Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Review articles
- Current perspectives in stem cell therapies for osteoarthritis of the knee
- Gi Beom Kim, Oog-Jin Shon
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):149-158. Published online April 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00157
- 10,736 View
- 308 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
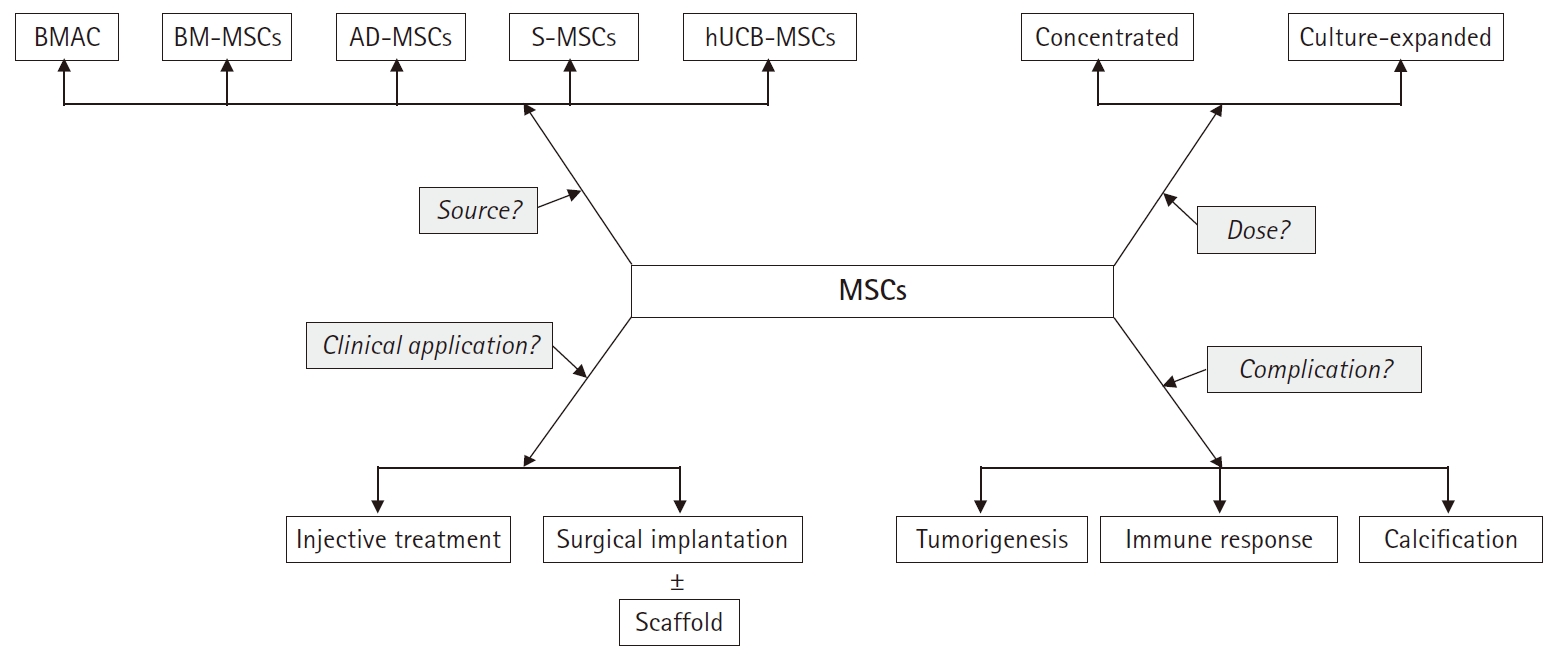
PDF - Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are emerging as an attractive option for osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee joint, due to their marked disease-modifying ability and chondrogenic potential. MSCs can be isolated from various organ tissues, such as bone marrow, adipose tissue, synovium, umbilical cord blood, and articular cartilage with similar phenotypic characteristics but different proliferation and differentiation potentials. They can be differentiated into a variety of connective tissues such as bone, adipose tissue, cartilage, intervertebral discs, ligaments, and muscles. Although several studies have reported on the clinical efficacy of MSCs in knee OA, the results lack consistency. Furthermore, there is no consensus regarding the proper cell dosage and application method to achieve the optimal effect of stem cells. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to review the characteristics of various type of stem cells in knee OA, especially MSCs. Moreover, we summarize the clinical issues faced during the application of MSCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of a Central Current Good Manufacturing Practices Laboratory Produced Autologous Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cell Therapy Product for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis
Christopher J. Rogers, Robert Harman, Mitchell B. Sheinkop, Peter Hanson, Mary A. Ambach, Tal David, Rahul Desai, Steven Sampson, Danielle Aufierro, Jay Bowen, Gerard Malanga
Stem Cells and Development.2024; 33(7-8): 168. CrossRef - Safety and Efficacy of an allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell preparation in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a Phase I/IIa randomised controlled trial.
Julien Freitag, Matthew Chamberlain, James Wickham, Kiran Shah, Flavia Cicuttini, Yuanyuan Wang, Ann Solterbeck
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Open.2024; : 100500. CrossRef - Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promoting knee joint chondrogenesis for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review
Pengwei Zhang, Bo Dong, Puwei Yuan, Xun Li
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Scaffold-Free Cartilage Construct from Infrapatellar Fat Pad Stem Cells for Cartilage Restoration
Orada Sriwatananukulkit, Tulyapruek Tawonsawatruk, Kasem Rattanapinyopituk, Ticomporn Luangwattanawilai, Narongrit Srikaew, Ruedee Hemstapat
Tissue Engineering Part A.2022; 28(5-6): 199. CrossRef - Autologous Protein Solution Effect on Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue and Bone Marrow in an Osteoarthritic Environment
Stefania Pagani, Francesca Veronesi, Gianluca Giavaresi, Giuseppe Filardo, Tiziana Papio, Iacopo Romandini, Milena Fini
CARTILAGE.2021; 13(2_suppl): 225S. CrossRef - Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potential for Osteoarthritis
Gi Beom Kim, Oog-Jin Shon, Min-Soo Seo, Young Choi, Wook Tae Park, Gun Woo Lee
Biology.2021; 10(4): 285. CrossRef - Molecular basis for new approaches to therapy of osteoarthritis (part I)
E. V. Chetina, G. A. Markova, A. M. Lila
Modern Rheumatology Journal.2021; 15(4): 7. CrossRef - The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in treating osteoporosis
Tianning Chen, Tieyi Yang, Weiwei Zhang, Jin Shao
Biological Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Chronic Inflammatory Bone and Joint Disorders in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Alzheimer's Disease
Robert A. Culibrk, Mariah S. Hahn
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of a Central Current Good Manufacturing Practices Laboratory Produced Autologous Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cell Therapy Product for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis
- Drug selection for sedation and general anesthesia in children undergoing ambulatory magnetic resonance imaging
- Sung Mee Jung
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):159-168. Published online April 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00171

- 12,363 View
- 387 Download
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The demand for drug-induced sedation for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans have substantially increased in response to increases in MRI utilization and growing interest in anxiety in children. Understanding the pharmacologic options for deep sedation and general anesthesia in an MRI environment is essential to achieve immobility for the successful completion of the procedure and ensure rapid and safe discharge of children undergoing ambulatory MRI. For painless diagnostic MRI, a single sedative/anesthetic agent without analgesia is safer than a combination of multiple sedatives. The traditional drugs, such as chloral hydrate, pentobarbital, midazolam, and ketamine, are still used due to the ease of administration despite low sedation success rate, prolonged recovery, and significant adverse events. Currently, dexmedetomidine, with respiratory drive preservation, and propofol, with high effectiveness and rapid recovery, are preferred for children undergoing ambulatory MRI. General anesthesia using propofol or sevoflurane can also provide predictable rapid time to readiness and scan times in infant or children with comorbidities. The selection of appropriate drugs as well as sufficient monitoring equipment are vital for effective and safe sedation and anesthesia for ambulatory pediatric MRI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prioritisation of data-poor pharmaceuticals for empirical testing and environmental risk assessment
Cristiana Cannata, Thomas Backhaus, Irene Bramke, Maria Caraman, Anna Lombardo, Rhys Whomsley, Caroline T.A. Moermond, Ad M.J. Ragas
Environment International.2024; 183: 108379. CrossRef - Review of pediatric sedation and anesthesia for radiological diagnostic and therapeutic procedures
Mohammed Ageel
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences.2024; 17(1): 100833. CrossRef - Comparison of airway collapsibility following single induction dose ketamine with propofol versus propofol sedation in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging: A randomised controlled study
Pooja Bhardwaj, Sakthirajan Panneerselvam, Priya Rudingwa, Kirthiha Govindaraj, M.V.S. Satya Prakash, Ashok S. Badhe, Krishnan Nagarajan
Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.2024; 68(2): 189. CrossRef - Evaluating Sedation Strategies for Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Comprehensive Review of Intravenous Fentanyl, Butorphanol, and Midazolam in Adult and Pediatric Populations
Neeta Verma, Janhavi S Dahake
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Dexmedetomidine Compared to Other Needle-Free Pharmacological Sedation Methods in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Imaging Procedures
Mohammed Alsabri Hussein Alsabri, Abdelrahman Abdelshafi, Ahmed Bostamy Elsnhory, Noha S. amir Ahmed, Alaa Bostamy Elsnhory, Douaa Albelal, Fatima Ikram
Pediatric Emergency Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Adverse events and sedation characteristics of propofol and dexmedetomidine during magnetic resonance imaging: An observational study in neuropsychiatric population
Shyamala Narayanan, Sriganesh Kamath, Dhritiman Chakrabarti
Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice.2024; 0: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of oral triclofos and intranasal midazolam and dexmedetomidine for sedation in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): an open-label, three-arm, randomized trial
Shyam Chandrasekar, Bhagirathi Dwibedi, Rashmi Ranjan Das, Biswa Mohan Padhy, Bikram Kishore Behera
European Journal of Pediatrics.2023; 182(3): 1385. CrossRef - Correlation between the actual sleep time 24 hours prior to an examination and the time to achieve chloral hydrate sedation in pediatric patients in South Korea: a prospective cohort study
Mijung Park, Ji Um, So Hyun Kim, Jiseon Yoon, Yeonjae Lee, Jiyeong Kwon, Seonhee Baek, Dong Yeon Kim
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(1): 51. CrossRef - COMPARISON OF INTRAMUSCULAR VERSUS INTRAVENOUS KETAMINE FOR SEDATION IN CHILDREN UNDERGOING MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING EXAMINATION
Jasim M. Salman, Jasim N. Al-Asadi, Husham H. Abdul-Ra’aoof, Jawad H. Ahmed, Ali H Reshak
Wiadomości Lekarskie.2023; 76(1): 198. CrossRef - Does sevoflurane sedation in pediatric patients lead to “pseudo” leptomeningeal enhancement in the brain on 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging?
Kiran Hilal, Kumail Khandwala, Saima Rashid, Faheemullah Khan, Shayan Sirat Maheen Anwar
World Journal of Radiology.2023; 15(4): 127. CrossRef - Intranasal dexmedetomidine versus intranasal midazolam as sole sedative agents for pelviabdominal magnetic resonance imaging in pediatrics: A randomized double-blind trial
TaysserM Abdelraheem, HamdyA Hendawy, AmiraM Elkeblawy
Bali Journal of Anesthesiology.2023; 7(2): 99. CrossRef - Prospective, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled, phase 3 clinical trial comparing the safety and efficacy of intranasal dexmedetomidine to oral midazolam as premedication for propofol sedation in pediatric patients undergoing magnet
Olivia Nzungu Wabelo, Denis Schmartz, Mario Giancursio, Françoise De Pooter, Giulia Caruso, Jean-François Fils, Philippe Van der Linden
Trials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of age on outpatient pediatric procedural sedation with intranasal dexmedetomidine and oral midazolam
Xiaqing Zhou, Jialian Zhao, Haiya Tu, Kunwei Chen, Yaoqin Hu, Yue Jin
European Journal of Pediatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the normal conus medullaris level in term infants: the role of MRI in early infancy
Mengchun Sun, Benzhang Tao, Gan Gao, Hui Wang, Aijia Shang
Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics.2022; 29(1): 100. CrossRef - Patient background related to success and adverse event in pediatric sedated MRI
Yutaka Konda, Hajime Mihira, Louis Akiyama, Yuki Shiko, Yoshihito Ozawa, Yohei Kawasaki, Katsunori Fujii, Ryugo Hiramoto
Pediatrics International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Risk Factors for Chloral Hydrate Sedative Failure with Initial Dose in Pediatric Patients: a Retrospective Analysis
Yu Cui, Langtao Guo, Qixia Mu, Lu Kang, Qin Chen, Qunying Wu, Yani He, Min Tang
Pediatric Drugs.2022; 24(4): 403. CrossRef - Using intranasal dexmedetomidine with buccal midazolam for magnetic resonance imaging sedation in children: A single-arm prospective interventional study
Bi Lian Li, Hao Luo, Jun Xiang Huang, Huan Huan Zhang, Joanna R. Paquin, Vivian M. Yuen, Xing Rong Song
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Novel Propofol Dosing Regimen for Pediatric Sedation during Radiologic Tests
Ji-Young Min, Jeong-Rim Lee, Hye-Mi Lee, Ho-Jae Nam, Hyo-Jin Byon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(17): 5076. CrossRef - Psychiatric outcomes following ketamine administration for orthopedic surgical anesthesia
Alec E. Mansour, Elijah W. Hale, Daniel S. Saks
Frontiers in Anesthesiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in paediatric radiology: Future opportunities
Natasha Davendralingam, Neil J Sebire, Owen J Arthurs, Susan C Shelmerdine
The British Journal of Radiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prioritisation of data-poor pharmaceuticals for empirical testing and environmental risk assessment
- Current aspects and prospects of glass ionomer cements for clinical dentistry
- Eun Young Park, Sohee Kang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):169-178. Published online July 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00374

- 15,831 View
- 724 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Glass ionomer cement (GIC) is a tailor-made material that is used as a filling material in dentistry. GIC is cured by an acid-base reaction consisting of a glass filler and ionic polymers. When the glass filler and ionic polymers are mixed, ionic bonds of the material itself are formed. In addition, the extra polymer anion reacts with calcium in enamel or dentin to increase adhesion to the tooth tissue. GICs are widely used as adhesives for artificial crowns or orthodontic brackets, and are also used as tooth repair material, cavity liner, and filling materials. In this review, the current status of GIC research and development and its prospects for the future have been discussed in detail.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement Incorporated with Nonfluoridated Remineralizing Agents
Nagalakshmi Chowdhary, Shri Mahalakshmi, Veena Shivanna, M Hema, N Karthikeyan, CM Jayashankar
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(2): 125. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of microleakage of self-cure, dual-cure, and light cure glass ionomer cement in a simulated oral environment - an invitro study
Sruthi Chandran, Chandru T P, Faizal C Peedikayil, Soni Kottayi, Athira Aravindan
International Journal of Pedodontic Rehabilitation.2024; 9(1): 26. CrossRef - Clinical Effectiveness of Ion-Releasing Restorations versus Composite Restorations in Dental Restorations: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Heber Isac Arbildo-Vega, Fredy Hugo Cruzado-Oliva, Franz Tito Coronel-Zubiate, Sara Antonieta Luján-Valencia, Joan Manuel Meza-Málaga, Rubén Aguirre-Ipenza, Adriana Echevarria-Goche, Eduardo Luján-Urviola, Tania Belú Castillo-Cornock, Katherine Serquen-Ol
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(6): 158. CrossRef - Effect of E-glass fibers addition on compressive strength, flexural strength, hardness, and solubility of glass ionomer based cement
Tamer M. Hamdy
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anticariogenic and Mechanical Characteristics of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cement Containing Lignin-Decorated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
Zuleikha Malik, Nawshad Muhammad, Muhammad Kaleem, Maleeha Nayyar, Asma Saleem Qazi, Danial Qasim Butt, Sher Zaman Safi, Abdul Samad Khan
ACS Applied Bio Materials.2023; 6(2): 425. CrossRef - Evaluation of compressive strength, surface microhardness, solubility and antimicrobial effect of glass ionomer dental cement reinforced with silver doped carbon nanotube fillers
Tamer M. Hamdy
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Concept of a Novel Glass Ionomer Restorative Material with Improved Mechanical Properties
Philipp Messer-Hannemann, Henrik Böttcher, Sven Henning, Falk Schwendicke, Susanne Effenberger
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(11): 534. CrossRef - Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology in Dentistry
Shiza Malik, Yasir Waheed
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(11): 266. CrossRef - Color stability of nano resin-modified glass Ionomer restorative cement after acidic and basic medications challenge
Zainab R Hasan, Noor R Al-Hasani, Osamah Malallah
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2023; 35(4): 10. CrossRef - Do bioactive materials show greater retention rates in restoring permanent teeth than non-bioactive materials? A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Juliana Benace Fernandes, Sheila Mondragón Contreras, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Graziela Ribeiro Batista, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Marginal microleakage and modified microtensile bond strength of Activa Bioactive, in comparison with conventional restorative materials
Saba Tohidkhah, Hamid Kermanshah, Elham Ahmadi, Behnous Jalalian, Ladan Ranjbar Omrani
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2022; 8(1): 329. CrossRef - Usefulness of conventional glass ionomer cements in an environment of insufficient moisture exclusion
Yukihiro Naganuma, Masatoshi Takahashi, Yukyo Takada, Kumi Hoshi, Aki Kitaoka, Atsushi Takahashi, Keiichi Sasaki
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(3): 242. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Method to Determine Wear Resistance of Class I Tooth Restorations during Cyclic Loading
Philipp Messer-Hannemann, Mariam Samadi, Henrik Böttcher, Sebastian Duy, Daniela Duy, Niclas Albrecht, Falk Schwendicke, Susanne Effenberger
Materials.2022; 15(15): 5440. CrossRef - Update on Dental Luting Materials
Gary Kwun-Hong Leung, Amy Wai-Yee Wong, Chun-Hung Chu, Ollie Yiru Yu
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(11): 208. CrossRef - Effects of Curing Mode on the Bond Strength of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements
Yongxiang Xu, Yuan Li, Hong Lin, Bin Yu
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The Attitude of the General Dentist in the Republic of Croatia toward Treating Children
Lidia Gavić, Ivana Nikolić, Sharanbir K. Sidhu, Daniel Jerković, Antonija Tadin
Children.2022; 9(12): 1888. CrossRef - Effects of Protective Surface Coating on Fluoride Release and Recharge of Recent Uncoated High-Viscosity Glass Ionomer Cement
Nantawan Krajangta, Chayanee Dulsamphan, Tongjai Chotitanmapong
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(12): 233. CrossRef - Comparison of Shear Bond Strength of Three Luting Materials Used in Band and Loop Space Maintainer Cementation: An In Vitro Study
SaraMuhannad Zaidan, ReemAtta Rafeeq
Dental Hypotheses.2022; 13(4): 136. CrossRef - Applications of Antioxidants in Dental Procedures
Fan Qi, Haofei Huang, Ming Wang, Weifeng Rong, Jing Wang
Antioxidants.2022; 11(12): 2492. CrossRef - Conventional glass-ionomer cements: a guide for practitioners
Petros Mylonas, Jing Zhang, Avijit Banerjee
Dental Update.2021; 48(8): 643. CrossRef - Difference in Bonding Strength of RMGIC according to Type of Hemostatic Agent in Primary Tooth
Seolah Back, Joonhaeng Lee, Jongbin Kim, Miran Han, Jong Soo Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(4): 460. CrossRef - Effect of Aluminum Chloride Hemostatic Agent on Bonding Strength of RMGIC in Primary Tooth
Seung-Hee Woo, Jisun Shin, Joonhaeng Lee, Miran Han, Jong Soo Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2021; 48(4): 397. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement Incorporated with Nonfluoridated Remineralizing Agents
Original articles
- Clinical and histopathologic analysis of gynecological cancer: a single institute experience over 7 years
- Soo-Young Lee, Eunbyeol Kim, Hyo-Shin Kim, Yu-Jin Koo, Dae-Hyung Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):179-185. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00451
- 5,825 View
- 169 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Approximately 100,000 women are diagnosed with cancer each year in Korea. According to a survey by the Korean central cancer registry in 2016, uterine cervical cancer, uterine corpus cancer, and ovarian cancer were the 5th, 7th, and 8th most prevalent cancers respectively among Korean women. The present study aims to review the clinico-pathologic characteristics of patients who were treated for major gynecological malignancies at Yeungnam University Medical Center.
Methods
Patients with invasive gynecological cancers from January 2012 to February 2019 were retrospectively identified. We analyzed the clinical features, demographic profiles, pathologic data, treatment modality used, adjuvant treatment used, complications, recurrence, and survival outcomes.
Results
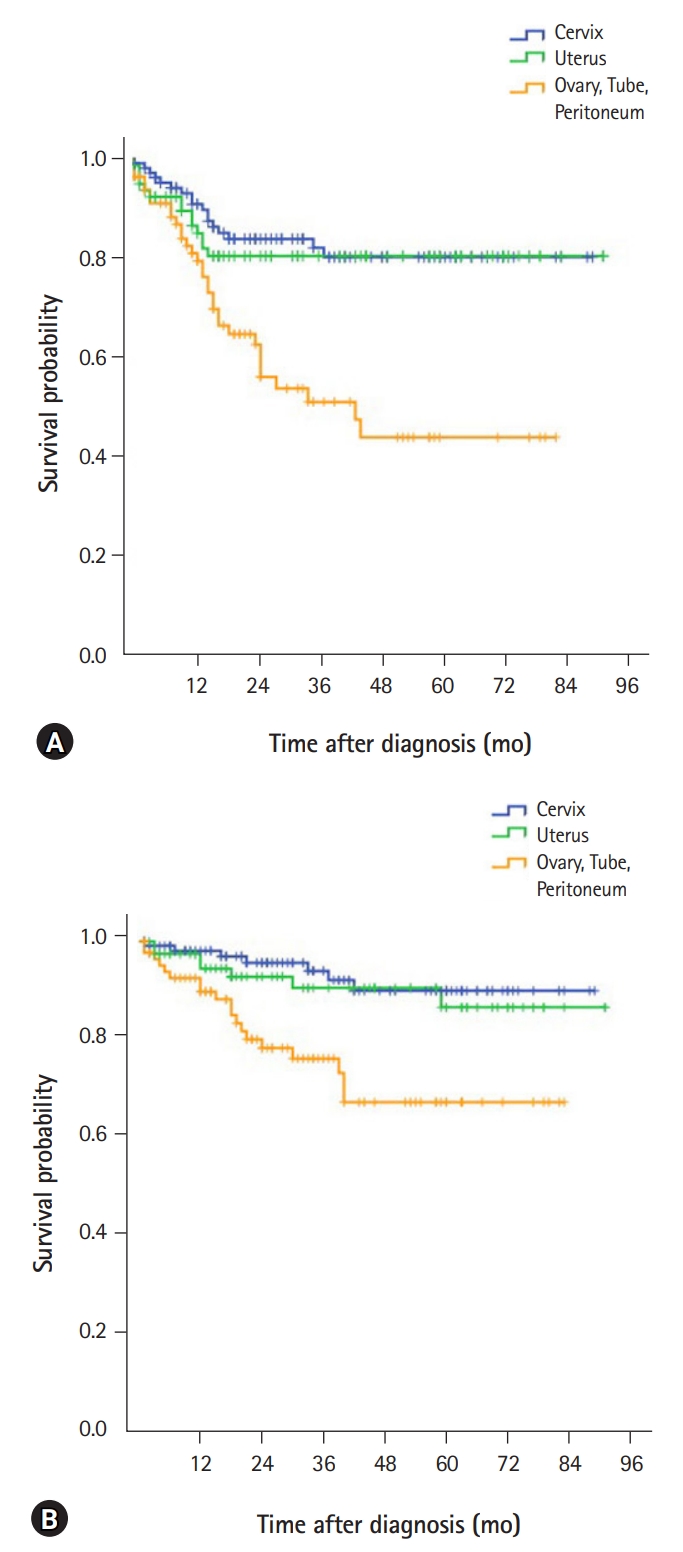
A total of 287 patients (cervical cancer 115; corporal cancer 86; and ovarian, tubal, or primary peritoneal cancer 90) were included. Most cervical (82.7%) and corporal cancers (89.5%) were diagnosed in the early stages (stage I or II), while more than half (58.9%) the cases of ovarian, tubal or peritoneal cancers were diagnosed in the advanced stages (stage III or IV). Surgical complications were observed in 12.2% of cervical cancers, 16.3% of uterine corpus cancers, and 11.1% of ovarian, tubal, and peritoneal cancers, respectively. The 5-year overall survival rate was 94.1%, 91.0%, and 77.1% for cervical, corporal, and ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancers, respectively.
Conclusion
Surgical treatment was satisfactory in terms of the incidence of complications, and survival outcomes were generally good. Clinicians should be aware of the clinical and histopathological characteristics of patients with gynecological cancers to be able to provide optimal strategies and counseling. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular landscape of recurrent cervical cancer
Divya Adiga, Sangavi Eswaran, Deeksha Pandey, Krishna Sharan, Shama Prasada Kabekkodu
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology.2021; 157: 103178. CrossRef - Histopathological Study of Gynecological Cancers in Patients Admitted to Baqiyatallah Hospital in Tehran during 2011-2019
Seyedeh Razieh Hashemi, Mohammad Reza Akbari, Zahra Soleimani
Avicenna Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 28(1): 42. CrossRef
- Molecular landscape of recurrent cervical cancer
- Improvement of catheter-related outcomes after application of tunneled cuffed hemodialysis catheter insertion without fluoroscopy
- Seok Hui Kang, Jun Young Do
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):186-193. Published online March 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00465
- 5,659 View
- 107 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Non-tunneled catheters (NTCs) are used for hemodialysis (HD) in many centers in which fluoroscopy is not easily accessed despite high complication rates and conditions requiring long-term HD. Therefore, here we aimed to evaluate the superiority of catheter-related outcomes after the application of tunneled cuffed catheter (TCC) without fluoroscopy versus unconditioned NTC insertion.
Methods
We divided the participants into two phases: those receiving NTCs between March 2010 and February 2011 (phase I), and those receiving TCCs or NTCs between March 2011 and February 2012 (phase II). Catheter survival, nurse satisfaction, and reasons for catheter removal were analyzed.
Results
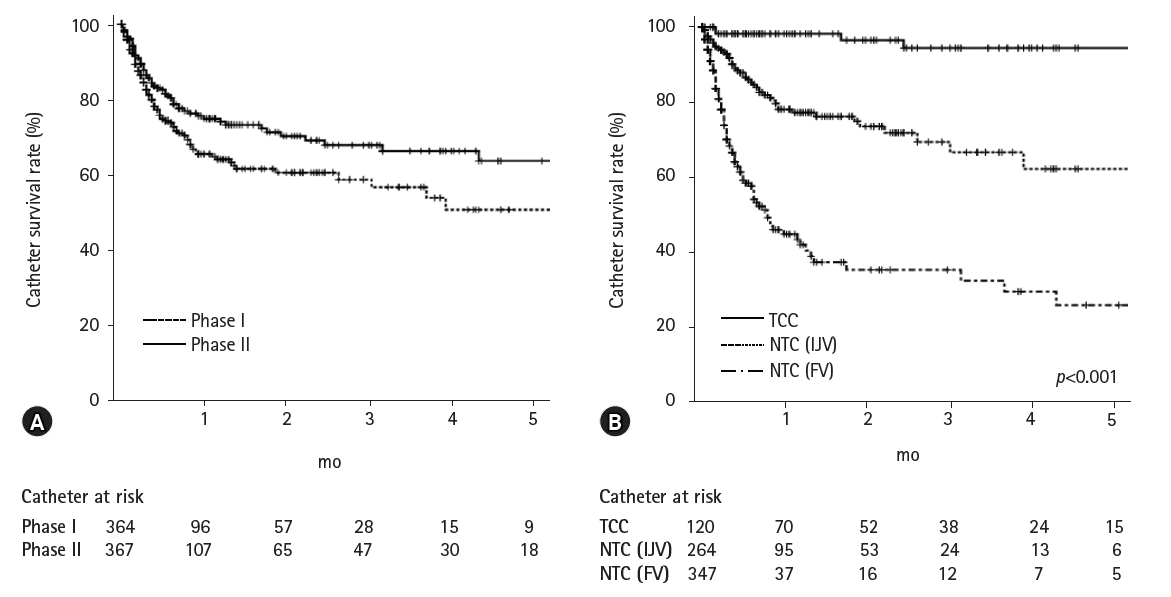
Two hundred and sixty patients in phase I and 300 patients in phase II were enrolled in this study. The success rate of TCC insertion was 99.2%. The catheter survival rate in phase I was 65.5% at 1 month, while that in phase II was 74.9% at 1 month (p=0.023). We compared catheter survival between TCCs and NTCs for all periods regardless of phase. The TCC survival rate was higher than the NTC survival rate (p<0.001). Catheter-associated problems led to catheter removal in 97 patients (26.6%) in phase I and 68 patients (18.5%) in phase II (p=0.009). Among 14 HD nurses, all reported being satisfied with manipulation during pre-/post-HD, manupulation during HD, and overall. Eleven HD nurses (78.6%) reported being satisfied with the workload.
Conclusion
Compared with unconditional NTC insertion for HD, TCC insertion without fluoroscopy improved the overall catheter survival and nurse satisfaction rates. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Validating the anatomical landmark technique for bedside tunneled central venous catheter placement in the medical intensive care unit
Hanny Sawaf, James Lane, Roman Shingarev, Matthew Siuba, Alvin G Kwon, Tarik Hanane, Tushar J Vachharajani
The Journal of Vascular Access.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Validating the anatomical landmark technique for bedside tunneled central venous catheter placement in the medical intensive care unit
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids, lung function, and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Hyunji Choi, Taeyun Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):194-201. Published online April 7, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00052

- 5,023 View
- 107 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are thought to modify systemic inflammation. The present study aimed to evaluate the relationship between PUFA intake, lung function, and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods
In this study, we used the dataset of 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, in which, a total of 22,948 individuals including 573 participants with a high probability of developing COPD were enrolled. Participants with missing data for the investigated variables were excluded. Linear regression analyses were used to evaluate the association between PUFA intake (omega-3 [N3], omega-6 [N6], and total) with lung function, and HRQoL. HRQoL was determined according to the European Quality of Life-5 Dimensions (EQ-5D). Subgroup analysis of older patients was performed. Age, sex, body mass index, smoking, alcohol, education, residence, total calorie intake, and predicted FEV1% were adjusted in all analyses.
Results
Although lung function was not associated with PUFA intake, EQ-5D index was remarkably associated with N3, N6, and total PUFA intake in a dose-dependent manner. This association was more pronounced in elderly COPD patients. Mean levels of N3, N6, and total PUFA intake were significantly higher in patients having better HRQoL with respect to mobility, self-care, and usual activities.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that N3, N6, and total PUFA intake are associated with HRQoL in COPD patients. This association may be attributed to mobility, self-care, and usual activities. Further longitudinal study is required to clarify this relationship. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nutrition as a modifiable factor in the onset and progression of pulmonary function impairment in COPD: a systematic review
Lieke E J van Iersel, Rosanne J H C G Beijers, Harry R Gosker, Annemie M W J Schols
Nutrition Reviews.2022; 80(6): 1434. CrossRef - Medium and long chain free fatty acid receptors in the pathophysiology of respiratory diseases
O. Yu. Kytikova, T. P. Novgorodtseva, Yu. K. Denisenko, M. V. Antonyuk, T. A. Gvozdenko
Bulletin Physiology and Pathology of Respiration.2021; (80): 115. CrossRef
- Nutrition as a modifiable factor in the onset and progression of pulmonary function impairment in COPD: a systematic review
- The effectiveness of prophylactic ipsilateral central neck dissection in selected patients who underwent total thyroidectomy for clinically node-negative unilateral papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Jin Gu Kang, Young Ah Kim, Jung Eun Choi, Soo Jung Lee, Su Hwan Kang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):202-209. Published online April 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00031

- 5,352 View
- 130 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Prophylactic central neck dissection (CND) in clinically node-negative (cN0) papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) remains controversial. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the benefits of prophylactic ipsilateral CND compared with bilateral CND in total thyroidectomy for cN0 unilateral PTC.
Methods
We retrospectively enrolled 174 patients who underwent total thyroidectomies with prophylactic CND for cN0 unilateral PTC between January 2009 and May 2010. The prophylactic CND patients were divided into group 1, the ipsilateral CND group (n=74), and group 2, the bilateral CND group (n=100). The incidence of central lymph node metastasis (CLNM) and postoperative complications, such as hypoparathyroidism, recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, and recurrence were assessed.
Results
CLNM was found in 22 (29.8%) in group 1 and 69 (69%) in group 2. The incidence of postoperative severe hypocalcemia less than 7.0 was also significantly different (six patients [8.1%] in group 1 and 23 [23%] in group 2; p=0.009). Permanent hypoparathyroidism was significantly more frequent in group 2 (4.1% vs. 19%; p=0.005). However, the incidence of transient hypoparathyroidism, recurrence, and recurrent laryngeal nerve injury was not significantly different.
Conclusion
Prophylactic ipsilateral CND has advantage not only to reduce incidence of some complications but also to have similar recurrence rate compared with bilateral CND. We suggest that prophylactic ipsilateral CND may be safe and effective for selected patients undergoing total thyroidectomy for cN0 unilateral PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of prophylactic ipsilateral and bilateral central lymph node dissection in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Yujie Li, Lingling Lao
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2023; 89(6): 101318. CrossRef - Fine-Needle Pricking Test of the Parathyroid Gland during Thyroid Surgery in Predicting Parathyroid Function
Ying-Jun Wu, Jian-Biao Wang, Fei-Bo Li, Lei Jin, Liang Zhou, Lei Xie, Claudio Casella
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Comparison of prophylactic ipsilateral and bilateral central lymph node dissection in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- Factors to be considered in designing a faculty development program for medical education: local experience from the Western region of Saudi Arabia
- Hussein Algahtani, Bader Shirah, Lana Alshawwa, Ara Tekian, John Norcini
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):210-216. Published online April 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00115
- 5,719 View
- 118 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Among the different aims of medical education, the provision of society with skilled, professional, and knowledgeable healthcare workers who maintain and develop their expertise over a lifetime career is important. The achievement of this goal is linked with the professional development of both faculty members and healthcare workers. This study aims to measure the perception of faculty members regarding their views about the goals of faculty development programs, practices and activities, and factors that determine their achievement.
Methods
A cross-sectional survey was conducted in multiple universities in the Western region of Saudi Arabia. The participants were given a pre-designed self-administered questionnaire generated from literature. The survey questionnaire consisted of three sections that were designed to assess the faculty members’ perception on the faculty development program.
Results
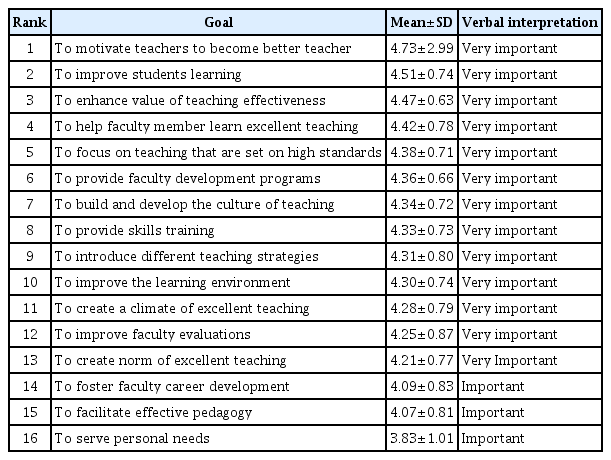
A total of 210 faculty members participated in the study. The most important perceived goal was to motivate teachers to become better teachers. The most important perceived practice was establishing a positive climate for teaching and learning. The most important perceived factor was skilled and dedicated staff support.
Conclusion
The results of this study demonstrate that faculty members have positive perceptions regarding all aspects of faculty development programs. This study will raise awareness regarding the importance of faculty development programs in sustaining educational vitality. We recommend the implementation and maintenance of comprehensive faculty development programs in Saudi universities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Transforming Continuing Professional Development for Healthcare Professionals to Meet National Goals in Saudi Arabia
Graham T. McMahon, Manal Alnasser, Haya Alzouman, Lama Aldakhil, Asma Ababtain
Journal of CME.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Facilitators’ Competencies and Characteristics on Faculty Enhancement Activities in Saudi Arabia: A Mixed-Methods Research
Abdulaziz I Alhassan, Njoud A Alghofaily
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Transforming Continuing Professional Development for Healthcare Professionals to Meet National Goals in Saudi Arabia
- Mineralization-inducing potentials of calcium silicate-based pulp capping materials in human dental pulp cells
- Sohee Kang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):217-225. Published online May 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00248
- 6,411 View
- 151 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
To provide a long-term bacterial seal through the formation of reparative dentin bridge, calcium silicate-based pulp capping materials have been used at sites of pulpal exposure. The aim of this study was to evaluate the mineralization-inducing potentials of calcium silicate-based pulp capping materials (ProRoot MTA [PR], Biodentine [BD], and TheraCal LC [TC]) in human dental pulp cells (HDPCs).
Methods
Specimens of test materials were placed in deionized water for various incubation times to measure the pH variation and the concentration of calcium released. The morphology of HDPCs cultured on the specimens was examined using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Alizarin red S staining and alkaline phosphatase assays were used to evaluate mineralization-inducing potentials of the capping materials.
Results
BD showed the highest calcium release in all test periods, followed by PR and TC. (p<0.05). All experimental groups showed high alkalinity after 1 day, except at 14 days. BD showed the highest cell viability compared with PR and TC after 1 and 3 days, while TC showed the lowest value (p<0.05). The CLSM analysis showed that cells were well adhered and expressed actin filaments for all pulp capping materials. Mineralization by PR and BD groups was higher than that by TC group based on alizarin red S staining. BD showed significantly higher alkaline phosphatase activity than PR and TC, while TC showed the lowest value (p<0.05).
Conclusion
Within the limitations of the in vitro study, BD had higher mineralization-inducing potential than PR and TC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of pulp capping materials on odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro study
Mahmoud M. Bakr, Mohamed Shamel, Shereen N. Raafat, Robert M. Love, Mahmoud M. Al‐Ankily
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ex Vivo Osteogenesis Induced by Calcium Silicate-Based Cement Extracts
Gabriel Kato, Rita Araújo, Cláudia Rodrigues, Pedro Sousa Gomes, Liliana Grenho, Maria Helena Fernandes
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(6): 314. CrossRef - Evaluation of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of a newly developed bioceramic cement derived from cockle shells: an in vitro study
Monthip Wannakajeepiboon, Chankhrit Sathorn, Chatvadee Kornsuthisopon, Busayarat Santiwong, Thanakorn Wasanapiarnpong, Pairoj Linsuwanont
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of dental self-curing resin for a temporary crown: an in vitro study
Jae-wan Ko, Joon Sakong, Sohee Kang
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2023; 40(Suppl): S1. CrossRef - Ion release, biocompatibility, and bioactivity of resin-modified calcium hydroxide cavity liners
Nastaran Taghvaei, Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Mehdi Evazalipour, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Ehsan Zamani
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Morphogenesis of Osteoid Structures during Cultivation of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Fibrillary Collagen in the Presence of Silicoaluminophosphate
A. A. Gaidash, M. I. Blinova, S. A. Aleksandrova, Yu. A. Nashchekina, V. K. Krutko, O. N. Musskaya, K. V. Skrotskaya, A. V. Nashchekin, N. A. Mikhailova, A. I. Kulak
Cell and Tissue Biology.2022; 16(1): 52. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Hydraulic materials for endodontic use
Josette Camilleri, Amre Atmeh, Xin Li, Nastaran Meschi
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 710. CrossRef - The scientific management of deep carious lesions in vital teeth using contemporary materials—A narrative review
M. Al-Ali, J. Camilleri
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of pulp capping materials on odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro study
Case reports
- Synchronous ileal inflammatory fibroid polyp and Meckel’s diverticulum found during laparoscopic surgery for adult intussusception
- Sung Il Kang, Mi Jin Gu
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):226-229. Published online December 18, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00388
- 8,013 View
- 98 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
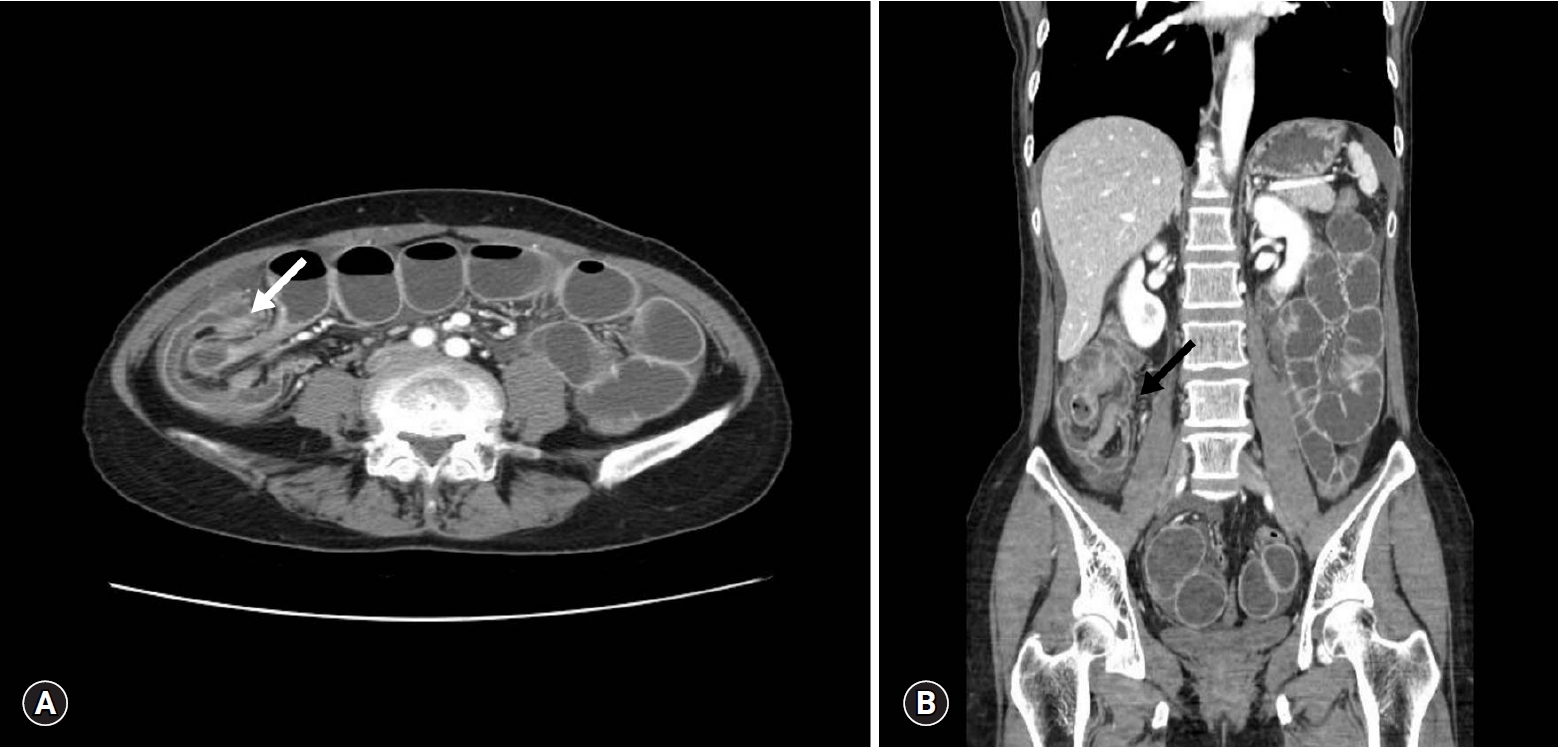
PDF - We present a rare case of synchronous ileal inflammatory fibroid polyp and Meckel’s diverticulum detected during laparoscopic surgery for adult intussusception. A 48-year-old woman presented with sudden onset of severe abdominal pain. Abdominal computed tomography revealed a segment of ileocecal intussusception. Thus, laparoscopic exploration was performed, which revealed an ileal mass with an outpouching closed luminal structure in the distal ileum. Two abnormal structures were resected via mini-laparotomy, and the patient was discharged without postoperative complications. Histopathological examination confirmed an ileal inflammatory fibroid polyp and Meckel’s diverticulum with ectopic pancreatic tissue.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intestinal intussusception of Meckel’s diverticulum, a case report and literature review of the last five years
Dora Sandoval Schaedlich, Pedro Custodio de Mello Borges, Arnaldo Lacombe, Renato Alonso Moron
einstein (São Paulo).2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Rare Cause of Colonic Obstruction: Inflammatory Fibroid Polyp
Sevinc Dagistanli, Nermin Gunduz, Osman Sibic, Suleyman Sonmez
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Case Report: Ileo-Ileal Intussusception Secondary to Inflammatory Fibroid Polyp: A Rare Cause of Intestinal Obstruction
Claudio Guerci, Francesco Colombo, Gloria Goi, Pietro Zerbi, Barbara Pirrò, Piergiorgio Danelli
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adult intussusception: a challenge to laparoscopic surgery?
Mingze Sun, Zhongmin Li, Zhenbo Shu, Qi Wu, Xue Liu
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14495. CrossRef - Adult Jejuno-jejunal intussusception due to inflammatory fibroid polyp
Yi-Kai Kao, Jian-Han Chen
Medicine.2020; 99(36): e22080. CrossRef
- Intestinal intussusception of Meckel’s diverticulum, a case report and literature review of the last five years
- Impressive effect of cisplatin monotherapy on a patient with heavily pretreated triple-negative breast cancer with poor performance
- Dong Won Baek, Ji-Young Park, Soo Jung Lee, Yee Soo Chae
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):230-235. Published online January 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00423

- 7,924 View
- 154 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Systemic therapy for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) still remains challenging because there are no targeted agents or endocrine therapies currently available. The present case report documents the successful use of cisplatin monotherapy to manage a heavily pretreated TNBC patient showing poor response to therapy. The patient was a 51-year-old woman who had already undergone several lines of systemic chemotherapy for widespread TNBC. Although the mutation analysis performed on DNA isolated from blood cells and progressed lesion samples confirmed the tumor to be germline BRCA wild-type, cisplatin monotherapy was administered based on the increasing evidence of safety and efficacy of platinum for breast cancer. After three cycles of cisplatin treatment, the patient’s metastatic lesions dramatically improved without any major toxicity, and she completed 17 cycles with good response. This case study indicates that patients with heavily pretreated TNBC can potentially achieve a good response to cisplatin monotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Zeolitic Imidazole Framework/Silica Nanocomposite for Targeted Cancer Therapeutics: Comparative Study of Chemo-Drug Cisplatin (CPt) and Green Platinum (GPt) Efficacy
Hend Ghnaim Alotaibi, Eman Al-Abbad, Dana Almohazey, Vijaya Ravinayagam, Sultan Akhtar, Hatim Dafalla, B. Rabindran Jermy
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(6): 3157. CrossRef - Cisplatin Monotherapy as a Treatment Option for Patients with HER-2 Negative Breast Cancer Experiencing Hepatic Visceral Crisis or Impending Visceral Crisis
Mirosława Püsküllüoğlu, Małgorzata Pieniążek, Agnieszka Rudzińska, Agnieszka Pietruszka, Renata Pacholczak-Madej, Aleksandra Grela-Wojewoda, Marek Ziobro
Oncology and Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoxia: syndicating triple negative breast cancer against various therapeutic regimens
Nityanand Srivastava, Salman Sadullah Usmani, Rajasekaran Subbarayan, Rashmi Saini, Pranav Kumar Pandey
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibiting L1CAM Reverses Cisplatin Resistance of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Blocking AKT Signaling Pathway
Lu-Yao Zhang, Zhi-Xin Shen, Lu Guo
Cancer Investigation.2022; 40(4): 313. CrossRef - Curcumin as an Enhancer of Therapeutic Efficiency of Chemotherapy Drugs in Breast Cancer
Reyhaneh Farghadani, Rakesh Naidu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(4): 2144. CrossRef - Atorvastatin improves cisplatin sensitivity through modulation of cholesteryl ester homeostasis in breast cancer cells
Diandra Zipinotti dos Santos, Isabella dos Santos Guimaraes, Mariam F. Hakeem-Sanni, Blake J. Cochran, Kerry-Anne Rye, Thomas Grewal, Andrew J. Hoy, Leticia B. A. Rangel
Discover Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting Hypoxia Sensitizes TNBC to Cisplatin and Promotes Inhibition of Both Bulk and Cancer Stem Cells
Andrew Sulaiman, Sarah McGarry, Jason Chambers, Emil Al-Kadi, Alexandra Phan, Li Li, Karan Mediratta, Jim Dimitroulakos, Christina Addison, Xuguang Li, Lisheng Wang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(16): 5788. CrossRef - Antioxidant Supplementation in the Treatment of Neurotoxicity Induced by Platinum-Based Chemotherapeutics—A Review
Jelena S. Katanic Stankovic, Dragica Selakovic, Vladimir Mihailovic, Gvozden Rosic
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(20): 7753. CrossRef
- Zeolitic Imidazole Framework/Silica Nanocomposite for Targeted Cancer Therapeutics: Comparative Study of Chemo-Drug Cisplatin (CPt) and Green Platinum (GPt) Efficacy
- Jejunogastric intussusception prone to misdiagnosis as gastric cancer
- Yong-Eun Park, Sang-Woon Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):236-241. Published online April 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00038

- 4,615 View
- 57 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The authors report a case of a 78-year-old female with a history of gastric surgery 35 years ago. She was initially misdiagnosed as gastric cancer bleeding and underwent an emergency laparotomy under the diagnosis of jejunogastric intussusception (JGI), 23 hours after the onset of symptoms. We also reviewed 116 JGI case reports and analyzed clinical features and outcomes. Compared to the past, diagnosis of JGI is easier with diagnostic examinations such as an endoscopy, computed tomography, and the upper gastrointestinal series. And a good prognosis can be expected with proper fluid resuscitation and surgical reduction, even if the symptoms persist more than 48 hours.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Jejunogastric intussusception after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a case report
Konosuke Yogo, Masanori Sando, Ryutaro Kobayashi, Genta Yano, Noriaki Ohara, Kiyotaka Kawai, Kenji Takagi, Satoru Kawai, Satoaki Kamiya
Surgical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Jejunogastric intussusception after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a case report
- Spontaneous resolution of serous retinal detachment caused by choroidal mass after a first trimester abortion
- You Hyun Lee, Yu Cheol Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):242-245. Published online April 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00087
- 5,516 View
- 66 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
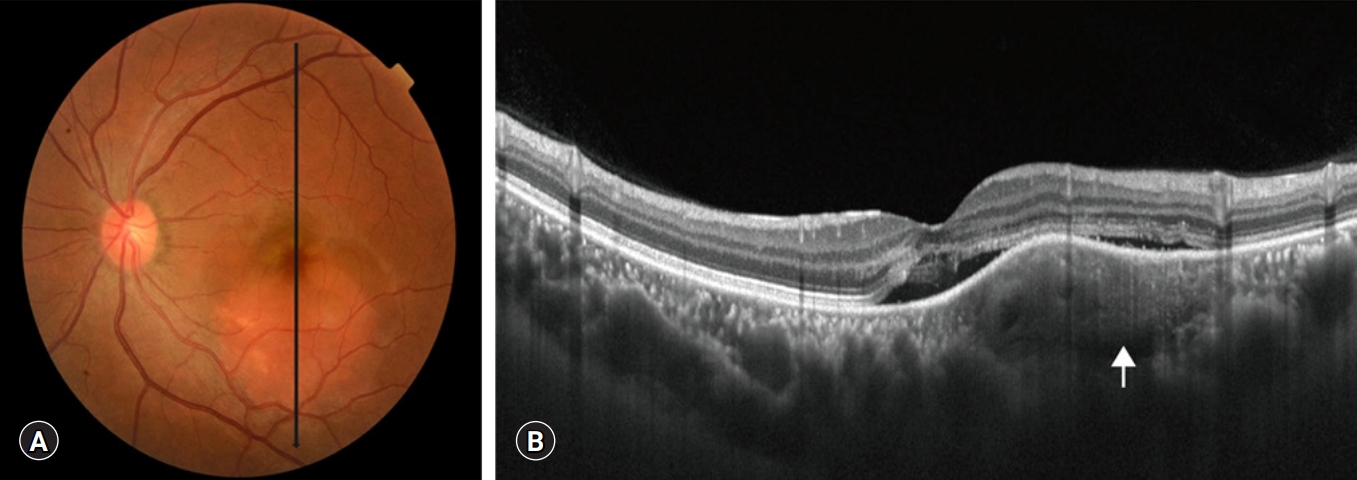
PDF - Pregnancy-related ocular diseases develop mostly in the third trimester of pregnancy. Here, we describe a case of a pregnant woman with a choroidal mass that caused a serous retinal detachment during the first trimester of pregnancy. The patient’s condition resolved spontaneously after an abortion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical features and therapeutic management of choroidal osteoma: A systematic review
Li Zhang, Qi-Bo Ran, Chun-Yan Lei, Mei-Xia Zhang
Survey of Ophthalmology.2023; 68(6): 1084. CrossRef - FPR2 serves a role in recurrent spontaneous abortion by regulating trophoblast function via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
Anna Li, Shuxian Li, Chongyu Zhang, Zhenya Fang, Yaqiong Sun, Yanjie Peng, Xietong Wang, Meihua Zhang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical features and therapeutic management of choroidal osteoma: A systematic review
- Gastric cancer and adenomatous colorectal polyp concomitant with pyogenic liver abscess and bacteremia
- Min Kyu Kang, Hee Jung Kwon, Min Cheol Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(3):246-249. Published online April 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00094
- 5,105 View
- 101 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
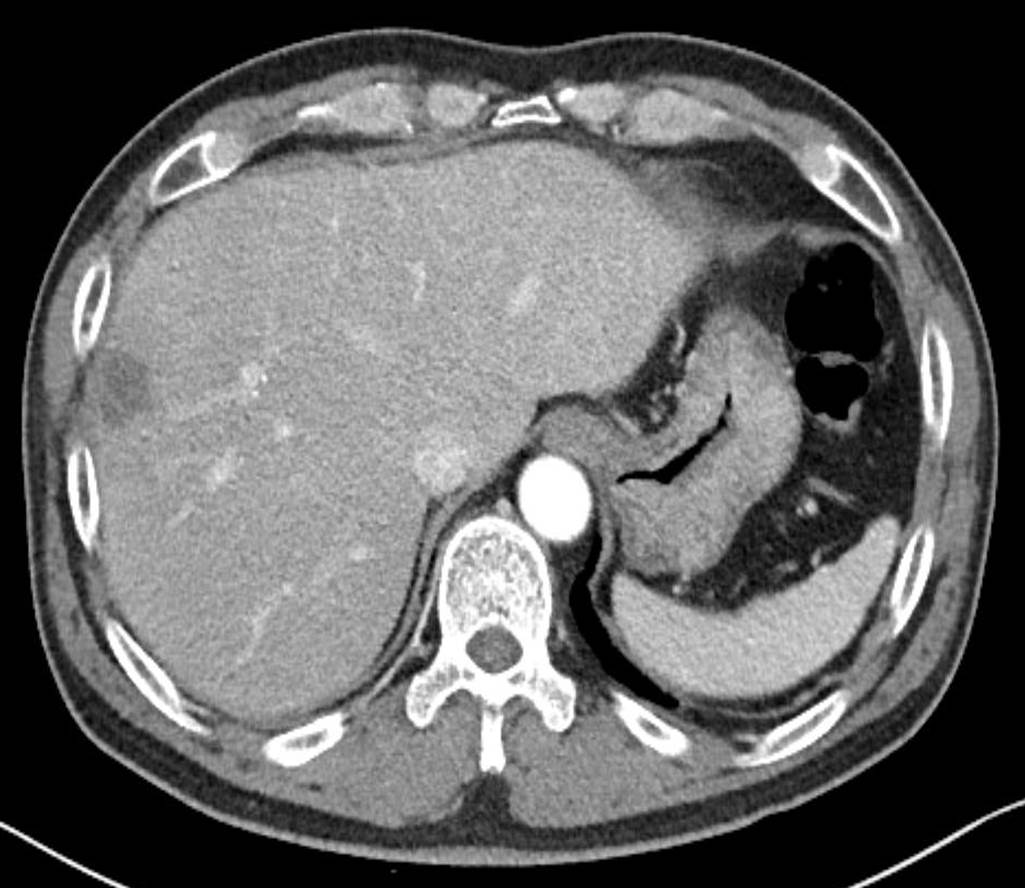
PDF - Synchronous gastric cancer and adenomatous colorectal polyp in patients with Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pyogenic liver abscess (KP-PLA) and bacteremia is a rare presentation. A 58-year-old man with a 6-month history of diabetes mellitus (DM) presented with febrile sensation and dull abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. Subsequent to laboratory test results and abdominal computed tomography findings, KP-PLA with bacteremia was diagnosed. After intravenous antibiotic administration, his symptoms improved, and upper endoscopy and colonoscopy were performed to evaluate the cause of KP-PLA. Biopsy specimens of the prepyloric anterior wall revealed a moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma. Endoscopic mucosal resection of the colon revealed high-grade dysplasia. Early gastric cancer (EGC) and adenomatous colorectal polyps with high-grade dysplasia concomitant with KP-PLA and bacteremia were diagnosed in our patient who had DM. Intravenous antibiotic treatment for KP-PLA, subtotal gastrectomy for EGC, and colonoscopic mucosal resection for the colon polyp were performed. After 25 days of hospitalization, subtotal gastrectomy with adjacent lymph node dissection was performed. Follow-up ultrasound imaging showed resolution of the abscess 5 weeks post-antibiotic treatment, as well as no tumor metastasis. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy should be performed to evaluate gastric cancer in patients with PLA or bacteremia, accompanied with DM or an immunocompromised condition.

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



