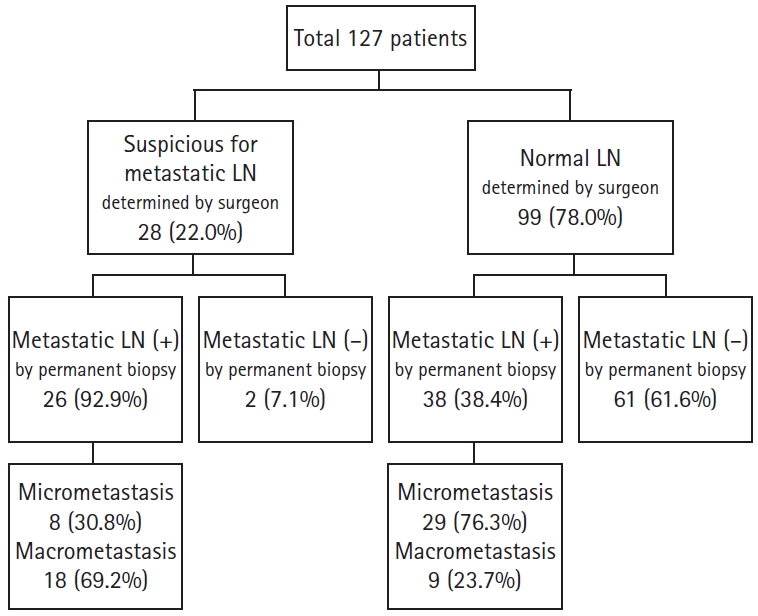
- Usefulness of intraoperative determination of central lymph node metastasis by palpation in papillary thyroid cancer
- Wan Wook Kim, Jeeyeon Lee, Jin Hyang Jung, Ho Yong Park, Won Hwa Kim, Hye Jung Kim, Ji-Young Park, Ralph P. Tufano
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):302-307. Published online April 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00122
- 5,394 View
- 73 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study evaluated the usefulness of judgment of central lymph node (LN) metastasis by surgeon’s palpation in papillary thyroid cancer.
Methods
This study included 127 patients who underwent thyroidectomy and central compartment node dissection between October 2014 and February 2015. The criterion for suspicious LNs was hardness.
Results
Of the 20.5% (28/127) of suspicious for metastatic LNs according to surgeon determination, 92.8% (26/28) were confirmed to be metastatic in the final pathological examinations. Metastatic LNs were found in 38 (38.3%) of 99 patients without suspicious LNs, 29 of whom (76.3%) had micrometastases. The sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for the determination of LN metastasis by a surgeon were 40.6%, 96.8%, 92.9%, and 61.6%, respectively.
Conclusion
Determination of central LN metastasis by a surgeon’s palpation may be useful to evaluate LNs owing to the high specificity and positive predictive values, especially in macrometastasis or high-risk LN disease.
- Clinical outcomes of hysterectomy for benign diseases in the female genital tract: 6 years’ experience in a single institute
- Hyo-Shin Kim, Yu-Jin Koo, Dae-Hyung Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):308-313. Published online April 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00185

- 5,637 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Hysterectomy is one of the major gynecologic surgeries. Historically, several surgical procedures have been used for hysterectomy. The present study aims to evaluate the surgical trends and clinical outcomes of hysterectomy performed for benign diseases at the Yeungnam University Hospital.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed patients who underwent a hysterectomy for benign diseases from 2013 to 2018. Data included the patients’ demographic characteristics, surgical indications, hysterectomy procedures, postoperative pathologies, and perioperative outcomes.
Results
A total of 809 patients were included. The three major indications for hysterectomy were uterine leiomyoma, pelvic organ prolapse, and adenomyosis. The most common procedure was total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH, 45.2%), followed by open hysterectomy (32.6%). During the study period, the rate of open hysterectomy was nearly constant (29.4%–38.1%). The mean operative time was the shortest in the single-port laparoscopic assisted vaginal hysterectomy (LAVH, 89.5 minutes), followed by vaginal hysterectomy (VH, 96.8 minutes) and TLH (105 minutes). The mean decrease in postoperative hemoglobin level was minimum in single-port LAVH (1.8 g/dL) and VH (1.8 g/dL). Conversion to open surgery or multi-port surgery occurred in five cases (0.6%). Surgical complications including wound dehiscence, organ injuries, and conditions requiring reoperation were observed in 52 cases (6.4%).
Conclusion
Minimally invasive approach was used for most hysterectomies for benign diseases, but the rate of open hysterectomy has mostly remained constant. Single-port LAVH and VH showed the most tolerable outcomes in terms of operative time and postoperative drop in hemoglobin level in selected cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Different Routes of Hysterectomy Based on a Prospective Algorithm and Their Complications in a Tertiary Care Institute
Subrat Panda, Ananya Das, Rituparna Das, Nalini Sharma, Wansalan Shullai, Vinayak Jante, Anusuya Sharma, Kaushiki Singh, Prateeti Baruah, Ruksana Makakmayum, Imtiaz Wani
Minimally Invasive Surgery.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Analysis of Different Routes of Hysterectomy Based on a Prospective Algorithm and Their Complications in a Tertiary Care Institute
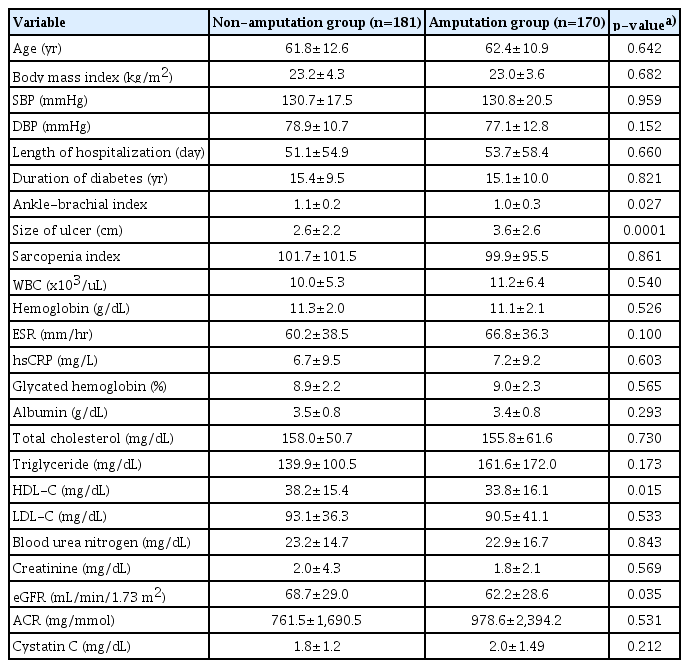
- Risk factors affecting amputation in diabetic foot
- Jun Ho Lee, Ji Sung Yoon, Hyoung Woo Lee, Kyu Chang Won, Jun Sung Moon, Seung Min Chung, Yin Young Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):314-320. Published online May 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00129
- 6,282 View
- 202 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
A diabetic foot is the most common cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations (LEA). The study seeks to assess the risk factors of amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcers (DFU).
Methods
The study was conducted on 351 patients with DFUs from January 2010 to December 2018. Their demographic characteristics, disease history, laboratory data, ankle-brachial index, Wagner classification, osteomyelitis, sarcopenia index, and ulcer sizes were considered as variables to predict outcome. A chi-square test and multivariate logistic regression analysis were performed to test the relationship of the data gathered. Additionally, the subjects were divided into two groups based on their amputation surgery.
Results
Out of the 351 subjects, 170 required LEA. The mean age of the subjects was 61 years and the mean duration of diabetes was 15 years; there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of these averages. Osteomyelitis (hazard ratio [HR], 6.164; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.561−10.671), lesion on percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (HR, 2.494; 95% CI, 1.087−5.721), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR; HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.981−0.999), ulcer size (HR, 1.247; 95% CI, 1.107−1.405), and forefoot ulcer location (HR, 2.475; 95% CI, 0.224−0.73) were associated with risk of amputation.
Conclusion
Osteomyelitis, peripheral artery disease, chronic kidney disease, ulcer size, and forefoot ulcer location were risk factors for amputation in diabetic foot patients. Further investigation would contribute to the establishment of a diabetic foot risk stratification system for Koreans, allowing for optimal individualized treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of Chinese and Western Medical Techniques in Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers With Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Lower Leg
Yongchong Chen, Yunzhu Wang, TaiAn Zhang, Chao Meng, Qing Li, Bohui Zhang, Kai Zhang, Chunfang Qin
The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds.2024; 23(1): 70. CrossRef - Classification of foot ulcers in people with diabetes: A systematic review
Matilde Monteiro‐Soares, Emma J. Hamilton, David A. Russell, Gulapar Srisawasdi, Edward J. Boyko, Joseph L. Mills, William Jeffcoate, Fran Game
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Renal function is highly associated with podiatric risk in diabetic patients
Jean-Baptiste Bonnet, Ilan Szwarc, Antoine Avignon, Sébastien Jugant, Ariane Sultan
Clinical Kidney Journal.2023; 16(11): 2156. CrossRef - Risk factor analysis for diabetic foot ulcer‐related amputation including Controlling Nutritional Status score and neutrophil‐to‐lymphocyte ratio
Yandan Zhu, Hongtao Xu, Yuzhen Wang, Xia Feng, Xinyu Liang, Liying Xu, Zhiqiang Liang, Zhongjia Xu, Yawen Li, Yi Le, Manchen Zhao, Jianfei Yang, Ji Li, Yemin Cao
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(10): 4050. CrossRef - The association between estimated glomerular filtration rate and prognosis in patients with diabetic foot osteomyelitis
Jinghang Zhang, Dong Chen, Xuemei Li, Min Ding, Jun Xu, Meijun Wang, Bai Chang
International Wound Journal.2022; 19(7): 1650. CrossRef - Renal Function Status in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Having Diabetic Foot Infection and Role of Antibiotics
Shabab Hussain, . Arrham, Syeda Javeriya Saeed, Ahmad Murtaza Anwar, Asif Khan, Saifullah Brohi
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2022; : 189. CrossRef - Re-understanding and focusing on normoalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease
Na An, Bi-tao Wu, Yu-wei Yang, Zheng-hong Huang, Jia-fu Feng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of curcumin intake on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial
Mehrdad Mokhtari, Reza Razzaghi, Mansooreh Momen‐Heravi
Phytotherapy Research.2021; 35(4): 2099. CrossRef - Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Its Association With Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Community-Dwelling Asian Population
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Min Cheol Chang
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcomes among patients with chronic kidney disease hospitalized with diabetic foot disorders: A nationwide retrospective study
Michael Salim
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Efficacy of Chinese and Western Medical Techniques in Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers With Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Lower Leg
- Perioperative outcomes of interrupted anticoagulation in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation undergoing non-cardiac surgery
- Bo Eun Park, Myung Hwan Bae, Hyeon Jeong Kim, Yoon Jung Park, Hong Nyun Kim, Se Yong Jang, Jang Hoon Lee, Dong Heon Yang, Hun Sik Park, Yongkeun Cho, Shung Chull Chae
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):321-328. Published online July 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00353
- 5,337 View
- 98 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study aimed to investigate the incidences of and risk factors for perioperative events following anticoagulant discontinuation in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) undergoing non-cardiac surgery.
Methods
A total of 216 consecutive patients who underwent cardiac consultation for suspending perioperative anticoagulants were enrolled. A perioperative event was defined as a composite of thromboembolism and major bleeding.
Results
The mean anticoagulant discontinuation duration was 5.7 (±4.2) days and was significantly longer in the warfarin group (p<0.001). Four perioperative thromboembolic (1.85%; three strokes and one systemic embolization) and three major bleeding events (1.39%) were observed. The high CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores and a prolonged preoperative anticoagulant discontinuation duration (4.4±2.1 vs. 2.9±1.8 days; p=0.028) were associated with perioperative events, whereas the anticoagulant type (non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants or warfarin) was not. The best cut-off levels of the HAS-BLED and CHA2DS2-VASc scores were 3.5 and 2.5, respectively, and the preoperative anticoagulant discontinuation duration for predicting perioperative events was 2.5 days. Significant differences in the perioperative event rates were observed among the four risk groups categorized according to the sum of these values: risk 0, 0%; risk 1, 0%; risk 2, 5.9%; and risk 3, 50.0% (p<0.001). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the HAS-BLED score was an independent predictor for perioperative events.
Conclusion
Thromboembolic events and major bleeding are not uncommon during perioperative anticoagulant discontinuation in patients with NVAF, and interrupted anticoagulation strategies are needed to minimize these. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bleeding risk in female patients undergoing intravesical injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for overactive bladder: a Danish retrospective cohort study
Meryam El Issaoui, Sophia Elissaoui, Marlene Elmelund, Niels Klarskov
International Urogynecology Journal.2023; 34(10): 2581. CrossRef
- Bleeding risk in female patients undergoing intravesical injection of onabotulinumtoxinA for overactive bladder: a Danish retrospective cohort study
Case reports
- Negative myoclonus associated with tramadol use
- Seong Yoon Bae, Se-Jin Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):329-331. Published online April 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00108
- 6,584 View
- 179 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Negative myoclonus (NM) is a shock-like jerky involuntary movement caused by a sudden, brief interruption of tonic muscle contraction. NM is observed in patients diagnosed with epilepsy, metabolic encephalopathy, and drug toxicity and in patients with brain lesions. A 55-year-old man presented with NM in both his arms and neck. He has taken medications containing tramadol at a dose of 80–140 mg/day for 5 days due to common cold. He had no history of seizures. Acute lesions were not observed during magnetic resonance imaging, and abnormal findings in his laboratory tests were not noted. His NM resolved completely after the discontinuation of tramadol and the oral administration of clonazepam. Our case report suggests that tramadol can cause NM in patients without seizure history or metabolic disorders, even within its therapeutic dose.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Tramadol Induced Jerks
Waiz Wasey, Imad Aziz, Sharefi Saleh, Naila Manahil, Neha Wasey
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Tramadol Induced Jerks
- Prevention of thiopurine-induced early leukopenia in a Korean pediatric patient with Crohn’s disease who turned out to possess homozygous mutations in NUDT15 R139C
- Jaewoan Bae, Byung-Ho Choe, Ben Kang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):332-336. Published online May 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00178

- 5,145 View
- 86 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Homozygous mutations in NUDT15 R139C are known as the major factor associated with thiopurine-induced early leukopenia, particularly in Asian patients. Therefore, NUDT15 genotyping is currently recommended before thiopurine treatment to identify patients who are NUDT15 poor metabolizers and consider the use of an alternative immunomodulatory therapy. We report a case of a 12-year-old Korean girl with Crohn’s disease (CD), in whom thiopurine-induced leukopenia was prevented by initiation of azathioprine (AZA) therapy at a low dose (0.5 mg/kg/day) and early detection of significant hair loss and white blood cell (WBC) count decrease at 17 days from the start of AZA treatment. The WBC count dropped from 8,970/μL to 3,370/μL in 2 weeks, and AZA treatment was stopped because of concerns of potential leukopenia in the near future. Her WBC count recovered to 5,120/μL after 3 weeks. Gene analysis later revealed that she had a homozygous mutation in NUDT15 R139C, resulting in a poor metabolizing activity of NUDT15. In situations when NUDT15 genotyping is unavailable, initiation of AZA therapy at 0.5 mg/kg/day with close observation of hair loss and WBC counts within 2 weeks may be an alternative way to prevent thiopurine-induced early leukopenia in Asian children with CD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of Candidate Genes for Min Pig Villi Hair Traits by Genome-Wide Association of Copy Number Variation
Xinmiao He, Ming Tian, Wentao Wang, Yanzhong Feng, Zhongqiu Li, Jiahui Wang, Yan Song, Jinfeng Zhang, Di Liu
Veterinary Sciences.2023; 10(5): 307. CrossRef - Case report: NUDT15 polymorphism and severe azathioprine-induced myelosuppression in a young Chinese female with systematic lupus erythematosus: a case analysis and literature review
Juan Gu, Yupei Lin, Yuhe Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - KASL clinical practice guidelines for management of autoimmune hepatitis 2022
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(3): 542. CrossRef
- Identification of Candidate Genes for Min Pig Villi Hair Traits by Genome-Wide Association of Copy Number Variation
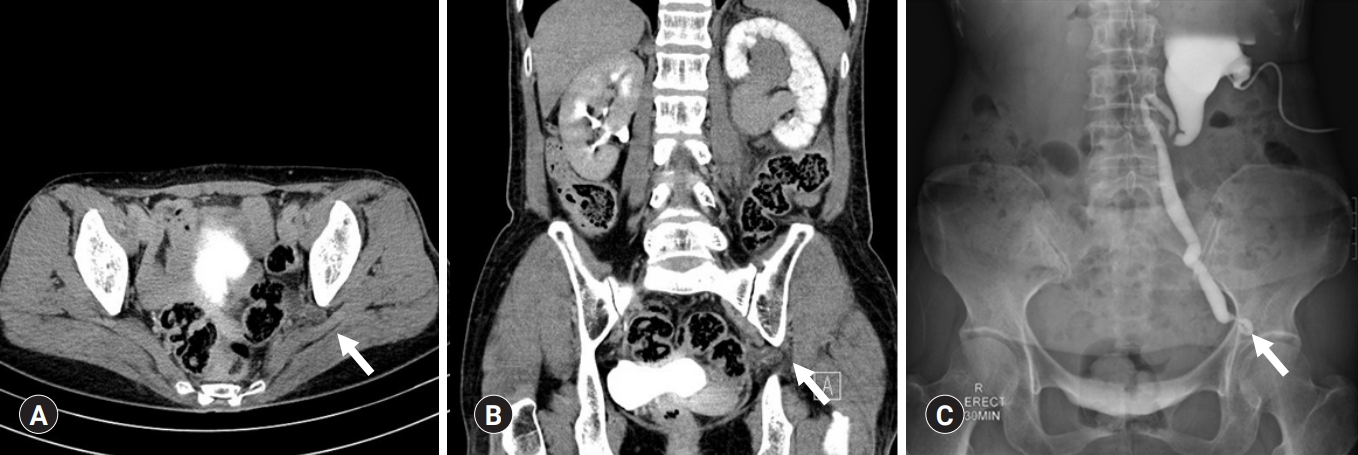
- Ureterosciatic hernia causing obstructive uropathy successfully managed with minimally invasive procedures
- Yeong Uk Kim, Jae Ho Cho, Phil Hyun Song
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):337-340. Published online July 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00402
- 4,347 View
- 98 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Ureterosciatic hernia is extremely rare. In ureteral herniation, ureter prolapses occur through either the greater or lesser sciatic foramen. Atrophy of the piriformis muscle, hip joint diseases, and defects in the parietal pelvic fascia are predisposing factors for the development of ureterosciatic hernia. Most symptomatic patients have been treated surgically, with conservative treatment reserved only for asymptomatic patients. To the best of our knowledge, long-term follow-up outcomes after ureterosciatic hernia management are sparse. In this paper, we report the case of a 68-year-old woman who presented with colicky left abdominal pain. After computed tomography (CT) scan and anterograde pyelography, she was diagnosed ureterosciatic hernia with obstructive uropathy. We performed ureteral balloon dilatation and double-J ureteral stent placement. After this minimally invasive procedure, CT scan demonstrated that the left ureter had returned to its normal anatomical position without looping into the sciatic foramen. The patient remained asymptomatic with no adverse events 7 years after the minimally invasive procedures. This brief report describes ureterosciatic hernia successfully managed with minimally invasive procedures with long-term follow-up outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ureterosciatic Hernia in Focus: A Narrative Review of the Literature
Mohamed Mustafa, Afiq Pouzi, Peter Senada, Lokesh Suraparaju, Suresh Gupta
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Urosepsis secondary to ureterosciatic hernia corrected with ureteral stent placement: a case report and literature review
Kohei Kakimoto, Mayu Hikone, Ko Nagai, Jun Yamakawa, Kazuhiro Sugiyama, Yuichi Hamabe
International Journal of Emergency Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Ureterosciatic Hernia in Focus: A Narrative Review of the Literature
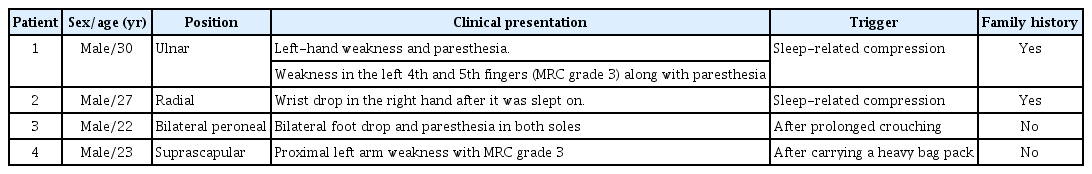
- Clinical characteristics of hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsy presenting with monoparesis in the emergency department
- Changho Kim, Jin-Sung Park
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(4):341-344. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00472
- 5,174 View
- 66 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsy (HNPP) is a rare neurological genetic disease caused by deletion of the peripheral myelin protein 22 gene and presents in childhood or young adulthood. We report four cases of HNPP with typical and rare presentations, reflecting the broad clinical spectrum of this disease. Two patients presented with mononeuropathies that are frequently observed in HNPP; the remaining two presented with bilateral neuropathy or mononeuropathy anatomically present in the deep layer. This reflects the broad clinical presentation of HNPP, and clinicians should differentiate these conditions in young patients with monoparesis or bilateral paresis. Although HNPP is currently untreatable, early diagnosis in the emergency department can lead to early detection, eventually resulting in less provocation and recurrence which may cause early motor nerve degeneration.

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



