Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Review articles
- Can antioxidants be effective therapeutics for type 2 diabetes?
- Soyoung Park, So-Young Park
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):83-94. Published online October 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00563
- 10,669 View
- 220 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
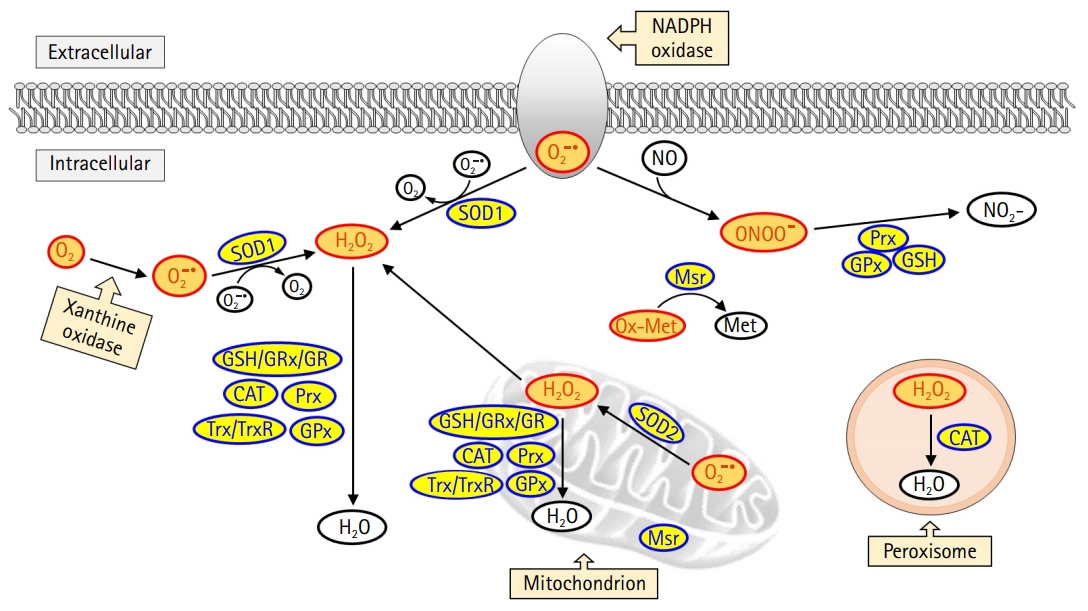
PDF - The global obesity epidemic and the growing elderly population largely contribute to the increasing incidence of type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance acts as a critical link between the present obesity pandemic and type 2 diabetes. Naturally occurring reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulate intracellular signaling and are kept in balance by the antioxidant system. However, the imbalance between ROS production and antioxidant capacity causes ROS accumulation and induces oxidative stress. Oxidative stress interrupts insulin-mediated intracellular signaling pathways, as supported by studies involving genetic modification of antioxidant enzymes in experimental rodents. In addition, a close association between oxidative stress and insulin resistance has been reported in numerous human studies. However, the controversial results with the use of antioxidants in type 2 diabetes raise the question of whether oxidative stress plays a critical role in insulin resistance. In this review article, we discuss the relevance of oxidative stress to insulin resistance based on genetically modified animal models and human trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of substitution of wheat flour with chickpea flour on their physico-chemical characteristics
Jiwan S. Sidhu, Tasleem Zafar, Abdulwahab Almusallam, Muslim Ali, Amani Al-Othman
Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The consumption of date palm fruits as a source of bioactive compounds in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross sectional study
M.Q. Al-Mssallem
Acta Horticulturae.2023; (1371): 381. CrossRef - Aging, oxidative stress and degenerative diseases: mechanisms, complications and emerging therapeutic strategies
Mani Raj Chaudhary, Sakshi Chaudhary, Yogita Sharma, Thokchom Arjun Singh, Alok Kumar Mishra, Shweta Sharma, Mohammad Murtaza Mehdi
Biogerontology.2023; 24(5): 609. CrossRef - Development and Characterization of Oxidatively Responsive Thiol–Ene Networks for Bone Graft Applications
Tyler Touchet, Samuel Briggs, Lance Graul, Duncan J. Maitland
ACS Applied Bio Materials.2022; 5(6): 2633. CrossRef - Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Its Association With Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Community-Dwelling Asian Population
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Min Cheol Chang
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Prx4, Total Oxidant Status, and Inflammatory Factors with Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Sahar Mazloomi, Nasrin Sheikh, Marzieh Sanoee Farimani, Shamim Pilehvari, Raffaele Pezzani
International Journal of Endocrinology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Plants Secondary Metabolites as Blood Glucose-Lowering Molecules
Mayadah Bashir Shehadeh, Ghadeer A. R. Y. Suaifan, Ala’ Mustafa Abu-Odeh
Molecules.2021; 26(14): 4333. CrossRef - An Epidemiological Study Report on the Antioxidant and Phenolic Content of Selected Mediterranean Functional Foods, Their Consumption Association with the Body Mass Index, and Consumers Purchasing Behavior in a Sample of Healthy Greek Adults
Aikaterini Kandyliari, Ioannis-Nektarios Elmaliklis, Olga Kontopoulou, Marianna Tsafkopoulou, Georgios Komninos, Christina Ntzatha, Andreas Petsas, Haralabos C. Karantonis, Antonios E. Koutelidakis
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(17): 7818. CrossRef - Sterculia tragacantha Lindl Leaf Extract Ameliorates STZ-Induced Diabetes, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Neuronal Impairment
Amos Sunday Onikanni, Bashir Lawal, Augustine O Olusola, Janet O Olugbodi, Saidu Sani, Basiru Olaitan Ajiboye, Omotayo B Ilesanmi, Mohammed Alqarni, Gomaa Mostafa-Hedeab, Ahmad J Obaidullah, Gaber El-Saber Batiha, Alexander TH Wu
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 6749. CrossRef - Methionine sulfoxide reductase B3 deficiency inhibits the development of diet-induced insulin resistance in mice
Hye-Na Cha, Chang-Hoon Woo, Hwa-Young Kim, So-Young Park
Redox Biology.2020; : 101823. CrossRef
- Effect of substitution of wheat flour with chickpea flour on their physico-chemical characteristics
- F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the infection of heart
- Eunjung Kong
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):95-106. Published online October 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00479

- 6,833 View
- 109 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Infections involving the heart are becoming increasingly common, and a timely diagnosis of utmost importance, despite its challenges. F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) is a recently introduced diagnostic tool in cardiology. This review focuses on the current evidence for the use of FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis of infective endocarditis, cardiac implantable device infection, left ventricular assist device infection, and secondary complications. The author discusses considerations when using FDG PET/CT in routine clinical practice, patient preparation for reducing physiologic myocardial uptake, acquisition of images, and interpretation of PET/CT findings. This review also functions to highlight the need for a standardized acquisition protocol.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of the 18F-FDG PET/CT in the Management of Patients Suspected of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices’ Infection
Antonio Rosario Pisani, Dino Rubini, Corinna Altini, Rossella Ruta, Maria Gazzilli, Angela Sardaro, Francesca Iuele, Nicola Maggialetti, Giuseppe Rubini
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(1): 65. CrossRef - The detection of infectious endocarditis may be enhanced by a repeat FDG-PET while maintaining patients on a ketogenic diet
Marine Germaini, Caroline Boursier, François Goehringer, Christine Selton-Suty, Benjamin Lefevre, Véronique Roch, Laetitia Imbert, Marine Claudin, Elodie Chevalier, Pierre-Yves Marie
Journal of Nuclear Cardiology.2022; 29(6): 3256. CrossRef
- The Role of the 18F-FDG PET/CT in the Management of Patients Suspected of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices’ Infection
- The role of microRNAs in cell death pathways
- Ji Hoon Jang, Tae-Jin Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):107-117. Published online January 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00836
- 10,263 View
- 210 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
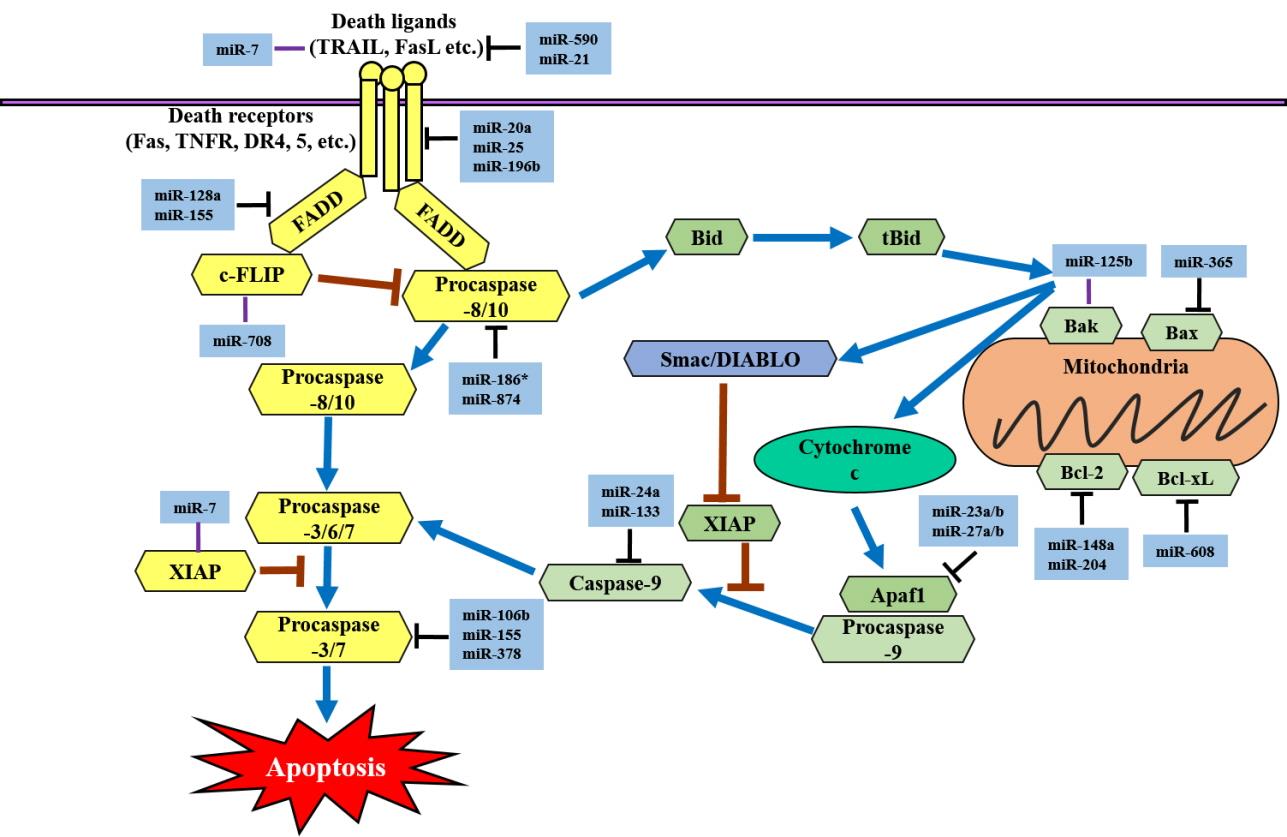
PDF - MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate target messenger RNAs. In multicellular eukaryotes, numerous miRNAs perform basic cellular functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and death. Abnormal expression of miRNAs weakens or modifies various apoptosis pathways, leading to the development of human cancer. Cell death occurs in an active manner that maintains tissue homeostasis and eliminates potentially harmful cells through regulated cell death processes, including apoptosis, autophagic cell death, and necroptosis. In this review, we discuss the involvement of miRNAs in regulating cell death pathways in cancers and the potential therapeutic functions of miRNAs in cancer treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- MicroRNAs (miRNAs) role in hypertension: pathogenesis and promising therapeutics
Nour Shaheen, Ahmed Shaheen, Rehab Adel Diab, Mariam Tarek Desouki
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(1): 319. CrossRef - Psychosocial Stress and MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Myometrial Tissue of Women Undergoing Surgical Treatment for Uterine Fibroids
Christian K. Dye, Haotian Wu, Brianna VanNoy, Stephanie Calluori, Cherie Q. Marfori, Andrea A. Baccarelli, Ami R. Zota
Reproductive Sciences.2024; 31(6): 1651. CrossRef - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of hypoxic/ischemic injury upon perinatal asphyxia—are we there yet?
Damian Mielecki, Jakub Godlewski, Elzbieta Salinska
Frontiers in Neurology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mapping the function of MicroRNAs as a critical regulator of tumor-immune cell communication in breast cancer and potential treatment strategies
Aimi Syamima Abdul Manap, Aini Athirah Wisham, Fei Wen Wong, Huda Raihanah Ahmad Najmi, Zhi Fei Ng, Rubaiyat Siddique Diba
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA dysregulation and its impact on apoptosis-related signaling pathways in myelodysplastic syndrome
Neda Hedayati, Mobina Safaei Naeini, Mohammad Mahdi Ale Sahebfosoul, Alireza Mafi, Yaser Eshaghi Milasi, Anahita Rizaneh, Noushin Nabavi, Najma Farahani, Mina Alimohammadi, Behrooz Ghezelbash
Pathology - Research and Practice.2024; : 155478. CrossRef - The role of miR-128 in cancer development, prevention, drug resistance, and immunotherapy
Hendrik Setia Budi, Laith A. Younus, Methaq Hadi Lafta, Sameena Parveen, Hawraa Jabbar Mohammad, Zahraa Haleem Al-qaim, Mohammed Abed Jawad, Rosario Mireya Romero Parra, Yasser Fakri Mustafa, Firas Rahi Alhachami, Sajad Karampoor, Rasoul Mirzaei
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - microRNAs (miRNAs) in Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)—Recent Literature Review
Marianna Makowska, Beata Smolarz, Hanna Romanowicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3521. CrossRef - The regulatory role of microRNAs in common eye diseases: A brief review
Javier A. Benavides-Aguilar, Jonathan I. Morales-Rodríguez, Héctor Ambriz-González, Luis M. Ruiz-Manriquez, Antara Banerjee, Surajit Pathak, Asim K. Duttaroy, Sujay Paul
Frontiers in Genetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel, non-conventional pathways of necroptosis in the heart and other organs: Molecular mechanisms, regulation and inter-organelle interplay
Csaba Horvath, Izabela Jarabicova, Branislav Kura, Barbora Kalocayova, Eva Faurobert, Sean M. Davidson, Adriana Adameova
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2023; 1870(7): 119534. CrossRef - Does exercise influence skeletal muscle by modulating mitochondrial functions via regulating MicroRNAs? A systematic review
Yu-Feng Long, Simon Kwoon-Ho Chow, Can Cui, Ronald Man Yeung Wong, Ning Zhang, Ling Qin, Sheung-Wai Law, Wing-Hoi Cheung
Ageing Research Reviews.2023; 91: 102048. CrossRef - Cellular signaling modulated by miRNA-3652 in ovarian cancer: unveiling mechanistic pathways for future therapeutic strategies
Komal Imran, Muhammad Javed Iqbal, Rameesha Abid, Muhammad Mushtaq Ahmad, Daniela Calina, Javad Sharifi-Rad, William C. Cho
Cell Communication and Signaling.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D and microRNAs: Role in the pathogenesis and prognosis of breast cancer (Review)
Luca Falzone, Giuseppe Gattuso, Saverio Candido, Alessandro Tomaselli, Simone Fagone, Demetrios Spandidos, Massimo Libra
International Journal of Epigenetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The regulation of necroptosis and perspectives for the development of new drugs preventing ischemic/reperfusion of cardiac injury
Leonid N. Maslov, Sergey V. Popov, Natalia V. Naryzhnaya, Alexandr V. Mukhomedzyanov, Boris K. Kurbatov, Ivan A. Derkachev, Alla A. Boshchenko, Igor Khaliulin, N. Rajendra Prasad, Nirmal Singh, Alexei Degterev, Evgenia A. Tomilova, Ekaterina V. Sapozhenko
Apoptosis.2022; 27(9-10): 697. CrossRef - Interleukin-10 Protects against Ureteral Obstruction-Induced Kidney Fibrosis by Suppressing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis
Kyongjin Jung, Taejin Lee, Jooyoung Kim, Eongi Sung, Inhwan Song
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(18): 10702. CrossRef - Immune Modulation as a Key Mechanism for the Protective Effects of Remote Ischemic Conditioning After Stroke
Sima Abbasi-Habashi, Glen C. Jickling, Ian R. Winship
Frontiers in Neurology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- MicroRNAs (miRNAs) role in hypertension: pathogenesis and promising therapeutics
Original articles
- A study on evaluator factors affecting physician-patient interaction scores in clinical performance examinations: a single medical school experience
- Young Soon Park, Kyung Hee Chun, Kyeong Soo Lee, Young Hwan Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):118-126. Published online August 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00423
- 5,371 View
- 108 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
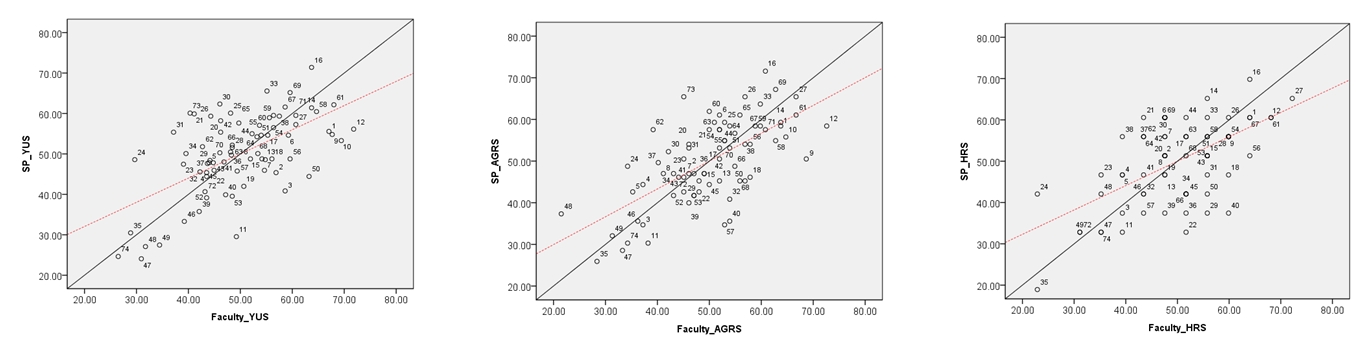
This study is an analysis of evaluator factors affecting physician-patient interaction (PPI) scores in clinical performance examination (CPX). The purpose of this study was to investigate possible ways to increase the reliability of the CPX evaluation.
Methods
The six-item Yeungnam University Scale (YUS), four-item analytic global rating scale (AGRS), and one-item holistic rating scale (HRS) were used to evaluate student performance in PPI. A total of 72 fourth-year students from Yeungnam University College of Medicine in Korea participated in the evaluation with 32 faculty and 16 standardized patient (SP) raters. The study then examined the differences in scores between types of scale, raters (SP vs. faculty), faculty specialty, evaluation experience, and level of fatigue as time passes.
Results
There were significant differences between faculty and SP scores in all three scales and a significant correlation among raters’ scores. Scores given by raters on items related to their specialty were lower than those given by raters on items out of their specialty. On the YUS and AGRS, there were significant differences based on the faculty’s evaluation experience; scores by raters who had three to ten previous evaluation experiences were lower than others’ scores. There were also significant differences among SP raters on all scales. The correlation between the YUS and AGRS/HRS declined significantly according to the length of evaluation time.
Conclusion
In CPX, PPI score reliability was found to be significantly affected by the evaluator factors as well as the type of scale.
- The relationship between disability and clinical outcomes in maintenance dialysis patients
- Seok Hui Kang, Jun Young Do, Jun Chul Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):127-135. Published online October 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00346
- 5,361 View
- 72 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Dialysis patients are prone to having disabilities. We aimed to evaluate the association between disability and various clinical outcomes in Korean dialysis patients.
Methods
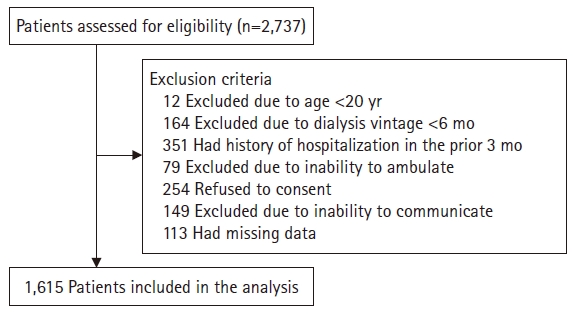
This study consisted of 1,615 dialysis patients from 27 centers. We evaluated disability by using four questions on the activities of daily living (ADLs) concerning whether help was needed for feeding, dressing/undressing, getting in/out of bed, or taking a bath/shower. We divided the patients into three groups: no disability (Non-D, none of the four ADL domains required help; n=1,312), mild disability (Mild-D, one ADL domain required some/full help; n=163), or moderate to severe disability (MS-D, two or more ADL domains required some/full help; n=140). We evaluated falls, frailty, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), mortality, and hospitalization.
Results
The numbers of participants with a fall during the last 1 year were 199 (15.2%), 42 (25.8%), and 44 (31.4%) in the Non-D, Mild-D, and MS-D groups, respectively (p<0.001). The numbers of participants with frailty in the Non-D, Mild-D, and MS-D groups were 381 (29.0%), 84 (51.5%), and 93 (66.4%), respectively (p<0.001). In both univariate and multivariate analyses, the physical component scale and mental component scale scores decreased as the grade of disability increased (p<0.001 for both scores). Hospitalization-free survival rate at 500 days was 64.2%, 56.7%, and 51.1% in the Non-D, Mild-D, and MS-D, respectively (p=0.001 for trend). Patient survival rate at 500 days was 95.3%, 89.5%, and 92.3% in the Non-D, Mild-D, and MS-D, respectively (p=0.005 for trend).
Conclusion
Disability was associated with falls, frailty, HRQoL scales, and survival trends in Korean dialysis patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The predictive role of hope and social relational quality in disability acceptance among Iranian patients under hemodialysis
Nilofar Pasyar, Mostafa Jowkar, Masoume Rambod
BMC Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Its Association With Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Community-Dwelling Asian Population
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Min Cheol Chang
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The predictive role of hope and social relational quality in disability acceptance among Iranian patients under hemodialysis
- Analysis of the risk factors of acute kidney injury after total hip or knee replacement surgery
- Yoo Jin Lee, Bong Soo Park, Sihyung Park, Jin Han Park, Il Hwan Kim, Junghae Ko, Yang Wook Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):136-141. Published online October 27, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00542

- 6,197 View
- 99 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Postoperative acute kidney injury (AKI), which increases the risk of postoperative morbidity and mortality, poses a major concern to surgeons. We conducted this study to analyze the risk factors associated with the occurrence of AKI after orthopedic surgery.
Methods
This was a retrospective study that included 351 patients who underwent total hip or knee replacement surgery at Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital between January 2012 and December 2016.
Results
AKI occurred in 13 (3.7%) of the 351 patients. The patients’ preoperative estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 66.66±34.02 mL/min/1.73 m2 in the AKI group and 78.07±21.23 mL/min/1.73 m2 in the non-AKI group. The hemoglobin levels were 11.21±1.65 g/dL in the AKI group and 12.39±1.52 g/dL in the non-AKI group. Hemoglobin level was related to increased risk of AKI (odds ratio [OR], 0.13; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.02–0.68; p=0.016). Administration of crystalloid or colloid fluid alone and the perioperative amount of fluid did not show any significant relationship with AKI. Further analysis of the changes in eGFR was performed using a cutoff value of 7.54. The changes in eGFR were significantly related to decreased risk of AKI (OR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.61–0.89; p=0.002).
Conclusion
Renal function should be monitored closely after orthopedic surgery if patients have chronic kidney disease and low hemoglobin level. Predicting the likelihood of AKI occurrence, early treatment of high-risk patients, and monitoring perioperative laboratory test results, including eGFR, will help improve patient prognosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Supplemental oxygen is associated with increased complications and readmission following total shoulder arthroplasty
Nikhil Vallabhaneni, Alexander S. Guareschi, Josef K. Eichinger, Richard J. Friedman
Seminars in Arthroplasty: JSES.2023; 33(3): 512. CrossRef - Acute kidney injury after primary total hip replacement
M. L. Lebed, M. G. Kirpichenko, E. V. Novikova, T. G. Lebed, A. V. Mankov
Acta Biomedica Scientifica.2023; 8(5): 125. CrossRef
- Supplemental oxygen is associated with increased complications and readmission following total shoulder arthroplasty
- Association between cystographic anastomotic urinary leakage following retropubic radical prostatectomy and early urinary incontinence
- Se Yun Kwon
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):142-147. Published online November 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00682

- 5,092 View
- 75 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study was performed to investigate the association between cystographic anastomotic urinary leakage (UL) after radical retropubic prostatectomy (RRP) and early urinary incontinence (UI).
Methods
The medical records of 53 patients who had undergone cystography after RRP at our institution between January 2015 and December 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. Cystography was performed 7 to 10 days after surgery. The duration of catheterization depended on the degree of UL, which was classified as mild, moderate, or severe. The study subjects were divided into the non-UL group and the UL group. Continence was defined as the use of no pads. The prostate was dissected in an antegrade fashion, and urethrovesical anastomosis was performed with a continuous suture.
Results
Incontinence rates at 1 and 3 months postoperatively were significantly higher in the UL group than the non-UL group (83.3% vs. 52.2%, p=0.014 and 76.7% vs. 47.8%, p=0.030, respectively); however, those at 6 and 12 months were not significantly different (23.3% vs. 17.4%, p=0.597 and 4.3% vs. 10.0%, p=0.440, respectively). The presence of cystographic anastomotic UL was found to be predictive of UI during the first 3 postoperative months (odds ratio, 3.3; p=0.045). The continence rates during the first 3 postoperative month continence rate showed significant difference with non-UL group regardless of the degree of UL.
Conclusion
The presence of anastomotic UL on cystography was associated with higher rates of UI in the early postoperative period, however the grade of UL was not related to the late recovery of UI. Incontinence rates in patients with or without anastomotic UL immediately after RRP equalized at 6 months. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recognition of Postoperative Cystography Features by Artificial Intelligence to Predict Recovery from Postprostatectomy Urinary Incontinence: A Rapid and Easy Way to Predict Functional Outcome
I-Hung Shao, Hung-Cheng Kan, Hung-Yi Chen, Ying-Hsu Chang, Liang-Kang Huang, Yuan-Cheng Chu, Po-Hung Lin, Kai-Jie Yu, Cheng-Keng Chuang, See-Tong Pang, Chun-Te Wu
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(1): 126. CrossRef
- Recognition of Postoperative Cystography Features by Artificial Intelligence to Predict Recovery from Postprostatectomy Urinary Incontinence: A Rapid and Easy Way to Predict Functional Outcome
Case reports
- Pudendal nerve entrapment syndrome caused by ganglion cysts along the pudendal nerve
- Young Je Kim, Du Hwan Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):148-151. Published online July 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00437
- 8,002 View
- 116 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
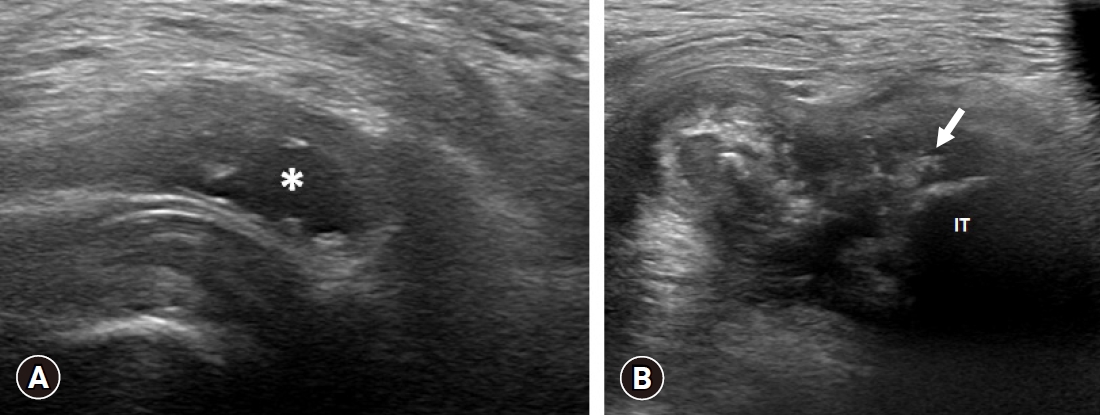
PDF - Pudendal nerve entrapment (PNE) syndrome refers to the condition in which the pudendal nerve is entrapped or compressed. Reported cases of PNE associated with ganglion cysts are rare. Deep gluteal syndrome (DGS) is defined as compression of the sciatic or pudendal nerve due to a non-discogenic pelvic lesion. We report a case of PNE caused by compression from ganglion cysts and treated with steroid injection; we discuss this case in the context of DGS. A 77-year-old woman presented with a 3-month history of tingling and burning sensations in the left buttock and perineal area. Ultrasonography showed ganglion cystic lesions at the subgluteal space. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed cystic lesions along the pudendal nerve from below the piriformis to the Alcock’s canal and a full-thickness tear of the proximal hamstring tendon. Aspiration of the cysts did not yield any material. We then injected steroid into the cysts, which resolved her symptoms. Steroid injection into a ganglion cyst should be considered as a treatment option for PNE caused by ganglion cysts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pudendal neuralgia
I. V. Borodulina, G. V. Kovalev
Neuromuscular Diseases.2024; 13(4): 83. CrossRef - Overview of the anatomical basis of the piriformis syndrome‑dissection with magnetic resonance correlation
Ofelia-Costina Goidescu, Mihaly Enyedi, Adrian-Daniel Tulin, Raluca Tulin, Ileana Vacaroiu, Adriana Nica, Dorin Dragos, Dorin Ionescu, Dragos Georgescu, Adrian Miron, Florin-Mihail Filipoiu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Pudendal neuralgia
- Diplopia developed by cervical traction after cervical spine surgery
- Ji-Yoon Kim, Hyuna Kim, So Jeong Kang, Hyunjee Kim, Young-Seok Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):152-156. Published online July 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00241

- 7,129 View
- 188 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Diplopia is a rare complication of spine surgery. The abducens nerve is one of the cranial nerves most commonly related to diplopia caused by traction injury. We report a case of a 71-year-old woman who presented with diplopia developing from abducens nerve palsy after C1–C2 fixation and fusion due to atlantoaxial subluxation with cord compression. As soon as we discovered the symptoms, we suspected excessive traction by the instrument and subsequently performed reoperation. Subsequently, the patient’s symptoms improved. In other reported cases we reviewed, most were transient. However, we thought that our rapid response also helped the patient’s fast recovery in this case. The mechanisms by which postoperative diplopia develops vary and, thus, remain unclear. We should pay attention to the fact that the condition is sometimes an indicator of an underlying, life-threatening condition. Therefore, all patients with postoperative diplopia should undergo thorough ophthalmological and neurological evaluations as well as careful observation by a multidisciplinary team.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transient internuclear ophthalmoplegia following anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
Kevin N. Cordeiro, Garret P. Greeneway, Paul S. Page, Nathaniel P. Brooks
Surgical Neurology International.2022; 13: 527. CrossRef
- Transient internuclear ophthalmoplegia following anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
- Ultrasonographic and magnetic resonance images of a gluteus maximus tear
- Jong Bum Kim, Wonho Lee, Min Cheol Chang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):157-159. Published online July 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00500
- 7,006 View
- 127 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
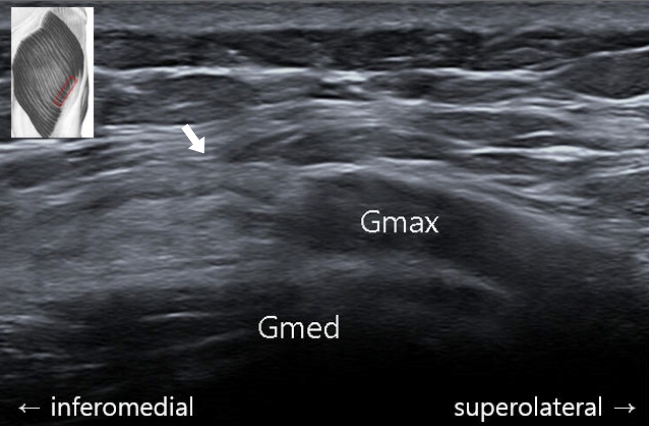
PDF - The diagnosis of a gluteal muscle tear or strain is based on clinical findings. However, for an accurate diagnosis, imaging examinations are also needed. Herein, we describe the case of a patient with a gluteus maximus muscle tear confirmed by ultrasonography (US) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A 58-year-old woman complained of dull pain in the left lateral gluteal region that she had been experiencing for 8 days. In the axial US image, retraction of the left gluteus maximus muscle was noted around its insertion site in the iliotibial band. On an MRI, a partial tear in the left gluteus maximus was observed at its insertion site in the left iliotibial band. In addition, fluid infiltration due to edema and hemorrhage was observed. A partial left gluteal muscle tear was diagnosed. The patient was treated with physical therapy at the involved region and oral analgesics. She reported relief from the pain after 1 month of treatment. Based on this experience, we recommend US or MRI for accurate diagnosis of muscle tear or strain.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gluteus Maximus Distal Myotendinous Junction Tear in a Pickleball Player: A Case Report
Shanterian King, Adam Johnson, Elena Jelsing
Current Sports Medicine Reports.2024; 23(6): 213. CrossRef - Essentials of thoracic outlet syndrome: A narrative review
Min Cheol Chang, Du Hwan Kim
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(21): 5804. CrossRef - Obturator hernia - a rare etiology of lateral thigh pain: A case report
Jun Young Kim, Min Cheol Chang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(34): 10728. CrossRef
- Gluteus Maximus Distal Myotendinous Junction Tear in a Pickleball Player: A Case Report
- A new type of oculocutaneous albinism with a novel OCA2 mutation
- Sang Yoon Lee, Eun Joo Lee, Jun Chul Byun, Kyung Mi Jang, Sae Yoon Kim, Su-Kyeong Hwang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):160-164. Published online August 3, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00339
- 8,738 View
- 214 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
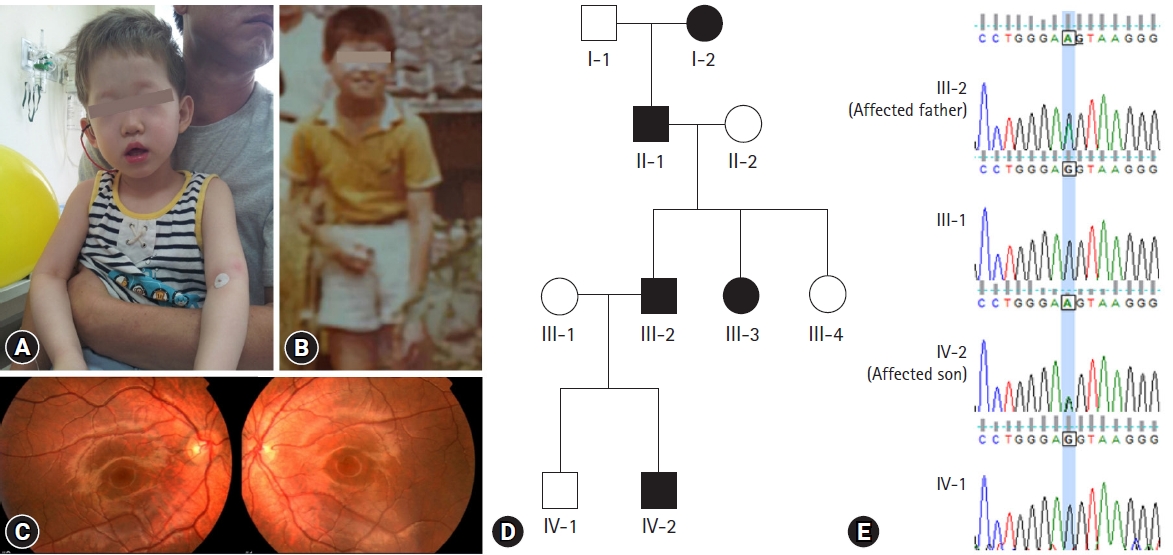
PDF - Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) is a group of rare genetically heterogeneous disorders, characterized by hypopigmentation of the eyes, skin, and hair, which result in ocular abnormalities and a risk of developing skin cancer. Currently, there is no ophthalmologic procedure or drug that prevents the clinical features of OCA. Here, we report a new type of OCA in two, unrelated Korean families with the same OCA2 mutation. Affected individuals in this study are different from those of previous reports in two aspects: an inheritance pattern and clinical presentation. All reported patients with OCA have shown an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, while our patients showed an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Small amounts of pigment can be acquired with age in OCA, but there is no substantial variation from adolescence to adulthood in this regard. A case where the patient attained normal pigmentation levels has never been reported. However, our patients displayed completely normal pigmentation in their late twenties. Whole exome sequencing and in-silico analysis revealed a novel mutation, OCA2 c.2338G>A p.(G780S) (NM_000275) with a high likelihood of pathogenicity. Sanger sequencing of p.G780S identified the same mutation in the affected individuals, which was not found in the family members with normal phenotype. We hypothesize that OCA2 G780S not only acts as a pathogenic variant of OCA but also induces pigmentation by enhancing the melanogenesis gene expression of other modifier genes, such as SLC45A2 and TPC2. These findings may provide further understanding of melanin biosynthesis and new treatment methods for OCA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in OCA2 gene were identified in a Chinese family with oculocutaneous albinism
Beilei Jiang, Hua Zhang, Yuling Kan, Xueping Gao, Zhaoli Du, Quan Liu
Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Mutation Spectrum of Autosomal Recessive Non-Syndromic Oculocutaneous Albinism (nsOCA) in Pakistan: A Review
Muhammad Ikram Ullah
Genes.2022; 13(6): 1072. CrossRef
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in OCA2 gene were identified in a Chinese family with oculocutaneous albinism
- Delayed treatment-free response after romiplostim discontinuation in pediatric chronic immune thrombocytopenia
- Hyun Ji Lim, Young Tae Lim, Jeong Ok Hah, Jae Min Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):165-168. Published online August 7, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00493
- 5,414 View
- 136 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
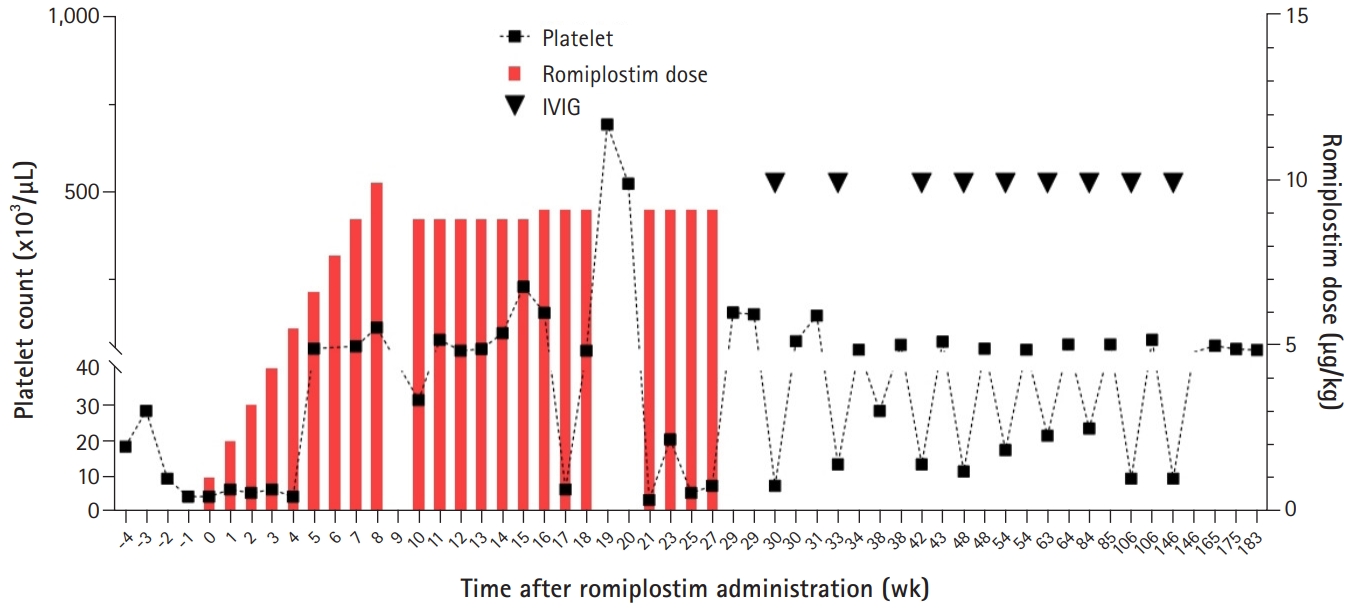
PDF - We report the case of a 16-month-old patient with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) patient who experienced delayed treatment-free response (TFR) after romiplostim treatment. He received intravenous immunoglobulin every month to maintain a platelet count above 20,000/μL for 2 years. Thereafter, he received rituximab and cyclosporine as second-line therapy, with no response, followed by romiplostim. After 4 weeks of treatment, the platelet count was maintained above 50,000/μL. Following 7 months of treatment, he discontinued romiplostim, and the platelet count decreased. His platelet counts remained above 50,000/μL, without any bleeding symptoms, 2 years after romiplostim discontinuation. This is the first report of TFR after romiplostim treatment in pediatric chronic ITP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A cost–utility analysis of thrombopoietin receptor agonists for treating pediatric immune thrombocytopenia purpura after failure of first‐line therapies
Huimin Du, Jiamin Wang, Joel Livingston, Ziyad Alrajhi, Melanie Kirby‐Allen, Brian Chan, Rebecca Hancock‐Howard, Peter C. Coyte
Pediatric Blood & Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Generic romiplostim for children with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia: Experience from a tertiary care centre in North India
Chandana Mareddy, Manas Kalra, Anupam Sachdeva
British Journal of Haematology.2022; 197(5): 618. CrossRef - Tapering of the thrombopoietin receptor agonist in paediatric patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia: Is it possible?
María Solsona, Rubén Berrueco, Elena Sebastián, Áurea Cervera, Ana Sastre, Itziar Astigarraga, Bienvenida Argilés, María Ángeles Dasí, José Luís Dapena, Emilio Monteagudo
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 88(9): 4220. CrossRef
- A cost–utility analysis of thrombopoietin receptor agonists for treating pediatric immune thrombocytopenia purpura after failure of first‐line therapies
- High-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma in the thyroid gland with poor prognosis
- Hyeong Chan Shin
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021;38(2):169-174. Published online March 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2021.00941
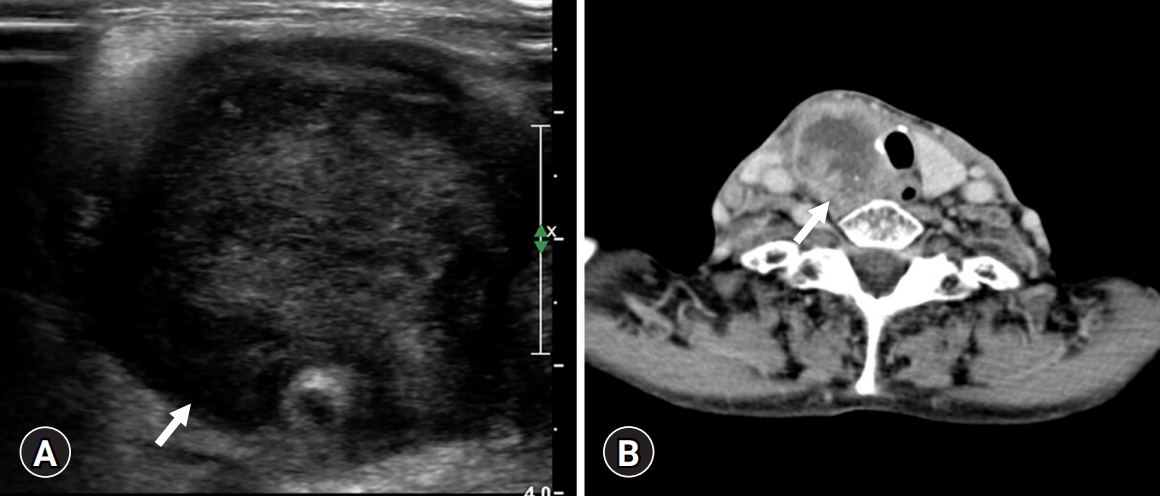
- 5,550 View
- 91 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) is the most common malignant neoplasm of the salivary gland, but primary thyroid MEC has rarely been reported and usually has a good prognosis. Herein, I report a case of thyroidal MEC with a poor prognosis in an 82-year-old woman with an anterior neck mass. Ultrasonography and computed tomography revealed a thyroid mass. The patient initially underwent fine-needle aspiration, was diagnosed with malignancy, and underwent a right lobectomy. On gross examination, a 4.0×3.6×2.6 cm-sized ill-defined, unencapsulated, and infiltrative tan to whitish mass with necrosis was identified. Microscopically, epidermoid tumor cell nests or solid sheets were identified. Mucous cells that were positive for periodic acid–Schiff and mucicarmine stains were also identified within epidermoid cell nests. Frequent mitosis and necrosis were observed. Immunohistochemical staining for p40 and p63 was positive, and that for thyroid transcription factor-1 and PAX8 was focally positive. According to the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology grading system for salivary gland MEC, the current case was classified as high-grade MEC. After surgery, the patient suffered from dyspnea due to a remnant neck mass that compressed and obstructed the trachea; therefore, the patient refused further treatment. Thyroidal MECs are considered low-grade with a favorable prognosis, but there are several reported cases of thyroidal MEC with poor prognosis. The current case is a rare presentation of high-grade thyroidal MEC with a poor prognosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the thyroid with concomitant MAML2 gene rearrangement and BRAF V600E mutation – A case report
Frederica Loghides, Brigid Aherne
Oral Oncology Reports.2024; 9: 100154. CrossRef - Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the pancreas: A case report and literature review
Huan Zhang, Shuyan Wang, Chunnian Wang
Medicine.2024; 103(4): e36993. CrossRef - Primary Thyroid Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma (MEC) Is Clinically, Prognostically, and Molecularly Different from Sclerosing MEC with Eosinophilia: A Multicenter and Integrated Study
Hieu Trong Le, Truong P. X. Nguyen, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Ryohei Katoh, Norisato Mitsutake, Michiko Matsuse, Ayaka Sako, Tetsuo Kondo, Nilesh Vasan, Young Mi Kim, Ying Liu, Lewis Hassell, Kennichi Kakudo, Huy Gia Vuong
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(1): 100. CrossRef - Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Thyroid Neoplasms
Zubair W. Baloch, Sylvia L. Asa, Justine A. Barletta, Ronald A. Ghossein, C. Christofer Juhlin, Chan Kwon Jung, Virginia A. LiVolsi, Mauro G. Papotti, Manuel Sobrinho-Simões, Giovanni Tallini, Ozgur Mete
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(1): 27. CrossRef
- Primary mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the thyroid with concomitant MAML2 gene rearrangement and BRAF V600E mutation – A case report

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



