Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Editorial
- First step to international journal by indexing PMC and DOAJ
- Joon Hyuk Choi
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):1-1. Published online December 18, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00395
- 4,269 View
- 82 Download
- 1 Crossref
Review articles
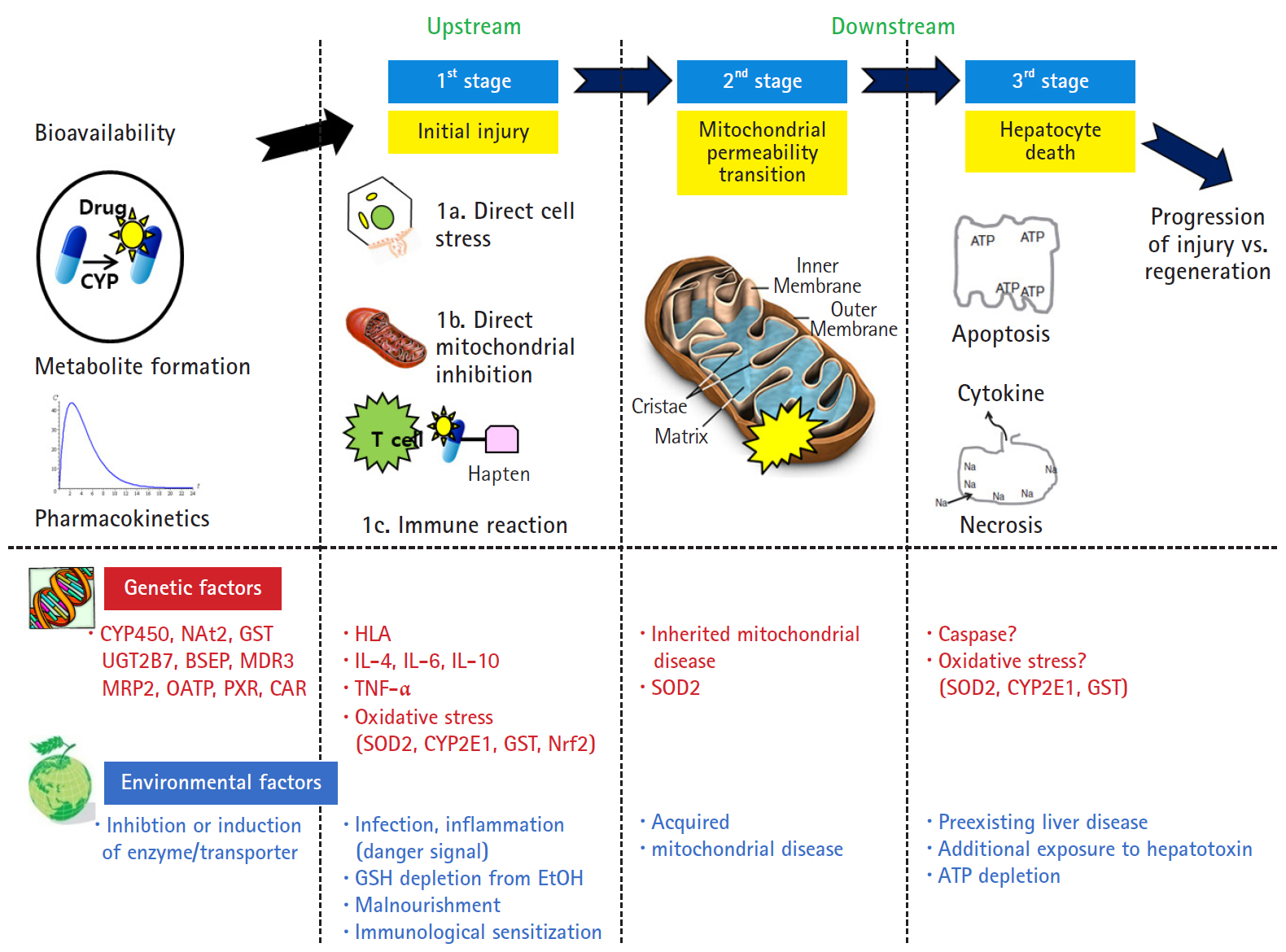
- Drug-induced liver injury
- Jeong Ill Suh
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):2-12. Published online August 27, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00297
- 14,381 View
- 358 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Drug-induced liver injury (DILI), including herbal and dietary supplement hepatotoxicity, is often passed lightly; however, it can lead to the requirement of a liver transplant or may even cause death because of liver failure. Recently, the American College of Gastroenterology, Chinese Society of Hepatology and European Association for the Study of the Liver guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of DILI have been established, and they will be helpful for guiding clinical treatment decisions. Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method scoring is the most commonly used method to diagnose DILI; however, it has some limitations, such as poor validity and reproducibility. Recently, studies on new biomarkers have been actively carried out, which will help diagnose DILI and predict the prognosis of DILI. It is expected that the development of new therapies such as autophagy inducers and various other technologies of the fourth industrial revolution will be applicable to DILI research.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study
Amal Oweid Almutairi, Mahmoud Zaki El-Readi, Mohammad Althubiti, Yosra Zakariyya Alhindi, Nahla Ayoub, Abdullah R. Alzahrani, Saeed S. Al-Ghamdi, Safaa Yehia Eid
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2023; 8(2): 129. CrossRef - Hepatotoxic Components Effect of Chebulae Fructus and Associated Molecular Mechanism by Integrated Transcriptome and Molecular Docking
Liwen Ai, Fan Yang, Wanjun Hu, Liyang Guo, Weixue Liu, Xuexue Xue, Lulu Li, Zunlai Sheng
Molecules.2023; 28(8): 3427. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Safety of Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators in Healthy Adults: Implications for Recreational Users
Jonathan D. Vignali, Kevin C. Pak, Holly R. Beverley, Jesse P. DeLuca, John W. Downs, Adrian T. Kress, Brett W. Sadowski, Daniel J. Selig
Journal of Xenobiotics.2023; 13(2): 218. CrossRef - Antitubercular drugs induced liver injury: an updated insight into molecular mechanisms
Devaraj Ezhilarasan
Drug Metabolism Reviews.2023; 55(3): 239. CrossRef - Advances in Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury Issues: New Clinical and Mechanistic Analysis Due to Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method Use
Rolf Teschke, Gaby Danan
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 10855. CrossRef - Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in early detection of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and drug-induced toxicity
Siyun Yang, Supratik Kar
Artificial Intelligence Chemistry.2023; 1(2): 100011. CrossRef - Rifampicin-induced ER stress and excessive cytoplasmic vacuolization instigate hepatotoxicity via alternate programmed cell death paraptosis in vitro and in vivo
KM Kainat, Mohammad Imran Ansari, Nuzhat Bano, Pankaj Ramji Jagdale, Anjaneya Ayanur, Mahadeo Kumar, Pradeep Kumar Sharma
Life Sciences.2023; 333: 122164. CrossRef - Establishment of a Stable Acute Drug-Induced Liver Injury Mouse Model by Sodium Cyclamate
Quan Zhou, Zhongtian Peng, Xialing Huang
Journal of Inflammation Research.2022; Volume 15: 1599. CrossRef - Mitochondrial toxicants in Xian-Ling-Gu-Bao induce liver injury by regulating the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway: an in vitro study
Shujuan Piao, Hongwei Lin, Xia Tao, Wansheng Chen
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Kratom-Induced Liver Injury: A Case Series and Clinical Implications
Mahesh Botejue, Gurjot Walia, Omar Shahin, Jyotsna Sharma, Rasiq Zackria
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Colestasis inducida por anabólicos: reporte de caso y revisión de la literatura
Diana Lizeth Cabrera-Rojas, Juliana Soto-Cardona, Jorge Luis Toro-Molina, Juan Camilo Pérez-Cadavid, Juan Ignacio Marín-Zuluaga
Hepatología.2021; : 273. CrossRef - Hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters in Wilson’s disease patients with liver failure
Sylwia Szeląg-Pieniek, Stefan Oswald, Mariola Post, Joanna Łapczuk-Romańska, Marek Droździk, Mateusz Kurzawski
Pharmacological Reports.2021; 73(5): 1427. CrossRef - Prediction of Drug-Induced Liver Toxicity Using SVM and Optimal Descriptor Sets
Keerthana Jaganathan, Hilal Tayara, Kil To Chong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(15): 8073. CrossRef - Five Constituents Contributed to the Psoraleae Fructus-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis
Zhaojuan Guo, Pin Li, Chunguo Wang, Qianjun Kang, Can Tu, Bingqian Jiang, Jingxuan Zhang, Weiling Wang, Ting Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Liver Function Test Results after Korean Medicine Treatment in Patients of a Korean Medicine Hospital: A Retrospective Chart Review
Min Young Yim, Han Byeol Park, Jae Soo Kim, Hyun Jong Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Yun Kyu Lee
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2021; 38(4): 275. CrossRef - Herb-induced Liver Injury in Asia and Current Role of RUCAM for Causality Assessment in 11,160 Published Cases
Rolf Teschke, Yun Zhu, Jing Jing
Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.2020; 8(2): 200. CrossRef - Embarazo y lesión hepática inducida por medicamentos. Reporte de un caso y revisión de la literatura
Christian Labrador-López, Martín Garzón-Olarte, Rodrigo Daza-Fernández, Julián Martínez-Marín, Jorge Lizarazo-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos Molano-Villa, Juan Carlos Marulanda-Gómez, Mario Rey-Tovar
Hepatología.2020; : 157. CrossRef
- Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study
- Maturity-onset diabetes of the young: update and perspectives on diagnosis and treatment
- Kyung Mi Jang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):13-21. Published online January 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00409

- 13,044 View
- 359 Download
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a clinically heterogeneous group of monogenic disorders characterized by ß-cell dysfunction. MODY accounts for between 2% and 5% of all diabetes cases, and distinguishing it from type 1 or type 2 diabetes is a diagnostic challenge. Recently, MODY-causing mutations have been identified in 14 different genes. Sanger DNA sequencing is the gold standard for identifying the mutations in MODY-related genes, and may facilitate the diagnosis. Despite the lower frequency among diabetes mellitus cases, a correct genetic diagnosis of MODY is important for optimizing treatment strategies. There is a discrepancy in the disease-causing locus between the Asian and Caucasian patients with MODY. Furthermore, the prevalence of the disease in Asian populations remains to be studied. In this review, the current understanding of MODY is summarized and the Asian studies of MODY are discussed in detail.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 7 (MODY7) and mutation in the Krüppel-like transcription factor 11 (KLF11) gene
Y Wang, X Ye, X Chen, H Zang, Q Shen, L Chen
QJM: An International Journal of Medicine.2024; 117(3): 219. CrossRef - Novel gene mutation in maturity-onset diabetes of the young: A case report
Na Zhang, Hui Zhao, Cui Li, Feng-Zhi Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(5): 1099. CrossRef - Cardio-cerebrovascular Outcomes in MODY, Type 1 Diabetes, and Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study
Hui-Xuan Wu, Tian-Yao Chu, Junaid Iqbal, Hong-Li Jiang, Long Li, Yan-Xuan Wu, Hou-De Zhou
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(11): 2970. CrossRef - Genetic and Clinical Characterization of Patients with HNF1B-Related MODY in Croatia
Maja Baretić, Domagoj Caban, Jadranka Sertić
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(7): 1063. CrossRef - Quantitative profiling and diagnostic potential of one-carbon and central metabolism pools in MODY2 and T1DM
Jieying Liu, Ziyan Xie, Junling Fu, Miao Yu, Tong Wang, Cuijuan Qi, Peng Liu, Xiangyi Hui, Dongmei Wang, Lu Ding, Qian Zhang, Ting Xie, Xinhua Xiao
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - When do we need to suspect maturity onset diabetes of the young in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Özlem Üstay, Tugçe Apaydın, Onur Elbasan, Hamza Polat, Gizem Günhan, Ceyda Dinçer, Lamia Şeker, Esra Arslan Ateş, Ayşegül Yabacı, Ahmet lter Güney, Dilek Gogas Yavuz
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Meta-analysis of HNF1A-MODY3 variants among human population
Rachna Behl, Nishtha Malhotra, Vinay Joshi, Shruti Poojary, Sanniya Middha, Shalini Gupta, Arinola B. Olaonipekun, Ikechukwu Okoye, Bhushan Wagh, Dibyendu Biswas, Chukwuemelie Aginah, Bhavya Saini, Chinaza Nwanya, Sopuluchukwu Ugwu, Modupe M. Anthony, Xua
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(1): 1037. CrossRef - Unusual manifestations of young woman with MODY5 based on 17q12 recurrent deletion syndrome
Ying Cheng, Da-Peng Zhong, Li Ren, Hang Yang, Chen-Fu Tian
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Monogenic Forms of Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Mody-Diabetes
K. A. Aitbaev, I. T. Murkamilov, Zh. A. Murkamilova, V. V. Fomin, I. O Kudaibergenova, F. A. Yusupov
The Russian Archives of Internal Medicine.2022; 12(6): 430. CrossRef - Monogenic diabetes: recent updates on diagnosis and precision treatment: A narrative review
Kyung Mi Jang
Precision and Future Medicine.2022; 6(4): 209. CrossRef - Modeling Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young in Pluripotent Stem Cells: Challenges and Achievements
Carmel Braverman-Gross, Nissim Benvenisty
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Gençlerin Erişkin Başlangıçlı Diyabeti (MODY) Sorumlu HNF4A, GCK ve HNF1 Gen Varyasyonlarının Dünya Genelinde Coğrafik Dağılımı
Deniz KANCA DEMİRCİ, Nurdan GÜL, İlhan SATMAN, Oguz OZTURK, Hülya YILMAZ AYDOĞAN
Haliç Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Dergisi.2021; 4(1): 41. CrossRef - ABCC8 variants in MODY12: Review of the literature and report of a case with severe complications
Marijke Timmers, Eveline Dirinck, Patrick Lauwers, Wim Wuyts, Christophe De Block
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Monogenic Childhood Diabetes: Dissecting Clinical Heterogeneity by Next-Generation Sequencing in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young
Deniz Kanca Demirci, Feyza Darendeliler, Sukran Poyrazoglu, Asli Derya Kardelen Al, Nurdan Gul, Yildiz Tutuncu, Gizem Gulfidan, Kazim Yalcin Arga, Canan Cacina, Oguz Ozturk, Hulya Yilmaz Aydogan, Ilhan Satman
OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology.2021; 25(7): 431. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Hungarian MODY Patients—Part II: Glucokinase MODY Is the Most Prevalent Subtype Responsible for about 70% of Confirmed Cases
Zsolt Gaál, Zsuzsanna Szűcs, Irén Kántor, Andrea Luczay, Péter Tóth-Heyn, Orsolya Benn, Enikő Felszeghy, Zsuzsanna Karádi, László Madar, István Balogh
Life.2021; 11(8): 771. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Hungarian MODY Patients—Part I: Gene Panel Sequencing Reveals Pathogenic Mutations in HNF1A, HNF1B, HNF4A, ABCC8 and INS Genes
Zsolt Gaál, Zsuzsanna Szűcs, Irén Kántor, Andrea Luczay, Péter Tóth-Heyn, Orsolya Benn, Enikő Felszeghy, Zsuzsanna Karádi, László Madar, István Balogh
Life.2021; 11(8): 755. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of MODY: An Updated Mini Review
Abegail Tshivhase, Tandi Matsha, Shanel Raghubeer
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(20): 9436. CrossRef - Functional Genomics in Pancreatic β Cells: Recent Advances in Gene Deletion and Genome Editing Technologies for Diabetes Research
Ming Hu, Ines Cherkaoui, Shivani Misra, Guy A. Rutter
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on Monogenic Diabetes in Korea
Ye Seul Yang, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 627. CrossRef - The epidemiology, molecular pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY)
Ken Munene Nkonge, Dennis Karani Nkonge, Teresa Njeri Nkonge
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 7 (MODY7) and mutation in the Krüppel-like transcription factor 11 (KLF11) gene
- Reproductive toxic agents in work environments and related cases in Korea
- Chulyong Park
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):22-31. Published online January 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00416

- 8,507 View
- 88 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - There has been a growing concern and subsequent interest surrounding numerous reproductive toxic agents found in various working and non-working environments. Meanwhile, there have been many efforts in medical fields such as toxicology and epidemiology applying experimental studies to elucidate reproductive toxic agents’ characterization and health effects. However, there remains insufficient research data and inadequate evidence in humans. Adverse reproductive outcomes vary from transient, moderate health effects to severely detrimental consequences, such as permanent infertility or childhood cancer of one’s offspring. Furthermore, upon exposure to toxic agents, the latent period before reproductive health effects are observed is relatively short compared to other occupational diseases (e.g., occupational cancer); instant action is required once exposure to reproductive toxic agents is detected. Therefore, it is very important for workers and healthcare professionals to know about the reproductive toxic agents they are likely to be exposed to. In this review, we discuss the general epidemiology of reproductive health in Korea, and the information regarding these reproductive toxic agents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Occupational Chemical Exposure and Sperm Parameters; A Narrative Review
Soheila Pourmasumi, Reza Vazirinejad, Zahra Ahmadi, Ali Mehdipour, Alireza Nazari
Journal of Occupational Health and Epidemiology.2023; 12(1): 50. CrossRef
- Association between Occupational Chemical Exposure and Sperm Parameters; A Narrative Review
Original articles
- Nasal tip plasty using three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone (Smart Ball®)
- Joo Hyoung Kim, Geon Woo Kim, Won Kyung Kang
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):32-39. Published online September 5, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00290

- 7,580 View
- 157 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Rhinoplasty is one of the most commonly performed cosmetic surgery procedures. Most Asians desire elevation of their relatively flat nasal dorsum and tip to make them appear more prominent. This study introduces a simple method of nasal tip plasty using three-dimensional (3D)-printed polycaprolactone (PCL) (Smart Ball®), which provides the required length and volume for this purpose and enables the creation of a nasal tip of the desired shape in a safe and simple manner.
Methods
Between September 2014 and May 2017, 22 patients participated in a survey to assess postoperative satisfaction levels. Additionally, three plastic surgeons compared patients’ pre- and 1-year postoperative photographs to evaluate the results. All patients underwent 2- to 4-year postoperative follow-up.
Results
Levels of subjective satisfaction among patients were 3.59, 3.50, 3.82, 3.73, 3.55, and 3.82 for each of the 6 categories evaluated, with a mean of 3.67/4 points, indicating high satisfaction levels. The mean plastic surgeon-reported score for the 22 patients was 4.47/5 points, which also indicates highly successful outcomes. Postoperative nasal tip rotation and tip projection were ideal in most patients.
Conclusion
Our novel method using 3D-printed PCL (Smart Ball®) provides the optimal length and volume required for nasal tip plasty and enables the creation of a nasal tip of the desired shape, in a safe and simple manner. An advantage of our method is that it retains the original nasal structure in contrast to structural changes observed with the use of conventional methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nasal Tip and Alar Groove Plasty Through External Nasal Cutting in Asians: A Clinical Study
Meng-Qiong Xu, Yu-Xi Tang, Bao-Fu Yu, Qi Zeng, Jiao Wei, Chuan-Chang Dai
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2023; 34(3): 870. CrossRef - Cosmetic Open Rhinoplasty in Acute Nasal Bone Fracture With Pre-Existing Deformity
Yong-Ha Kim, Won Seob Lee, Jae-Won Kim, Kyu-Jin Chung
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2023; 34(4): e358. CrossRef - The latest trends in Asian rhinoplasty
Haibo Xiang, Wanwen Dang, Yang An, Yonghuan Zhen, Dong Li
Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery.2022; 4(2): 82. CrossRef - Ex Vivo Maturation of 3D-Printed, Chondrocyte-Laden, Polycaprolactone-Based Scaffolds Prior to Transplantation Improves Engineered Cartilage Substitute Properties and Integration
Carlos M. Chiesa-Estomba, Raquel Hernáez-Moya, Claudia Rodiño, Alba Delgado, Gonzalo Fernández-Blanco, Javier Aldazabal, Jacobo Paredes, Ander Izeta, Ana Aiastui
CARTILAGE.2022; 13(4): 105. CrossRef - The Nasal Tip Rotation After Primary Rhinoplasty Using Columellar Strut Graft
Yazeed Alghonaim , Fahad Alobaid, Jury Alnwaiser
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Aesthetic Nasal Lobule Correction Using a Three-Dimensional Printed Polycaprolactone Implant
Syeo Young Wee, Tae Hyung Kim, Hee Yong Kang, Eun Soo Park
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2021; 32(8): e808. CrossRef
- Nasal Tip and Alar Groove Plasty Through External Nasal Cutting in Asians: A Clinical Study
- Correlation between anterior thigh pain and morphometric mismatch of femoral stem
- Haksun Chung, So Hak Chung
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):40-46. Published online September 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00325

- 21,653 View
- 121 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Postoperative pain occurring after hip arthroplasty has become common since the expanded use of cementless femoral stems. The characteristic pain develop in the anterolateral thigh area. This study aimed to predict anterior thigh pain based on the measurements of postoperative anteroposterior (AP) and lateral (Lat) radiographs of the hip joint.
Methods
The present study included 26 patients (29 hips) who underwent total hip replacement or bipolar hemiarthroplasty between March 2010 and May 2016, whose complete clinical information was available. AP and Lat radiographs of the affected hip were taken on the day of surgery and 1 and 6 months postoperatively. Patients with improper radiographs were excluded. The distance from the femoral stem to the nearest cortical bone in the distal region of the stem was measured. The patient group with a visual analog scale (VAS) score of ≥6 points was designated as patients with anterior thigh pain.
Results
Sex, age, weight, height, body mass index, and bone mineral density in the lumbar spine and femur did not have a significant effect on postoperative VAS scores (p>0.05). Presence of contact between the femoral stem and cortical bone was associated with postoperative anterior thigh pain.
Conclusion
Hip AP and Lat radiographs are usually taken to confirm fixation and alignment of the femoral stem after hip arthroplasty. The measurement method introduced in this study can be utilized for predicting anterior thigh pain after hip arthroplasty. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hydroxyapatite ceramic-coated femoral components in younger patients followed up for 27 to 32 years
Piyush K. Upadhyay, Nirav Shah, Vishal Kumar, Saqeb B. Mirza
Bone & Joint Open.2024; 5(4): 286. CrossRef
- Hydroxyapatite ceramic-coated femoral components in younger patients followed up for 27 to 32 years
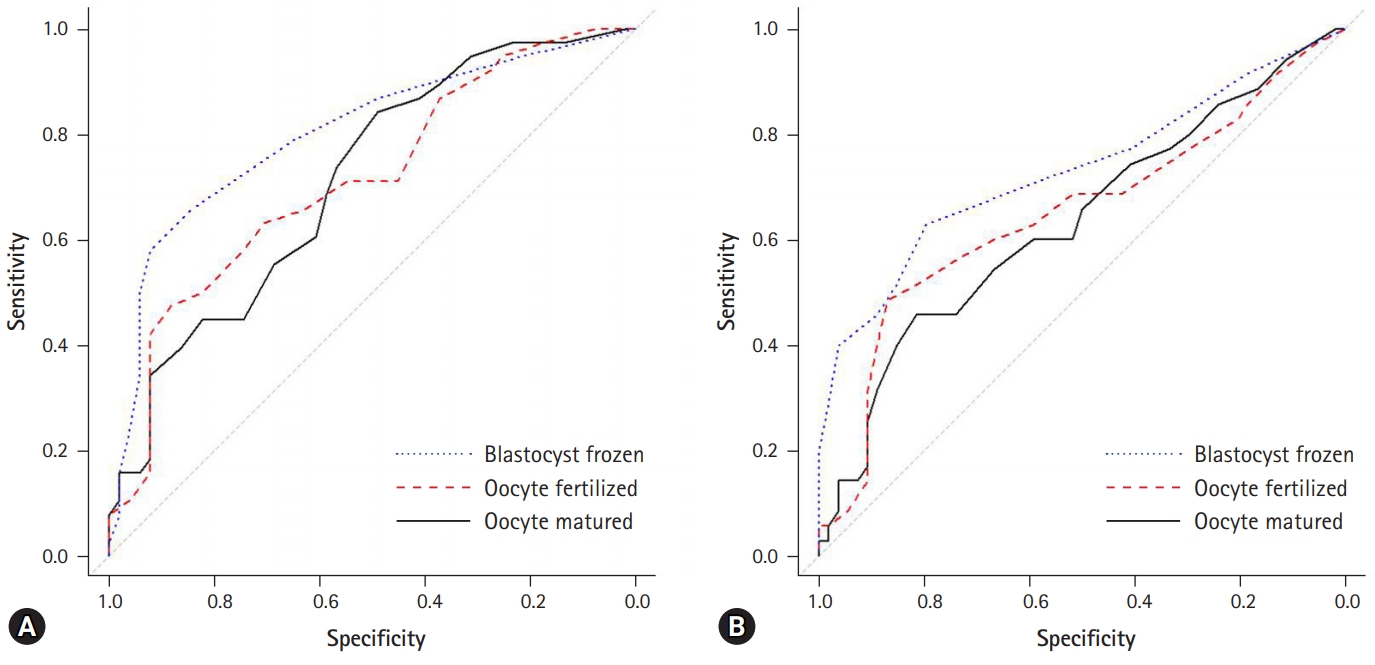
- Clinical factors that affect the pregnancy rate in frozen-thawed embryo transfer in the freeze-all policy
- Seo Yoon Hwang, Eun Hye Jeon, Seung Chul Kim, Jong Kil Joo
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):47-53. Published online September 27, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00346
- 6,913 View
- 116 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study was conducted to analyze clinical factors that can affect pregnancy rates in normal responders undergoing the freeze-all policy in in vitro fertilization.
Methods
We evaluated 153 embryo transfer cycles in 89 infertile women with normal response to controlled ovarian stimulation (COS). After COS, all embryos were cultured to the blastocyst stage, and good quality blastocysts were vitrified for elective frozen-thawed embryo transfer (FET). Clinical variables associated with COS and the results of COS and culture, including the number of retrieved oocytes, fertilized oocytes, and frozen blastocysts were compared between the pregnant group and the non-pregnant group.
Results
After a single cycle of COS for each patient, 52 patients became pregnant while 37 did not. Significant differences were observed in the number of matured oocytes, fertilized oocytes, frozen blastocysts, and transferred embryos. The number of frozen blastocysts in the pregnant group was almost twice that in the non-pregnant group (5.6±3.1 vs. 2.8±1.9, p<0.001). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for the 4 frozen blastocysts was 0.801 in the pregnant group.
Conclusion
In the freeze-all policy, the number of matured oocytes, number of fertilized oocytes, and number of frozen blastocysts might be predictive factors for pregnancy. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Even high normal blood pressure affects live birth rate in women undergoing fresh embryo transfer
Huijun Chen, Xiaoli Zhang, Sufen Cai, Jian Li, Sha Tang, Carl-Friedrich Hocher, Benjamin Rösing, Liang Hu, Ge Lin, Fei Gong, Bernhard K Krämer, Berthold Hocher
Human Reproduction.2022; 37(11): 2578. CrossRef
- Even high normal blood pressure affects live birth rate in women undergoing fresh embryo transfer
Case reports
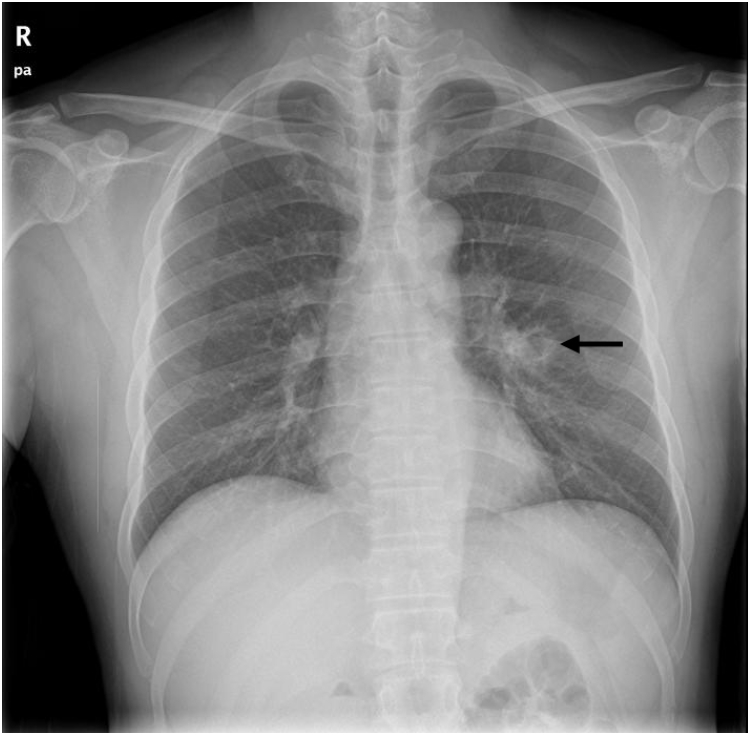
- Community-acquired Achromobacter xylosoxidans infection presenting as a cavitary lung disease in an immunocompetent patient
- Chan Hee Hwang, Woo Jin Kim, Hye Young Jwa, Sung Heon Song
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):54-58. Published online August 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00276
- 7,180 View
- 136 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Achromobacter xylosoxidans is a gram-negative bacterium that can oxidize xylose. It is commonly found in contaminated soil and water but does not normally infect immunocompetent humans. We report a case of a cavitary lung lesion associated with community-acquired A. xylosoxidans infection, which mimicked pulmonary tuberculosis or lung cancer in an immunocompetent man. The patient was hospitalized due to hemoptysis, and chest computed tomography (CT) revealed a cavitary lesion in the superior segment of the left lower lobe. We performed bronchoscopy and bronchial washing, and subsequent bacterial cultures excluded pulmonary tuberculosis and identified A. xylosoxidans. We performed antibiotic sensitivity testing and treated the patient with a 6-week course of amoxicillin/clavulanate. After 2 months, follow-up chest CT revealed complete resolution of the cavitary lesion.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Achromobacter species (sp.) outbreak caused by hospital equipment containing contaminated water: risk factors for infection
J. Tian, T. Zhao, R. Tu, B. Zhang, Y. Huang, Z. Shen, G. Du, Y. Wang
Journal of Hospital Infection.2024; 146: 141. CrossRef - Full characterization of plasmids from Achromobacter ruhlandii isolates recovered from a single patient with cystic fibrosis (CF)
Carla Steffanowski, Mariana Papalia, Andrés Iriarte, Mauricio Langleib, Laura Galanternik, Gabriel Gutkind, Vaughn Cooper, María Soledad Ramírez, Marcela Radice
Revista Argentina de Microbiología.2022; 54(1): 3. CrossRef - Nosocomial Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infection Presenting as a Cavitary Lung Lesion in a Lung Cancer Patient
Vinoja Sebanayagam, Paul Nguyen, Mo'ath Nassar, Ayman Soubani
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Achromobacter species (sp.) outbreak caused by hospital equipment containing contaminated water: risk factors for infection
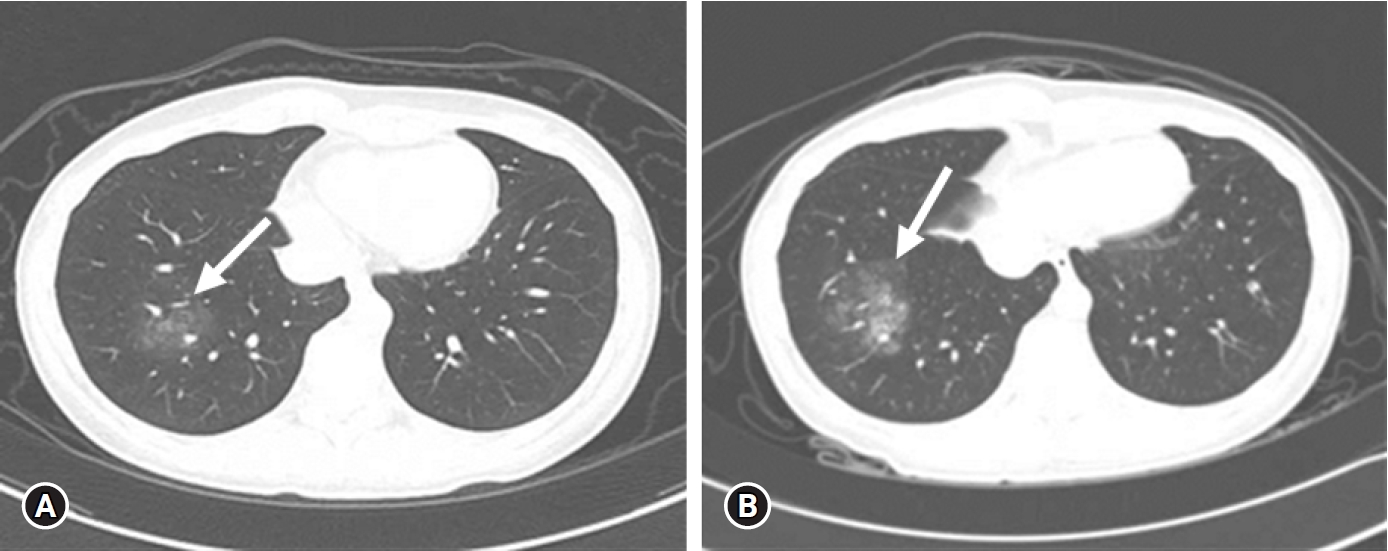
- Recurrent hemoptysis in a 26-year-old woman with a ground-glass opacity lesion of the lung
- Jong Ha Kim, Sin-Youl Park
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):59-62. Published online September 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00304
- 7,020 View
- 111 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hemoptysis is a major reason for emergency department (ED) visits. Catamenial hemoptysis (CH), a rare condition of thoracic endometriosis, can cause recurrent hemoptysis but is difficult to diagnose in the ED due to the scarcity of cases and nonspecific clinical findings. We report a case of a 26-year-old woman who presented to the ED with recurrent hemoptysis since 2 years without a definite cause. Her vital signs and blood test findings were unremarkable. Chest computed tomography (CT) did not show any specific lesions other than a non-specific ground-glass opacity pattern in her right lung. She was on day 4 of her menstrual cycle and her hemoptysis frequently occurred during menstruation. Although there was no histological confirmation, based on her history of hemoptysis during menstruation and no other cause of the hemoptysis, the patient was tentatively diagnosed with CH and was administered gonadotropin-releasing hormone. She had no recurrence of hemoptysis for 3 months. While CH is difficult to diagnose in the ED, the patient’s recurrent hemoptysis related to menstruation was a clue to the presence of CH. Therefore, physicians should determine the relationship between hemoptysis and menstruation for women of childbearing age presenting with repeated hemoptysis without a definite cause.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thoracic Endometriosis: A Review Comparing 480 Patients Based on Catamenial and Noncatamenial Symptoms
Nura Fitnat Topbas Selcuki, Salih Yilmaz, Cihan Kaya, Taner Usta, Ahmet Kale, Engin Oral
Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology.2022; 29(1): 41. CrossRef - Characteristics and Outcomes of a Sample of Patients With COVID-19 Identified Through Social Media in Wuhan, China: Observational Study
Dong Liu, Yuyan Wang, Juan Wang, Jue Liu, Yongjie Yue, Wenjun Liu, Fuhai Zhang, Ziping Wang
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(8): e20108. CrossRef - Cyclical Hemoptysis and Pelvic Pain in a Young Female: A Sign of Thoracic Endometriosis Syndrome
Areeg Bala, Raghda A Salim, Smit Deliwala, Michele Obeid, Ghassan Bachuwa
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Thoracic Endometriosis: A Review Comparing 480 Patients Based on Catamenial and Noncatamenial Symptoms
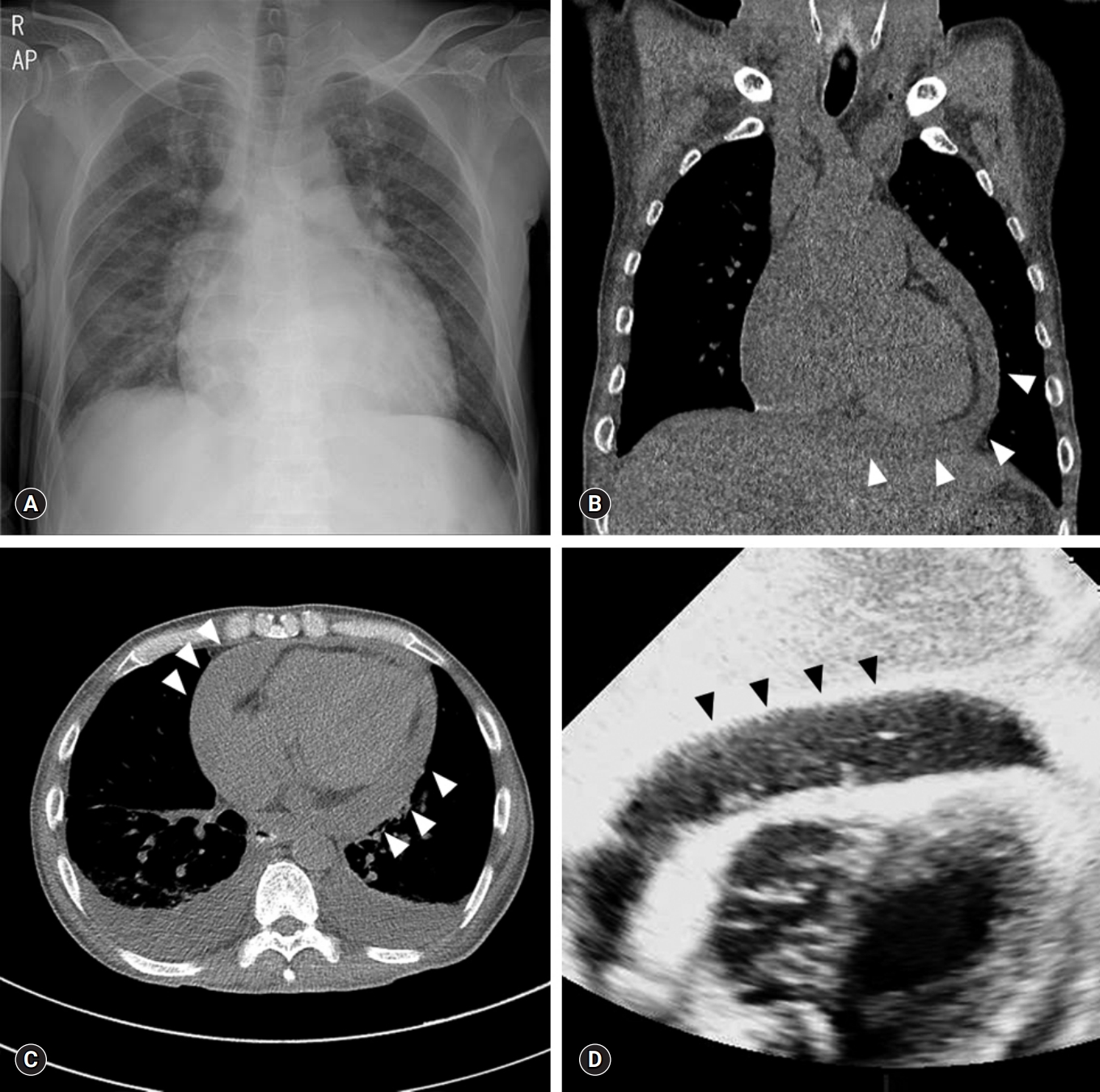
- Purulent pericarditis: subdiaphragmatic suppurative focus
- Kang-Un Choi, Chan-Hee Lee
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):63-66. Published online September 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00311
- 5,109 View
- 93 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Purulent pericarditis is defined as a localized pericardial infection with gross pus formation in the pericardial space. Although purulent pericarditis is now rare in the antibiotic era, it may be life-threatening. We describe a rare case of purulent pericarditis that originated from a subdiaphragmatic suppurative focus in an immunocompromised host.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Study on the Process of Posttraumatic Growth among Helping Professionals in Suicide Prevention: Focused on Grounded Theory
Sungkyu Lee, Hyeyeon Sung, Chonghee Seo
Journal of Social Science.2021; 32(3): 149. CrossRef
- A Study on the Process of Posttraumatic Growth among Helping Professionals in Suicide Prevention: Focused on Grounded Theory
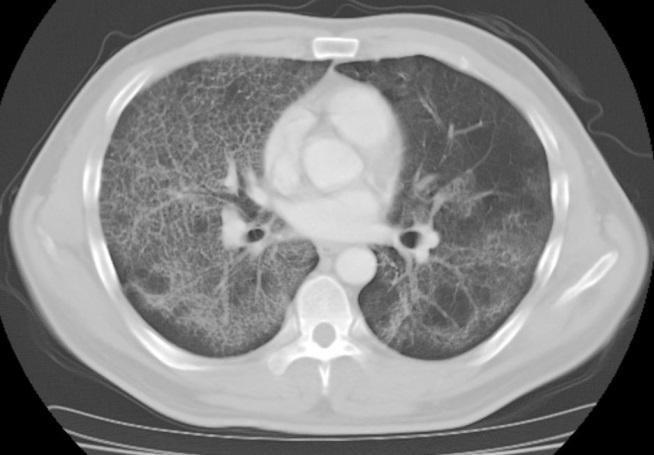
- Whole lung lavage using a rapid infusion system to treat a patient with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- Seung Won Ra, Soon Eun Park, Hyung Kwan Lee, Il Sang Han, Se Hun Park
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2020;37(1):67-72. Published online October 17, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00360
- 6,443 View
- 97 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Whole lung lavage (WLL) is a therapeutic procedure to remove accumulated material by infusing and draining the lungs with lavage fluid. This procedure has been regarded as the current standard of care to treat pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. However, the WLL protocol has not yet been standardized and the technique has been refined and modified a number of times. A rapid infusion system is a device used to infuse blood or other fluids at precise rates and normothermic conditions. This device is not typically used in WLL, which relies on the passive infusion of fluids using the gravitational force. However, in this study we performed WLL using a rapid infusion system, since we aimed to take advantage of its shorter operation time and greater degree of control over fluid volume and temperature. The patient’s symptoms improved without the occurrence of any complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Whole-Lung Lavage—a Narrative Review of Anesthetic Management
Santiago M. Mata-Suarez, Agustina Castro-Lalín, Santiago Mc Loughlin, Juan De Domini, Juan C. Bianco
Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia.2022; 36(2): 587. CrossRef - Lung injury induced by different negative suction pressure in patients with pneumoconiosis undergoing whole lung lavage
Mingyuan Yang, Baoping Li, Bin Wang, Lei Li, Yurong Ji, Yunzhi Zhou, Rui Huang, Qinghao Cheng
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anesthetic management during whole-lung lavage using lung ultrasound in a patient with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a case report
Jae Wan Jung, Hyunho Lee, Jimi Oh
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2021; 38(4): 374. CrossRef
- Whole-Lung Lavage—a Narrative Review of Anesthetic Management

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



