Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Review articles
- Function of hepatocyte growth factor in gastric cancer proliferation and invasion
- Sung Ae Koh, Kyung Hee Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):73-78. Published online February 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00437
- 6,281 View
- 150 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
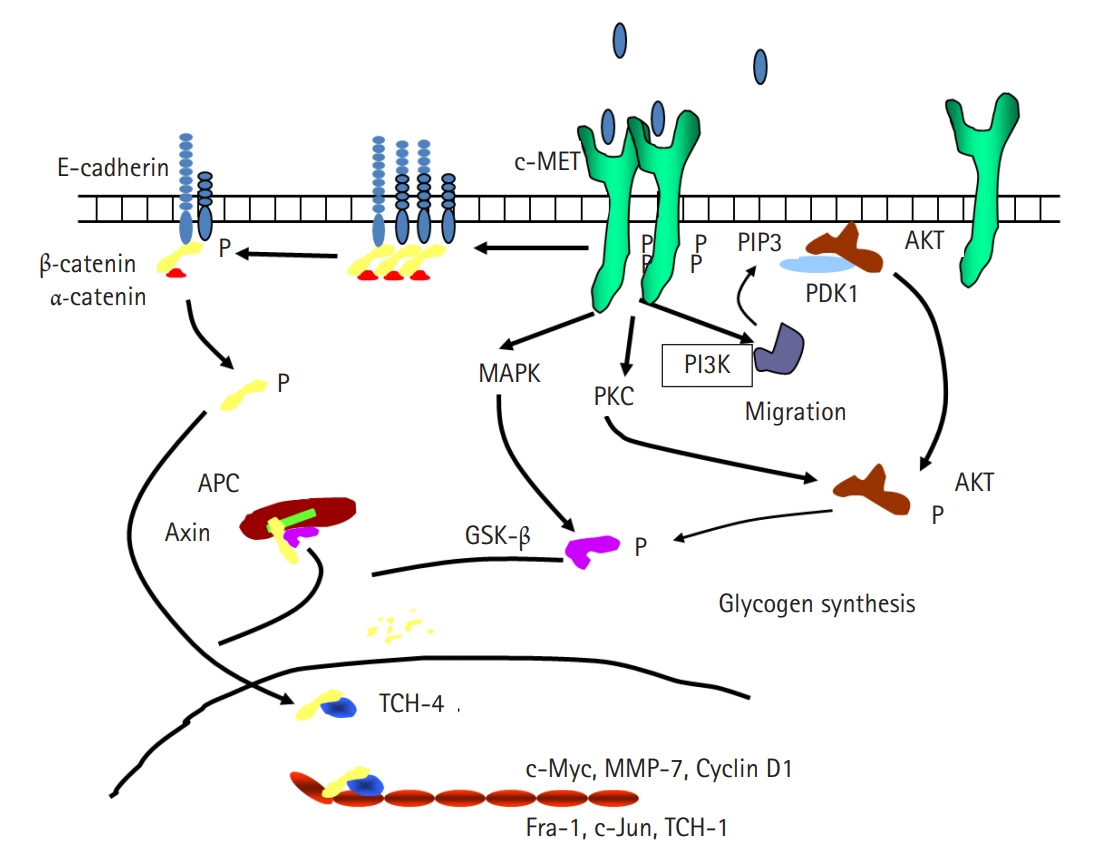
PDF - Cancer incidence has been increasing steadily and is the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Gastric cancer is still most common malignancy in Korea. Cancer initiation and progression are multistep processes involving various growth factors and their ligands. Among these growth factors, we have studied hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which is associated with cell proliferation and invasion, leading to cancer and metastasis, especially in gastric cancer. We explored the intercellular communication between HGF and other surface membrane receptors in gastric cancer cell lines. Using complimentary deoxyribonucleic acid microarray technology, we found new genes associated with HGF in the stomach cancer cell lines, NUGC-3 and MKN-28, and identified their function within the HGF pathway. The HGF/N-methyl-N’-nitroso-guanidine human osteosarcoma transforming gene (c-MET) axis interacts with several molecules including E-cadherin, urokinase plasminogen activator, KiSS-1, Jun B, and lipocalin-2. This pathway may affect cell invasion and metastasis or cell apoptosis and is therefore associated with tumorigenesis and metastasis in gastric cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Progress and prospects of biomarker-based targeted therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced gastric cancer
Zhu Zeng, Qing Zhu
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Reciprocal Regulation of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Tumor Microenvironment in Gastrointestinal Cancer: Implications for Cancer Dormancy
Shih-Hsuan Cheng, Hsin-Ying Clair Chiou, Jiunn-Wei Wang, Ming-Hong Lin
Cancers.2023; 15(9): 2513. CrossRef - Expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Osteosarcoma: A Systematic Review
Leo Issagholian, Ethan Tabaie, Akshay J Reddy, Muhammad S Ghauri, Rakesh Patel
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Remodelling of the tumour microenvironment by the kallikrein-related peptidases
Srilakshmi Srinivasan, Thomas Kryza, Jyotsna Batra, Judith Clements
Nature Reviews Cancer.2022; 22(4): 223. CrossRef - Identification of hub pathways and drug candidates in gastric cancer through systems biology
Seyed Reza Salarikia, Mohammad Kashkooli, Mohammad Javad Taghipour, Mahdi Malekpour, Manica Negahdaripour
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions in gastric cancer
Zi-Ning Lei, Qiu-Xu Teng, Qin Tian, Wei Chen, Yuhao Xie, Kaiming Wu, Qianlin Zeng, Leli Zeng, Yihang Pan, Zhe-Sheng Chen, Yulong He
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Proteomic Signatures of Diffuse and Intestinal Subtypes of Gastric Cancer
Smrita Singh, Mohd Younis Bhat, Gajanan Sathe, Champaka Gopal, Jyoti Sharma, Anil K. Madugundu, Neha S. Joshi, Akhilesh Pandey
Cancers.2021; 13(23): 5930. CrossRef
- Progress and prospects of biomarker-based targeted therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced gastric cancer
- Creativity in medical education: concepts related to creative capacity
- Yura Kim, Young Hwan Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):79-83. Published online March 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00458
- 7,556 View
- 91 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
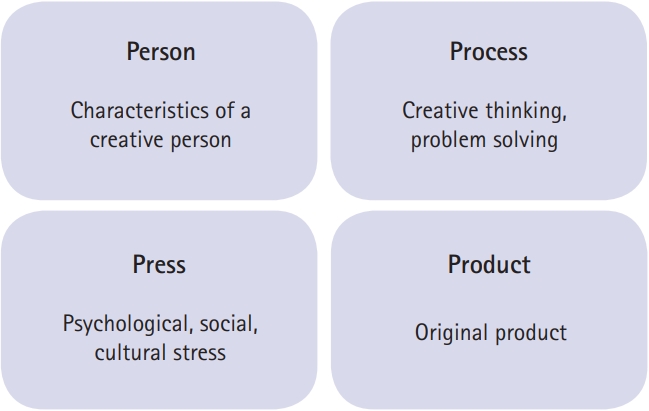
PDF - In the 21st-century postmodernism era, which represents diversity and relativity, one of the most essential elements in the field of education is to strengthen individual human values. Accordingly, we must focus on developing capacity in order to adapt to change. It is clear that the medical field maximizes the need for new judgments to solve life-related problems constantly, and this problem-solving capacity is an essential skill for a physician. Problem-solving capacity can be achieved simultaneously with creativity to apply them in an appropriate manner based on standardized expertise and well-trained skills. Creativity is also a key element that medical education is currently pursuing. Many studies on creativity have resulted in confusion and misunderstandings on the concept of creativity due to similar terms and varied definitions, such as creation, innovation, etc. In this study, we attempt to identify the importance of creativity in medical education by comparing and organizing concepts related to creative capacity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Creative Thinking: Its Importance and How to Cultivate It
Ahmad Munir, Omer A. Awan
Academic Radiology.2022; 29(10): 1610. CrossRef - A study on the mental health of students at a medical school during COVID-19 outbreak: a retrospective study
Yu Ra Kim, Hye Jin Park, Bon-Hoon Koo, Ji Young Hwang, Young Hwan Lee
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2022; 39(4): 314. CrossRef - Value-Added Roles of Medical Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Assessment of Medical Students’ Perceptions and Willingness in Sri Lanka
Nuwan Darshana Wickramasinghe, Shamalee Wasana Jayarathne, Senaka Devendra Pilapitiya
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 3187. CrossRef
- Creative Thinking: Its Importance and How to Cultivate It
- Effectiveness of orthoses for treatment in patients with spinal pain
- Yoo Jin Choo, Min Cheol Chang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):84-89. Published online March 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00150
- 8,535 View
- 175 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
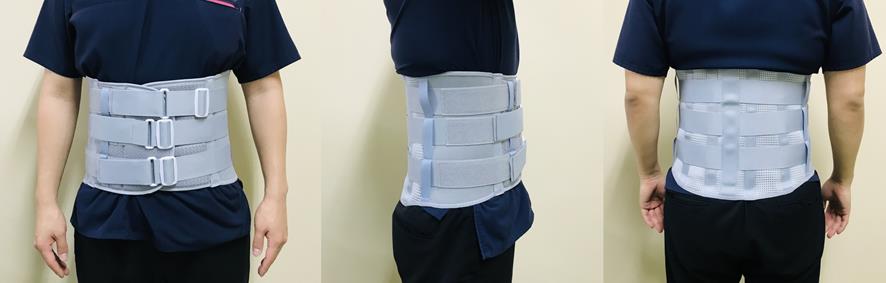
PDF - Spinal pain is a common patient complaint in clinical practice. Conservative treatment methods include oral medication, physical therapy, injections, and spinal orthoses. The clinical application of orthoses is debated because of potential complications associated with long-term use, such as muscle weakness and joint contracture. We reviewed the orthoses most frequently used to manage spinal pain. We review the use of soft cervical and Philadelphia collars, lumbosacral corsets, and thoracolumbosacral orthosis to manage spinal pain. Spinal orthoses can help reduce pain by protecting the muscles and joints of the injured spinal region, preventing or correcting malformations, and limiting trunk flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation. The short-term use of spinal orthoses is known to improve pain and disability during the treatment period without significant adverse effects. Spinal orthoses are expected to alleviate pain and improve patients’ lifestyle.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spinal Injections: A Narrative Review from a Surgeon’s Perspective
Dong Ah Shin, Yoo Jin Choo, Min Cheol Chang
Healthcare.2023; 11(16): 2355. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Safety of Inelastic Versus Elastic Lumbosacral Orthoses on Low Back Pain Prevention in Healthy Nurses
Jianzhong Hu, Liyuan Jiang, Yong Cao, Jin Qu, Hongbin Lu
Spine.2022; 47(9): 656. CrossRef - The mechanism of action of pulsed radiofrequency in reducing pain: a narrative review
Donghwi Park, Min Cheol Chang
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2022; 39(3): 200. CrossRef - Effectiveness of pulsed radiofrequency on the medial cervical branches for cervical facet joint pain
Min Cheol Chang, Seoyon Yang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(22): 7720. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of Facet Joint Injection with Steroid and Botulinum Toxin in Severe Lumbar Central Spinal Stenosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Sang Lee, Hyun Choi, Min Chang
Toxins.2022; 15(1): 11. CrossRef - Use of Pulsed Radiofrequency for the Treatment of Discogenic Back Pain: A Narrative Review
Seoyon Yang, Mathieu Boudier‐Revéret, Min Cheol Chang
Pain Practice.2021; 21(5): 594. CrossRef - YouTube as a Source of Information on Epidural Steroid Injection
Min Cheol Chang, Donghwi Park
Journal of Pain Research.2021; Volume 14: 1353. CrossRef - Comparison of Physical Activity Levels of Individuals Using Orthosis Without Pain and Kinesiophobia with Healthy Controls and within Themselves
Melek VOLKAN-YAZICI, Fatmagül VAROL
Ergoterapi ve Rehabilitasyon Dergisi.2021; 9(3): 79. CrossRef - The role of assistive devices in frail elderly people with fragility fractures: a narrative review
Giovanni Iolascon, Carla Michini, Robin Kuruvila Sentinella, Milena Aulicino, Antimo Moretti
International Journal of Bone Fragility.2021; 1(2): 53. CrossRef - Conservative Treatments Frequently Used for Chronic Pain Patients in Clinical Practice: A Literature Review
Min Cheol Chang
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Chronic Pain and Alterations in the Mesolimbic Dopaminergic System
Seoyon Yang, Mathieu Boudier-Revéret, Yoo Jin Choo, Min Cheol Chang
Brain Sciences.2020; 10(10): 701. CrossRef
- Spinal Injections: A Narrative Review from a Surgeon’s Perspective
Original articles
- Usefulness of subtraction pelvic magnetic resonance imaging for detection of ovarian endometriosis
- Hyun Jung Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):90-97. Published online October 10, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00353

- 6,086 View
- 120 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
To minimize damage to the ovarian reserve, it is necessary to evaluate the follicular density in the ovarian tissue surrounding endometrioma on preoperative imaging. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the usefulness of subtraction pelvic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect ovarian reserve.
Methods
A subtracted T1-weighted image (subT1WI) was obtained by subtracting unenhanced T1WI from contrast-enhanced T1WI (ceT1WI) with similar parameters in 22 patients with ovarian endometrioma. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in ovarian endometrioma, which was classified into the high signal intensity and iso-to-low signal intensity groups on the T2-weighted image, was compared to that in normal ovarian tissue. To evaluate the effect of contrast enhancement, a standardization map was obtained by dividing subT1WI by ceT1WI.
Results
On visual assessment of 22 patients with ovarian endometrioma, 16 patients showed a high signal intensity, and 6 patients showed an iso-to-low signal intensity on T1WI. Although SNR in endometrioma with a high signal intensity was higher than that with an iso-to-low signal intensity, there was no difference in SNR after the subtraction (13.72±77.55 vs. 63.03±43.90, p=0.126). The area of the affected ovary was smaller than that of the normal ovary (121.10±22.48 vs. 380.51±75.87 mm2, p=0.002), but the mean number of pixels in the viable remaining tissue of the affected ovary was similar to that of the normal ovary (0.53±0.09 vs. 0.47±0.09, p=0.682).
Conclusion
The subtraction technique used with pelvic MRI could reveal the extent of endometrial invasion of the normal ovarian tissue and viable remnant ovarian tissue. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Biaxial ultrasound driving technique for small animal blood–brain barrier opening
Carly Pellow, Siyun Li, Sagid Delgado, G Bruce Pike, Laura Curiel, Samuel Pichardo
Physics in Medicine & Biology.2023; 68(19): 195006. CrossRef - Magnetic resonance imaging texture analysis for the evaluation of viable ovarian tissue in patients with ovarian endometriosis: a retrospective case-control study
Dayong Lee, Hyun Jung Lee
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2022; 39(1): 24. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Nursing Intervention of Gynecological Ovarian Endometriosis with Magnetic Resonance Imaging under Artificial Intelligence Algorithm
Nijie Jiang, Hong Xie, Jiao Lin, Yun Wang, Yanan Yin, Arpit Bhardwaj
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Biaxial ultrasound driving technique for small animal blood–brain barrier opening
- Comparison of small bowel findings using capsule endoscopy between Crohn’s disease and intestinal tuberculosis in Korea
- Yong Gil Kim, Kyung-Jo Kim, Young-Ki Min
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):98-105. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00374
- 6,811 View
- 128 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Little is known about capsule endoscopy (CE) findings in patients with intestinal tuberculosis who exhibit small bowel lesions. The aim of the present study was to distinguish between Crohn’s disease (CD) and intestinal tuberculosis based on CE findings.
Methods
Findings from 55 patients, who underwent CE using PillCam SB CE (Given Imaging, Yoqneam, Israel) between February 2003 and June 2015, were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
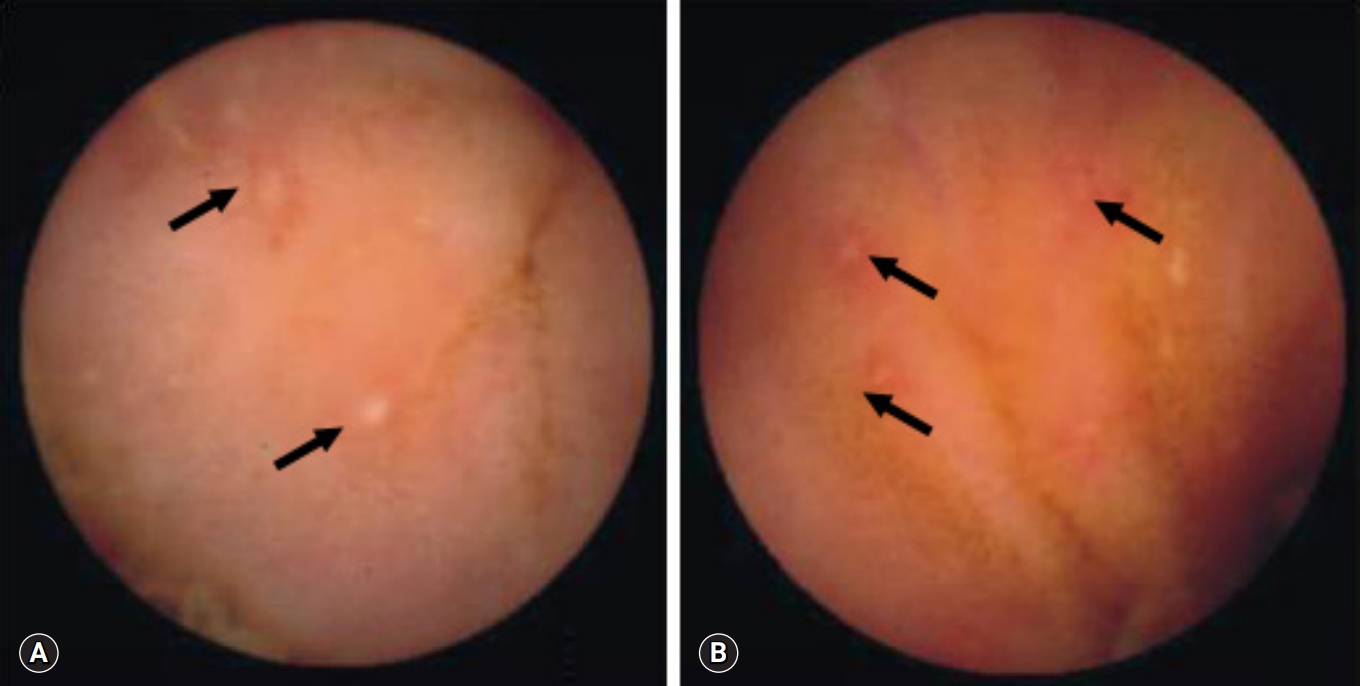
CE revealed small bowel lesions in 35 of the 55 patients: 19 with CD and 16 with intestinal tuberculosis. The median age at diagnosis for patients with CD was 26 years and 36 years for those with intestinal tuberculosis. On CE, three parameters, ≥10 ulcers, >3 involved segments and aphthous ulcers, were more common in patients with CD than in those intestinal tuberculosis. Cobblestoning was observed in five patients with CD and in none with intestinal tuberculosis. The authors hypothesized that a diagnosis of small bowel CD could be made when the number of parameters in CD patients was higher than that for intestinal tuberculosis. The authors calculated that the diagnosis of either CD or intestinal tuberculosis would have been made in 34 of the 35 patients (97%).
Conclusion
The number of ulcers and involved segments, and the presence of aphthous ulcers, were significantly higher and more common, respectively, in patients with CD than in those with intestinal tuberculosis. Cobblestoning in the small bowel may highly favor a diagnosis of CD on CE. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Deep Learning Radiomics Analysis of CT Imaging for Differentiating Between Crohn’s Disease and Intestinal Tuberculosis
Ming Cheng, Hanyue Zhang, Wenpeng Huang, Fei Li, Jianbo Gao
Journal of Imaging Informatics in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Differentiating gastrointestinal tuberculosis and Crohn's disease- a comprehensive review
Arup Choudhury, Jasdeep Dhillon, Aravind Sekar, Pankaj Gupta, Harjeet Singh, Vishal Sharma
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Difficulties in the differential diagnosis of intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn‘s disease
M. N. Reshetnikov, D. V. Plotkin, Yu. R. Zyuzya, A. A. Volkov, O. N. Zuban, E. M. Bogorodskaya
Acta Biomedica Scientifica.2021; 6(5): 196. CrossRef - Differentiating intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn disease: Quo Vadis
Vishal Sharma
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 14(8): 647. CrossRef
- Deep Learning Radiomics Analysis of CT Imaging for Differentiating Between Crohn’s Disease and Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Predictive value of C-reactive protein for the diagnosis of meningitis in febrile infants under 3 months of age in the emergency department
- Tae Gyoung Lee, Seung Taek Yu, Cheol Hwan So
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):106-111. Published online January 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00402

- 10,753 View
- 192 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Fever is a common cause of pediatric consultation in the emergency department. However, identifying the source of infection in many febrile infants is challenging because of insufficient presentation of signs and symptoms. Meningitis is a critical cause of fever in infants, and its diagnosis is confirmed invasively by lumbar puncture. This study aimed to evaluate potential laboratory markers for meningitis in febrile infants.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed infants aged <3 months who visited the emergency department of our hospital between May 2012 and May 2017 because of fever of unknown etiology. Clinical information and laboratory data were evaluated. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed.
Results
In total, 145 febrile infants aged <3 months who underwent lumbar punctures were evaluated retrospectively. The mean C-reactive protein (CRP) level was significantly higher in the meningitis group than in the non-meningitis group, whereas the mean white blood cell count or absolute neutrophil count (ANC) did not significantly differ between groups. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) for CRP was 0.779 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.701–0.858). The AUC for the leukocyte count was 0.455 (95% CI, 0.360–0.550) and that for ANC was 0.453 (95% CI, 0.359–0.547). The CRP cut-off value of 10 mg/L was optimal for identifying possible meningitis.
Conclusion
CRP has an intrinsic predictive value for meningitis in febrile infants aged <3 months. Despite its invasiveness, a lumbar puncture may be recommended to diagnose meningitis in young, febrile infants with a CRP level >10 mg/L. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fever without a source under 3 months of age: any predictive factors of Serious Bacterial Infection?
Rita Calejo Pereira Machado Ribeiro, Joana Raquel Pinto de Carvalho Queiros, Ana Ines Rodrigues Paiva Ferreira, Ines Isabel Aires Martins, Fabio David Monteiro Barroso
Pediatric Oncall.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunologic biomarkers for bacterial meningitis
Mina Yekani, Mohammad Yousef Memar
Clinica Chimica Acta.2023; 548: 117470. CrossRef - Febrile infants: written guidelines to reduce non-essential hospitalizations
Ji Yoon Oh, Soo-Young Lee
World Journal of Pediatrics.2021; 17(5): 555. CrossRef
- Fever without a source under 3 months of age: any predictive factors of Serious Bacterial Infection?
- Does oral doxycycline treatment affect eradication of urine vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus? A tertiary hospital study
- Yoonjung Kim, Sohyun Bae, Soyoon Hwang, Ki Tae Kwon, Hyun-Ha Chang, Su-Jeong Kim, Han-Ki Park, Jong-Myung Lee, Shin-Woo Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):112-121. Published online February 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00430
- 9,403 View
- 119 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
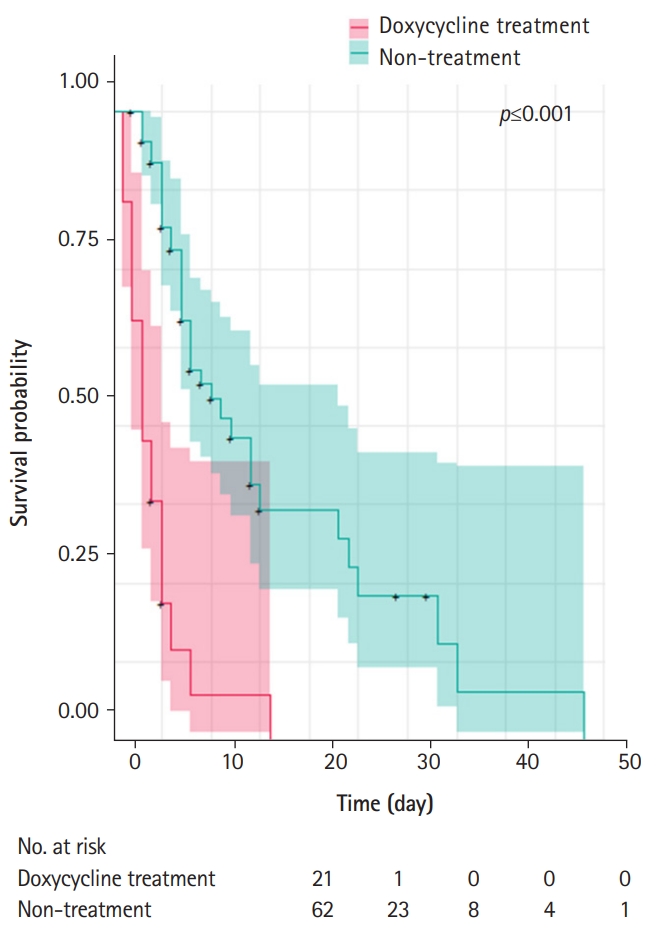
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) has become more common in nosocomial infections, especially in urine samples. However, until now, no treatment regimen has been proven to effectively eradicate urine VRE colonization. Therefore, to evaluate the efficacy of doxycycline in eradicating urine VRE and shortening VRE isolation period, we compared VRE colony detection period between doxycycline-treated and untreated patients.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study of 83 patients with VRE colonization in urine cultures was conducted at a tertiary academic hospital from January 2011 to February 2018. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to evaluate eradication rates in the treatment and non-treatment groups. Factors affecting urine VRE colonization persistence were analyzed by multiple logistic regression analysis.
Results
The overall rate of VRE eradication during the entire hospital stay was higher in the doxycycline treatment group (90.5%) than in the non-treatment group (58.1%, p=0.014). Survival analysis showed that the 5-, 10-, and 20-day cumulative eradication rates were 78.3%, 100%, and 100% in the doxycycline treatment group, and 18.5%, 45.7%, and 67.8% in the non-treatment group, respectively, thereby indicating that eradication rates were higher in the doxycycline treatment group than in the non-treatment group (p<0.001). Only doxycycline treatment was shown to affect urine VRE colonization persistence in multivariate logistic regression analysis
Conclusion
Doxycycline treatment enhanced the eradication rate of urine VRE colonization and appeared to be useful in shortening VRE isolation period. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Therapeutics for Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcal Bloodstream Infections
Kelly A. Cairns, Andrew A. Udy, Trisha N. Peel, Iain J. Abbott, Michael J. Dooley, Anton Y. Peleg
Clinical Microbiology Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Aminopenicillins for treatment of ampicillin-resistant enterococcal urinary tract infections
Kristen Bunnell, Amy Duong, Thomas Ringsred, Asia Mian, Sanaya Bhathena
American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy.2022; 79(13): 1056. CrossRef - Doxycycline for ESBL-E Cystitis
Tomasz Jodlowski, Charles R Ashby, Sarath G Nath
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 73(1): e274. CrossRef
- Therapeutics for Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcal Bloodstream Infections
Case reports
- Fatal progressive right heart failure in a pancreatic cancer patient
- Jeong Tae Byoun, Jae Young Cho
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):122-127. Published online September 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00332

- 7,579 View
- 105 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy (PTTM) is a rare but fatal complication of cancer and causes pulmonary hypertension and acute/subacute right heart failure. PTTM is most commonly associated with gastric cancer and more rarely associated with pancreatic cancer. We report a case of progressive right heart failure associated with clinically diagnosed pancreatic cancer, suggesting PTTM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A rare, life-threatening debut of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy
Pablo Jiménez-Labaig, Soledad Fernández Solé, Susana Gómez Varela, Jorge García Calvo, Sergio Carrera Revilla, Alberto Muñoz Llarena
Current Problems in Cancer: Case Reports.2023; 10: 100238. CrossRef - Evidence of sex differences in cancer‐related cardiac complications in mouse models of pancreatic and liver cancer
Anna Gams, Alejandro Nevarez, Stephanie Perkail, Aileen Venegas, Sharon A. George, Tatiana Efimova, Igor R. Efimov
Physiological Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prospective of Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis Using Cardiac Sensing
Mansunderbir Singh, Priyanka Anvekar, Bhavana Baraskar, Namratha Pallipamu, Srikanth Gadam, Akhila Sai Sree Cherukuri, Devanshi N. Damani, Kanchan Kulkarni, Shivaram P. Arunachalam
Journal of Imaging.2023; 9(8): 149. CrossRef - Fatal pulmonary tumour thrombotic microangiopathy in patient with ovarian adenocarcinoma: review and a case report
Gintare Neverauskaite-Piliponiene, Kristijonas Cesas, Darius Pranys, Skaidrius Miliauskas, Lina Padervinskiene, Jolanta Laukaitiene, Giedre Baksyte, Gintare Sakalyte, Egle Ereminiene
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A rare, life-threatening debut of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Pulmonary tumor thrombotic microangiopathy
- Extramedullary tanycytic ependymoma of the lumbar spinal cord
- Dong Ja Kim, Man-Hoon Han, SangHan Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):128-132. Published online November 11, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00367

- 5,909 View
- 122 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Tanycytic ependymoma is a rare variant of ependymoma that commonly affects the cervical and thoracic spinal cord. It usually arises as intramedullary lesions, and extramedullary cases are extremely rare. We report a case of a 44-year-old woman who was diagnosed with tanycytic ependymoma in her lumbar spine at level 2-3. The tumor mass developed in an intradural extramedullary location. Histopathologically, tanycytic ependymoma can be misdiagnosed as schwannoma or pilocytic astrocytoma. Immunohistochemical findings such as strong positivity for glial fibrillary acidic protein, perinuclear dot-like positive patterns for epithelial membrane antigen, and focal positivity for S-100 are helpful in diagnosing tanycytic ependymoma. It is important to be aware of this rare tumor to ensure appropriate patient management and accurate prognosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Whorling Sclerosing Ependymoma of the Cervical Spinal Cord Presenting Tanycytic Histopathologic Features: A Rare Case Report
Cumhur Kaan Yaltırık, Emin Oğuzcan Yamaner, Öznur Suakar, Sezin Gürkan, Aydın Sav, Uğur Türe
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2023; 31(2): 239. CrossRef - Stretched intradural extramedullary tanycytic ependymoma of the thoracic spine
Nicola Montemurro, Daniele Lorenzini, Valerio Ortenzi, Jacopo Giorgetti
Surgical Neurology International.2022; 13: 426. CrossRef - Intradural extramedullary tanycytic ependymoma of the cervical spine: A case report
Mahmoud M. Taha, Mazen M. Taha, Mohamed Kh. Elbadawy, Mohammad Ezzat
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery.2021; 26: 101319. CrossRef
- Whorling Sclerosing Ependymoma of the Cervical Spinal Cord Presenting Tanycytic Histopathologic Features: A Rare Case Report
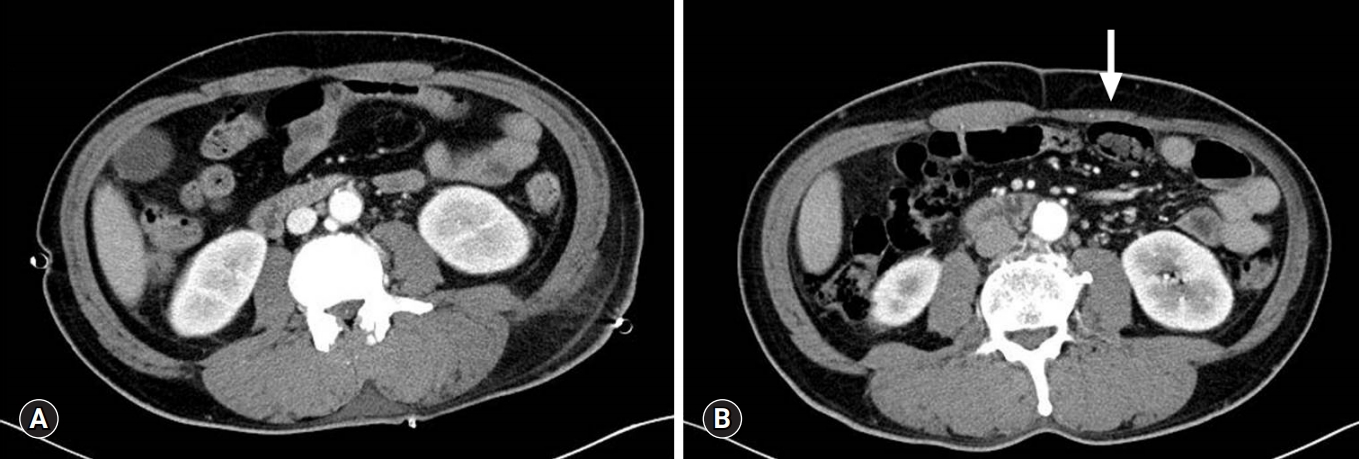
- Rectus abdominis muscle atrophy after thoracotomy
- Jang Hoon Lee, Seok Soo Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):133-135. Published online November 27, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00381
- 7,357 View
- 120 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Intercostal nerve injury is known to occur during thoracotomy; however, rectus abdominis muscle atrophy has rarely been reported. We describe a 52-year-old man who underwent primary closure of esophageal perforation and lung decortication via left thoracotomy. He was discharged 40 days postoperatively without any complications. He noticed an abdominal bulge 2 months later, and computed tomography revealed left rectus abdominis muscle atrophy. We report thoracotomy induced denervation causing rectus abdominis muscle atrophy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rectus Abdominis Muscle Atrophy and Asymmetry After Pulmonary Lobectomy
Aidan S. Weitzner, Myan Bhoopalam, Jeffrey Khong, Arushi Biswas, Allison Karwoski, Meron Haile, Natalie Waldron, Resham Mawalkar, Anjana Srikumar, Stephen Broderick, Jinny Ha, Kristen P. Broderick
Journal of Surgical Research.2024; 299: 137. CrossRef - Intercostal nerve electrodiagnostic testing in rib fractures
Kristen Gambardella, Cody Ashy, Dane Daley, Evert Eriksson, Matthew Sherrier
Muscle & Nerve.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ingenuity of minimally invasive thoracoscopic lobectomy for undiagnosed pulmonary tumour
Sumitaka Yamanaka, Takashi Yoshimatsu, Takeaki Miyata, Hanae Higa
Respirology Case Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Rectus Abdominis Muscle Atrophy and Asymmetry After Pulmonary Lobectomy
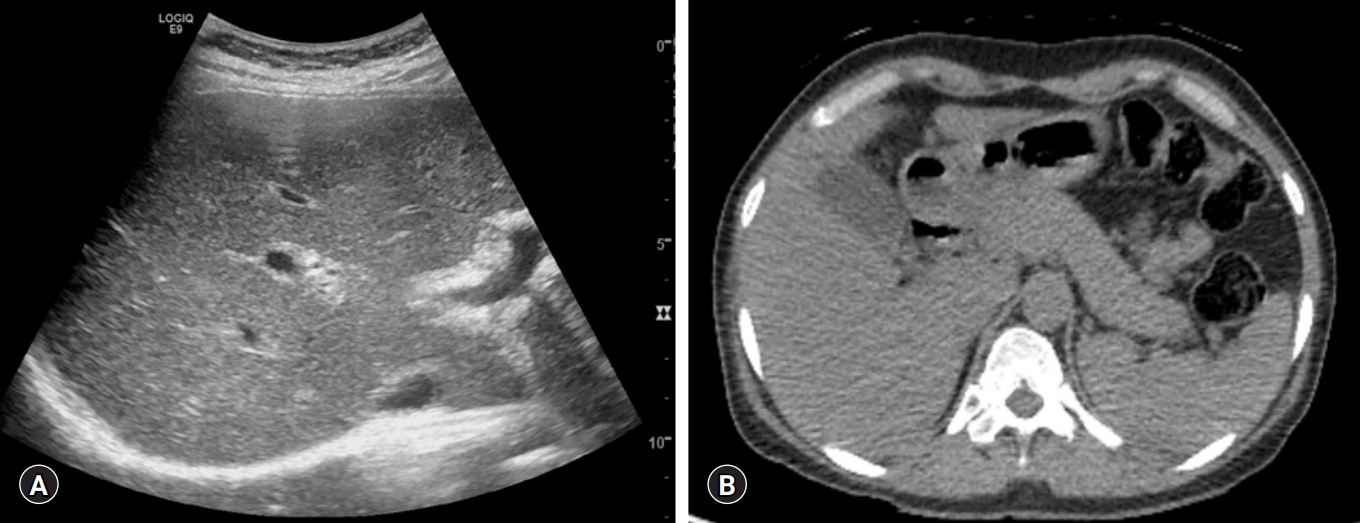
- Anti-nuclear antibody-negative immunoglobulin G4-associated autoimmune hepatitis mimicking lymphoproliferative disorders
- Min Kyu Kang, Jung Gil Park, Joon Hyuk Choi
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):136-140. Published online March 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2020.00066
- 5,245 View
- 119 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-associated autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a very rare subtype of autoimmune hepatitis and characterized by marked elevated serum IgG and hepatic infiltration of IgG4-expressing plasma cells. Pathologic confirmation of hepatic IgG4-expressing plasma cells is usually required for the final diagnosis of IgG4-associated AIH. Herein, we report the case of a 47-year-old female diagnosed with autoantibody-negative IgG4-associated AIH mimicking lymphoproliferative disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatic Involvement of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Mimicking Antinuclear Antibody-Negative Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed by Liver Biopsy
Euna Lee, Min-Kyu Kang, Gabin Moon, Mi-Jin Gu
Medicina.2022; 59(1): 77. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)‐related autoimmune hepatitis and IgG4‐hepatopathy: A histopathological and clinical perspective
Atsushi Tanaka, Kenji Notohara
Hepatology Research.2021; 51(8): 850. CrossRef
- Hepatic Involvement of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Mimicking Antinuclear Antibody-Negative Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed by Liver Biopsy
- Effective strategy in the treatment of aortobronchial fistula with recurrent hemoptysis
- Shin-Ah Son, Deok Heon Lee, Gun-Jik Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):141-146. Published online February 25, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00444

- 5,898 View
- 98 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Aortobronchial fistula (ABF) involves the formation of an abnormal connection between the thoracic aorta and the central airways or the pulmonary parenchyma and is associated with an increased risk of mortality. An ABF typically manifests clinically with symptoms of hemoptysis, and currently, there is a lack of defined guidelines for its treatment. Here, we report the cases of two patients who suffered from recurrent hemoptysis due to ABF with pseudoaneurysm. We propose that removal of the aorta with concomitant lung resection and coverage of the aorta using the pericardial membrane is a definite treatment to lower recurrence of ABF and persistent infection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Descending Thoracic Aorta Replacement in the Setting of Coexisting Aortobronchial and Aortoesophageal Fistula Formation After Open Thoracic Aortic Graft Placement and Subsequent Endovascular Aortic Repair
Rachel S. Dada, Jahnavi Kakuturu, Chris Cook, Alper Toker, Matthew Ellison
Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia.2024; 38(2): 499. CrossRef - Aortobronchopulmonary Fistula—An Unusual Cause of Hemoptysis
Laura Castellanos López, Elisa Martínez Besteiro, Adrián Martínez Vergara
Archivos de Bronconeumología.2023; 59(8): 510. CrossRef - Hybrid Management of an Aortobronchial Fistula after Patch Aortoplasty for Aortic Coarctation in a Patient with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Grigore Tinica, Andrei Tarus, Alberto Bacusca, Raluca Ozana Chistol, Alexandra Cristina Rusu, Mihaela Tomaziu Todosia, Cristina Furnica
Medicina.2022; 58(10): 1385. CrossRef
- Descending Thoracic Aorta Replacement in the Setting of Coexisting Aortobronchial and Aortoesophageal Fistula Formation After Open Thoracic Aortic Graft Placement and Subsequent Endovascular Aortic Repair
Correction
- Erratum to “Assessment of solid components of borderline ovarian tumor and stage I carcinoma: added value of combined diffusion- and perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging”
- See Hyung Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(2):147-147. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00234.e1
- Corrects: J Yeungnam Med Sci 2019;36(3):231
- 3,772 View
- 44 Download

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



