Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Imagery
- "Smiling sunflowers"
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):i. Published online July 18, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00423

- 1,913 View
- 53 Download
Review articles
- Hypertension and cognitive dysfunction: a narrative review
- Eun-Jin Cheon
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):225-232. Published online November 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00605

- 3,549 View
- 185 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Cognitive dysfunction is relatively less considered a complication of hypertension. However, there is sufficient evidence to show that high blood pressure in middle age increases the risk of cognitive decline and dementia in old age. The greatest impact on cognitive function in those with hypertension is on executive or frontal lobe function, similar to the area most damaged in vascular dementia. Possible cognitive disorders associated with hypertension are vascular dementia, Alzheimer disease, and Lewy body dementia, listed in decreasing strength of association. The pathophysiology of cognitive dysfunction in individuals with hypertension includes brain atrophy, microinfarcts, microbleeds, neuronal loss, white matter lesions, network disruption, neurovascular unit damage, reduced cerebral blood flow, blood-brain barrier damage, enlarged perivascular damage, and proteinopathy. Antihypertensive drugs may reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Given the high prevalence of dementia and its impact on quality of life, treatment of hypertension to reduce cognitive decline may be a clinically relevant intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Chronic Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Decline in Patients with Cardiac Disease: Evidence, Relevance, and Therapeutic Implications
Jan Traub, Anna Frey, Stefan Störk
Life.2023; 13(2): 329. CrossRef - The A-to-Z factors associated with cognitive impairment. Results of the DeCo study
María Gil-Peinado, Mónica Alacreu, Hernán Ramos, José Sendra-Lillo, Cristina García, Gemma García-Lluch, Teresa Lopez de Coca, Marta Sala, Lucrecia Moreno
Frontiers in Psychology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Chronic Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Decline in Patients with Cardiac Disease: Evidence, Relevance, and Therapeutic Implications
- Evaluation research in Korean medical education: a systematic review
- Hye Jin Park, Yu Ra Kim
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):233-240. Published online December 5, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00563

- 1,942 View
- 85 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - The purpose of this study aims to analyze research trends related to ‘evaluation’ in Korean medical education through a systematic review. This study used a systematic review method, which is a research methodology for research trends and ‘literature analysis.’ Researchers searched the Korean journal literature published until the end of December 2020 in the Korean research database with keywords related to medicine and evaluation. Thus, 5,205 cases were identified. Based on these data, 143 papers were selected through a logical screening process, requiring 1 month to complete the data search and analysis process. In terms of publications, medical journals overwhelmingly outnumbered nonmedical journals until 2015; however, after 2016, the number of papers published in nonmedical journals increased, and the number of published papers was similar to that of medical journals. In terms of evaluation-related research, research on student and program evaluations has been very active compared to that on accreditation. As the number of evaluation studies has gradually decreased over the past 10 years, preparing a plan to revitalize them in Korean medical education is necessary. Considering that the role of evaluation in education has been emphasized in recent years, research on reestablishing the concept of evaluation; developing evaluation indicators; analyzing the status of student evaluation, program evaluation, and accreditation; and deriving measures to improve medical education through evaluation is required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Patient-physician interaction education in Korea: a systematic review
Hwan Ho Lee, Yu Ra Kim, Hye Jin Park
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2024; 41(2): 74. CrossRef
- Patient-physician interaction education in Korea: a systematic review
- Advances in management of pediatric chronic immune thrombocytopenia: a narrative review
- Jae Min Lee
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):241-246. Published online January 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00745
- 3,643 View
- 226 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a disease in which thrombocytopenia occurs because of immune-mediated platelet destruction and decreased platelet production. Although many pediatric patients with ITP experience spontaneous remission or reach remission within 12 months of first-line therapy, approximately 20% progress to chronic ITP. Patients who do not respond to first-line treatment or experience frequent relapses are of great concern to physicians. This review summarizes recent treatments for second-line treatment of pediatric chronic ITP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Beta-Thalassemia with Initial Presentation as Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Case Report
Hyun Sik Kang
Clinical Pediatric Hematology-Oncology.2023; 30(1): 42. CrossRef
- Beta-Thalassemia with Initial Presentation as Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Case Report
Original articles
- Effects of propofol-remifentanil versus sevoflurane-remifentanil on acute postoperative pain after total shoulder arthroplasty: a randomized trial
- Eun Kyung Choi, Saeyoung Kim, Do young Kim
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):247-251. Published online March 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00129

- 3,041 View
- 107 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
While some evidence indicates that propofol-based anesthesia has less postoperative pain than sevoflurane-based anesthesia, these results are controversial. We compared acute postoperative pain intensity and opioid consumption after total shoulder arthroplasty between propofol-remifentanil (PR) and sevoflurane-remifentanil (SR) anesthesia.
Methods
Among 48 patients undergoing shoulder arthroscopic surgery anesthetized with PR or SR, postoperative pain intensity was assessed at 30 minutes and at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hours. The total patient-controlled analgesia volume and number of patients requiring rescue analgesics were assessed.
Results
No significant difference in postoperative pain intensity was observed between the two groups. Postoperative opioid consumption and analgesic requirements were also comparable in the first 24 hours after surgery.
Conclusion
PR and SR anesthesia for shoulder arthroscopic surgery provide comparable postoperative analgesia results.
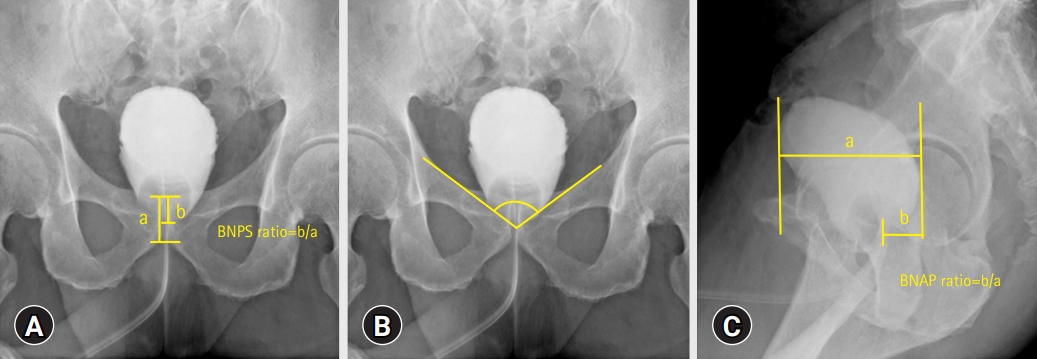
- Novel cystography parameter to predict early recovery from urinary continence after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer: a retrospective study
- Yeong Uk Kim
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):252-258. Published online July 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00311
- 2,578 View
- 89 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether postoperative cystography findings can predict early and long-term recovery from incontinence after radical prostatectomy (RP), compared with the other cystography parameters.
Methods
I retrospectively reviewed 118 patients who underwent robot-assisted RP (RARP) for localized prostate cancer at single institution between January 2016 and April 2021. One hundred and seven patients were included in the study. Postoperative cystography was routinely performed 7 days after surgery. The bladder neck to pubic symphysis ratio, vesicourethral angle, and bladder neck anteroposterior length (BNAP) ratio (the bladder neck-posterior margin distances divided by the anteroposterior lengths) were evaluated. Continence was defined as cessation of pad use. The association between these variables and urinary incontinence was also analyzed.
Results
The urinary incontinence recovery rates 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after RARP were 43.92%, 66.35%, 87.85%, and 97.19%, respectively. Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that a lower BNAP ratio and wider vesicourethral angle were significantly associated with continence restoration at 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery. In addition, in terms of days of pad usage, lower BNAP ratio, wider vesicourethral angle, and bladder neck preservation were significantly associated with recovery from urinary incontinence within 12 months as assessed by Cox proportional hazard analysis.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that vesicourethral angle and BNAP ratio were independent predictors of early recovery from post-prostatectomy incontinence. I suggest that both the sagittal and coronal views of postoperative cystography help anticipate early continence restoration after RARP. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A single‐center retrospective comparative analysis of urinary continence in robotic prostatectomy with a combination of umbilical ligament preservation and Hood technique
Hiroaki Shimmura, Taro Banno, Kazutaka Nakamura, Anju Murayama, Haruki Shigeta, Toyoaki Sawano, Yukiko Kouchi, Akihiko Ozaki, Fumito Yamabe, Junpei Iizuka, Toshio Takagi
International Journal of Urology.2023; 30(10): 889. CrossRef
- A single‐center retrospective comparative analysis of urinary continence in robotic prostatectomy with a combination of umbilical ligament preservation and Hood technique
- Impact of Controlling Nutritional Status score on short-term outcomes after carotid endarterectomy: a retrospective cohort study
- Hee Won Son, Gyeongseok Yu, Seung Jun Lee, Jimi Oh
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):259-267. Published online October 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00507

- 1,729 View
- 61 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Malnutrition and impaired immune responses significantly affect the clinical outcomes of patients with atherosclerotic stenosis. The Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score has recently been utilized to evaluate perioperative immunonutritional status. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between immunonutritional status, indexed by CONUT score, and postoperative complications in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA).
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 188 patients who underwent elective CEA between January 2010 and December 2019. The preoperative CONUT score was calculated as the sum of the serum albumin concentration, total cholesterol level, and total lymphocyte count. The primary outcome was postoperative complications within 30 days after CEA, including major adverse cardiovascular events, pulmonary complications, stroke, renal failure, sepsis, wounds, and gastrointestinal complications. Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was used to estimate the factors associated with postoperative complications during the 30-day follow-up period.
Results
Twenty-five patients (13.3%) had at least one major complication. The incidence of postoperative complications was identified more frequently in the high CONUT group (12 of 27, 44.4% vs. 13 of 161, 8.1%; p<0.001). Multivariate analyses showed that a high preoperative CONUT score was independently associated with 30-day postoperative complications (hazard ratio, 5.98; 95% confidence interval, 2.56–13.97; p<0.001).
Conclusion
Our results showed that the CONUT score, a simple and readily available parameter using only objective laboratory values, is independently associated with early postoperative complications.
- Rates and subsequent clinical course of fetal congenital anomalies detected by prenatal targeted ultrasonography of 137 cases over 5 years in a single institute: a retrospective observational study
- Haewon Choi, Hyo-Shin Kim, Joon Sakong
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):268-275. Published online November 2, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00514

- 1,712 View
- 61 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
With the establishment of international guidelines and changes in insurance policies in Korea, the role of targeted ultrasonography has increased. This study aimed to identify the rates and clinical course of anomalies detected using prenatal targeted ultrasonography.
Methods
This study was a retrospective analysis of all pregnancies with targeted ultrasonography performed in a single secondary medical center over 5 years.
Results
Fetal anomalies were detected by targeted ultrasonography in 137 of the 8,147 cases (1.7%). The rates of anomalies were significantly higher in female fetuses (2.0% vs. 1.3%). In cases of female fetuses, the rate of anomalies was significantly higher in the advanced maternal age group (2.4% vs. 1.2%). In cases of male fetuses, the rate of anomalies was significantly higher in nulliparous (2.4% vs. 1.5%) and twin (5.7% vs. 1.9%) pregnancies. Pulmonary anomalies were significantly more common in the multiparity group (17.6% vs. 5.8%). Among the 137 cases, 17.5% terminated the pregnancy, 16.8% were diagnosed as normal after birth, and 42.3% were diagnosed with anomalies after birth or required follow-up.
Conclusion
Through the first study on the rates and clinical course of anomalies detected by targeted ultrasonography at a single secondary center in Korea, we found that artificial abortions were performed at a high rate, even for relatively mild anomalies or anomalies with good prognosis. We suggest the necessity of a nationwide study to establish clinical guidelines based on actual incidences or prognoses.
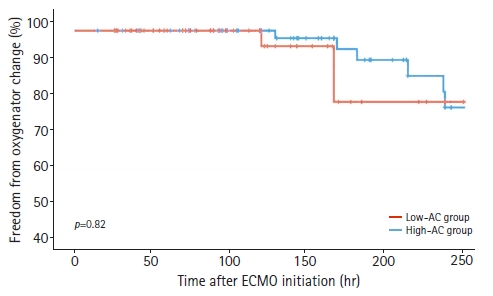
- Safety of low-dose anticoagulation in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation using the Permanent Life Support System: a retrospective observational study
- Kyungsub Song, Jae Bum Kim
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):276-282. Published online May 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2023.00339
- 1,889 View
- 71 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Bleeding and thrombosis are major complications associated with high mortality in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) management. Anticoagulant therapy should be adequate to reduce thrombosis. However, related studies are limited.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed all patients supported with ECMO at a single institution between January 2014 and July 2022 and included those on all types of ECMO using the Permanent Life Support System. Patients were classified into two groups according to their measured mean activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) during ECMO management: a high-anticoagulation (AC) group (aPTT, ≥55 seconds; n=52) and a low-AC group (aPTT, <55 seconds; n=79). The primary outcome was thrombotic or bleeding events during ECMO.
Results
We identified 10 patients with bleeding; significantly more of these patients were in the high-AC group (n=8) than in the low-AC group (15.4% vs. 2.5%, p=0.01). However, thrombus events and oxygenator change-free times were not significantly different between the two groups. Four patients in the high-AC group died of bleeding complications (brain hemorrhage, two; hemopericardium, one; and gastrointestinal bleeding, one). One patient in the low-AC group developed a thrombus and died of ECMO dysfunction due to circuit thrombosis.
Conclusion
Heparin did not significantly improve thrombotic outcomes. However, maintaining an aPTT of ≥55 seconds was a significant risk factor for bleeding events, especially those associated with mortality.
Case reports
- Severe congenital neutropenia mimicking chronic idiopathic neutropenia: a case report
- Juhyung Kim, Soyoon Hwang, Narae Hwang, Yeonji Lee, Hee Jeong Cho, Joon Ho Moon, Sang Kyun Sohn, Dong Won Baek
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):283-288. Published online July 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00353

- 2,643 View
- 128 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Severe chronic neutropenia is classified as severe congenital, cyclic, autoimmune, or idiopathic. However, there is a lot of uncertainty regarding the diagnosis of severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) and chronic idiopathic neutropenia, and this uncertainty affects further evaluations and treatments. A 20-year-old man presented with fever and knee abrasions after a bicycle accident. On admission, his initial absolute neutrophil count (ANC) was 30/µL. He had no medical history of persistent severe neutropenia with periodic oscillation of ANC. Although his fever resolved after appropriate antibiotic therapy, ANC remained at 80/µL. Bone marrow (BM) aspiration and biopsy were performed, and a BM smear showed myeloid maturation arrest. Moreover, genetic mutation test results showed a heterozygous missense variant in exon 4 of the neutrophil elastase ELANE: c597+1G>C (pV190-F199del). The patient was diagnosed with SCN. After discharge, we routinely checked his ANC level and monitored any signs of infection with minimum use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), considering its potential risk of leukemic transformation. Considering that SCN can be fatal, timely diagnosis and appropriate management with G-CSF are essential. We report the case of a patient with SCN caused by ELANE mutation who had atypical clinical manifestations. For a more accurate diagnosis and treatment of severe chronic neutropenia, further studies are needed to elucidate the various clinical features of ELANE.
- Crowned dens syndrome as a rare cause of anterior neck pain after transurethral resection of the prostate: a case report
- Myeong Geun Jeong, Bum Soon Park, Eun-Seok Son, Jang Hyuk Cho
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):289-292. Published online August 5, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00388

- 1,995 View
- 83 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We describe the case of a 79-year-old man who presented with progressive aggravation of severe axial neck pain and fever 3 days after transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), despite maintaining neutral neck posture during surgery. Laboratory examination revealed markedly elevated C-reactive protein levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rates. Computed tomography revealed crown-like calcifications surrounding the odontoid process. We diagnosed crowned dens syndrome (CDS) as the cause of acute-onset neck pain after TURP. The patient was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for 5 days, and his symptoms resolved completely. CDS is a rare disease characterized by calcific deposits around the odontoid process with acute onset of severe neck pain and restricted motion. Evidence of inflammation on serological testing and fever are typical of CDS. However, the prevalence and pathophysiology of CDS remain unclear. We hypothesized that systemic inflammation after prostate surgery may have induced a local inflammatory response involving calcification around the odontoid process.
- Oral chemical burns caused by topical application of policresulen: a case report
- Hwa Suk Chae, Sohee Kang
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):293-296. Published online October 20, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00472

- 3,125 View
- 177 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Oral mucosal burns can occur after contact with various chemical agents, and commonly manifest as areas of mucosal sloughing and ulceration. Policresulen (Albothyl, Celltrion Pharm Inc.) is an over-the-counter topical antiseptic that is frequently used to treat stomatitis. Policresulen solution is highly acidic, with an approximate pH of 0.6; it can thus cause mucosal injury when improperly applied in the oral cavity. Here, we present a rare case of an oral mucosal burn resulting from incorrect self-administration of policresulen and emphasize the importance of increasing understanding of this adverse drug event among consumers and health professionals.
- Effect of pulmonary rehabilitation on patients with acute COVID-19: a single-center case series
- Son Mi Lee, Min Woo Kim, Donghyun Shin, Songi Han, Ju Sun Oh
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):297-301. Published online November 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00591

- 1,703 View
- 79 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has been ongoing for more than 2 years. Many patients who recover from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection continue to have aftereffects such as dyspnea and fatigue, which may lead to functional decline. Therefore, the need for managing these symptoms using methods such as pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) has emerged. The purpose of this study was to report the effectiveness of PR in five patients with acute COVID-19. PR was performed in patients with persistent dyspnea and oxygen demand after COVID-19. All five patients were able to maintain an independent functional status before COVID-19. However, after acute COVID-19, they were unable to walk independently and needed assistance for activities of daily living due to dyspnea and fatigue. Therefore, they were referred to rehabilitation units, and PR was performed. The modified Medical Research Council dyspnea scale, maximal expiratory pressure (MEP), 6-minute walking test, forced vital capacity, and grip strength were assessed before and after PR, and the results were compared. After PR, the parameters improved, except for the MEP in one patient (patient 3) and the grip strength in another patient (patient 4). After PR, two out of five patients returned to work and the other three returned home. Therefore, we conclude that PR is necessary for patients with acute COVID-19 with activity limitations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Chest Physiotherapy Technique on Bilateral Bronchial Pneumonia Secondary to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Case Report
Urvini R Lokhande, H V Sharath, Vaishnavi M Thakre
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of Chest Physiotherapy Technique on Bilateral Bronchial Pneumonia Secondary to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Case Report
- Three-dimensional printing of temporary crowns with polylactic acid polymer using the fused deposition modeling technique: a case series
- Eun-Kyong Kim, Eun Young Park, Sohee Kang
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):302-307. Published online November 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00612

- 1,559 View
- 86 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - With recent developments in digital dentistry, research on techniques and materials for three-dimensional (3D) printing is actively underway. We report the clinical applications and outcomes of 3D printing of temporary crowns fabricated with polylactic acid (PLA) using a fused deposition modeling (FDM) printer. Five participants were recruited from among patients scheduled to be treated with a single full-coverage crown at a dental clinic in a university medical center from June to August 2022. We used 3D-printed crowns fabricated with PLA using an FDM printer as temporary crowns and were assessed for discomfort, fracture, and dislodging. The 3D-printed temporary crowns were maintained without fracture, dislodging, or discomfort until the permanent prosthesis was ready. The average time required for printing the temporary crowns was approximately 7 minutes. The 3D printing of temporary crowns with PLA using an FDM printer is a convenient process for dentists. However, these crowns have some limitations, such as rough surface texture and translucency; therefore, the 3D printing process should be improved to produce better prostheses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cytotoxicity of dental self-curing resin for a temporary crown: an in vitro study
Jae-wan Ko, Joon Sakong, Sohee Kang
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2023; 40(Suppl): S1. CrossRef - Wear resistance of dental resin crowns in accordance with different additive manufacturing technologies and abrader types during chewing simulations
Myoung Ji Choi, Jae-Sung Kwon
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2023; 50(4): 217. CrossRef
- Cytotoxicity of dental self-curing resin for a temporary crown: an in vitro study
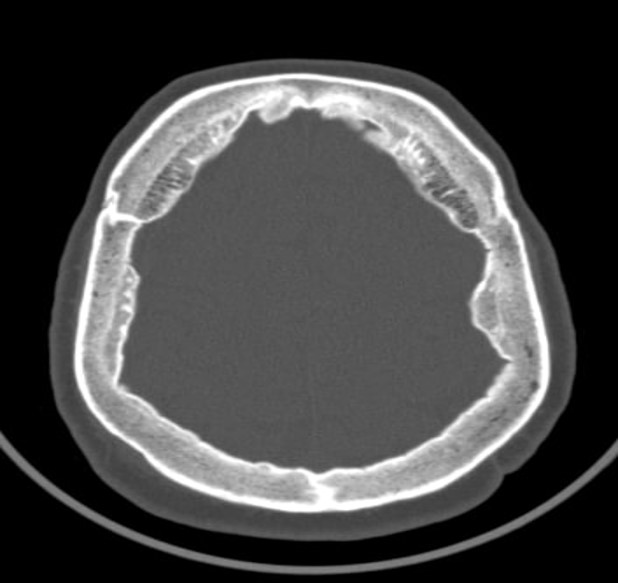
- Morgagni-Stewart-Morel syndrome presenting with neurological symptoms: a case report
- Bünyamin Tosunoğlu, Nazlıcan Ergin, Nilay Kaya, Levent Ertuğrul İnan
- J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(3):308-310. Published online December 1, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2022.00675
- 2,726 View
- 87 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Morgagni-Stewart-Morel (MSM) syndrome is characterized by the thickening of the frontal bone of the skull (hyperostosis frontalis interna) obesity, neurological symptoms, and hypertrichosis. We present the case of a 76-year-old patient who complained of confusion, extreme irritability, and headache and was diagnosed with MSM based on examination, imaging, and test results.

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



