Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse Articles > Previous issues
Review articles
- Implementation of a care coordination system for chronic diseases
- Jung Jeung Lee, Sang Geun Bae
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):1-7. Published online December 20, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00073
- 8,281 View
- 178 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The number of people with chronic diseases has been increasing steadily but the indicators for the management of chronic diseases have not improved significantly. To improve the existing chronic disease management system, a new policy will be introduced, which includes the establishment of care plans for hypertension and diabetes patients by primary care physicians and the provision of care coordination services based on these plans. Care coordination refers to a series of activities to assist patients and their families and it has been known to be effective in reducing medical costs and avoiding the unnecessary use of the hospital system by individuals. To offer well-coordinated and high-quality care services, it is necessary to develop a service quality assurance plan, track and manage patients, provide patient support, agree on patient referral and transition, and develop an effective information system. Local governance should be established for chronic disease management, and long-term plans and continuous quality improvement are necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Personalized, interdisciplinary patient pathway for cross-sector care of multimorbid patients (eliPfad trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Christoph Heinrich Lindemann, Volker Burst, Linus Alexander Völker, Sebastian Brähler, Dusan Simic, Ingrid Becker, Martin Hellmich, Clarissa Kurscheid, Nadine Scholten, Ruben Krauspe, Kerstin Leibel, Stephanie Stock, Paul Thomas Brinkkoetter
Trials.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Implementation of Integrated Primary Care for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension in Belgium, Cambodia, and Slovenia
Nataša Stojnić, Monika Martens, Edwin Wouters, Savina Chham, Josefien van Olmen, Katrien Danhieux, Nina Ružić Gorenjec, Ir Por, Antonija Poplas-Susič, Zalika Klemenc-Ketiš
International Journal of Integrated Care.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in the Quality of Primary Care and Acute Care in Korea From 2008 to 2020: A Cross-sectional Study
Yeong Geun Gwon, Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hoon Kim
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(3): 248. CrossRef
- Personalized, interdisciplinary patient pathway for cross-sector care of multimorbid patients (eliPfad trial): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- Pathological interpretation of connective tissue disease-associated lung diseases
- Kun Young Kwon
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):8-15. Published online January 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00101
- 9,120 View
- 179 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
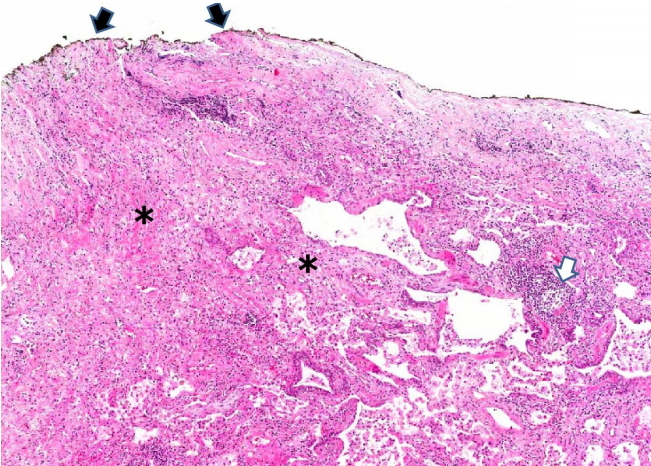
PDF - Connective tissue diseases (CTDs) can affect all compartments of the lungs, including airways, alveoli, interstitium, vessels, and pleura. CTD-associated lung diseases (CTD-LDs) may present as diffuse lung disease or as focal lesions, and there is significant heterogeneity between the individual CTDs in their clinical and pathological manifestations. CTD-LDs may presage the clinical diagnosis a primary CTD, or it may develop in the context of an established CTD diagnosis. CTD-LDs reveal acute, chronic or mixed pattern of lung and pleural manifestations. Histopathological findings of diverse morphological changes can be present in CTD-LDs airway lesions (chronic bronchitis/bronchiolitis, follicular bronchiolitis, etc.), interstitial lung diseases (nonspecific interstitial pneumonia/fibrosis, usual interstitial pneumonia, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia, diffuse alveolar damage, and organizing pneumonia), pleural changes (acute fibrinous or chronic fibrous pleuritis), and vascular changes (vasculitis, capillaritis, pulmonary hemorrhage, etc.). CTD patients can be exposed to various infectious diseases when taking immunosuppressive drugs. Histopathological patterns of CTD-LDs are generally nonspecific, and other diseases that can cause similar lesions in the lungs must be considered before the diagnosis of CTD-LDs. A multidisciplinary team involving pathologists, clinicians, and radiologists can adequately make a proper diagnosis of CTD-LDs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multidisciplinary Approach to the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Focus on the Pathologist’s Key Role
Stefano Lucà, Francesca Pagliuca, Fabio Perrotta, Andrea Ronchi, Domenica Francesca Mariniello, Giovanni Natale, Andrea Bianco, Alfonso Fiorelli, Marina Accardo, Renato Franco
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3618. CrossRef - Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: two case reports and literature review
Haihong Chen, Yukun Kuang, Xinyan Huang, Ziyin Ye, Yangli Liu, Canmao Xie, Ke-Jing Tang
Diagnostic Pathology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Multidisciplinary Approach to the Diagnosis of Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Focus on the Pathologist’s Key Role
Original articles
- Comparison of three different endoscopic approaches in the treatment of bladder calculi
- Jae Youn Jang, Young Hwii Ko, Phil Hyun Song, Jae Young Choi
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):16-19. Published online December 19, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00045

- 5,669 View
- 142 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
This study compared the following three endoscopic techniques used to treat bladder stones: transurethral cystoscope used with a pneumatic lithoclast or nephroscope used with a pneumatic lithoclast and nephroscope used with an ultrasonic lithoclast.
Methods
Between January 2013 and May 2016, 107 patients with bladder stones underwent endoscopic treatment. Patients were classified into 3 groups based on the endoscopic techniques and energy modalities used in each group as: group 1 (transurethral stone removal using a cystoscope with pneumatic lithoclast), group 2 (transurethral stone removal using a nephroscope with pneumatic lithoclast), and group 3 (transurethral stone removal using a nephroscope with ultrasonic lithoclast). Baseline and perioperative data were retrospectively compared between three groups.
Results
No statistically significant intergroup differences were observed in age, sex ratio, and stone size. A statistically significant intergroup difference was observed in the operation time—group 1: 71.3±46.6 min; group 2: 33.0±13.7 min; and group 3: 24.6±8.0 min. All patients showed complete stone clearance. The number of urethral entries was higher in group 1 than in the other groups. Significant complications did not occur in any patient.
Conclusion
Nephroscopy scores over cystoscopy for the removal of bladder stones with respect to operation time. Ultrasonic lithoclast is a safe and efficacious modality that scores over a pneumatic lithoclast with respect to the operation time. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of nephroscopy and cystoscopy used in the treatment of bladder stones: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Liping Gou, Zhenghao Wang, Ye Zhou, Xiaofeng Zheng
BMC Surgery.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of nephroscopy and cystoscopy used in the treatment of bladder stones: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Awareness of occupational hazards and personal protective equipment use among dental hygienists
- Hyun-Ju Choi, Tae-Yoon Hwang, Man-Joong Jeon
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):20-25. Published online December 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00052

- 5,789 View
- 144 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The aim of this study was to evaluate the awareness of occupational hazards and personal protective equipment use among dental hygienists (DHs).
Methods
A total of 271 self-administered questionnaires were obtained from 280 DHs working at dental hospitals or clinics in Daegu and Gyeongsangbuk-do, Korea.
Results
The occupational hazards included work involving dust (94.1%), volatile substances (86.0%), noise (97.0%), and light-curing units (96.7%). The proportion of dental hygiene tasks that participants perceived as harmful were 42.4%, 51.7%, 9.2%, and 31.4% in the same order as above. The proportion of participants who used dust-proof masks during work involving dust was 1.1%. Those who wore gas-proof masks and gloves for work using volatile substances were 0.7% and 31.2%, respectively. Participants who used goggles for work involving light-curing units were 31.0%. None of the participants used ear plugs for work involving noise. A total of 22.9% of the participants recognized the Material Safety Data Sheet, while 79.7% had never been educated about harmful work environments.
Conclusion
When compared to exposure status and perception of occupational hazards, the level of protective equipment use was very low. Extra measures to increase DHs’ use of personal protective equipment are necessary. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comprehensive Profiling through a Cross-sectional Assessment on the Awareness about Eye Protection Safety among Dental Professionals in Saudi Arabia
Mansour M. Al-Mohaimeed
Ophthalmic Epidemiology.2022; 29(5): 515. CrossRef - Relationship Between Job Satisfaction and Health of Hygienists in Lithuania
Gitana Rederiene, Yvonne Buunk-Werkhoven, Greta Aidukaite, Alina Puriene
International Dental Journal.2022; 72(4): 512. CrossRef - One-year impact of COVID-19 pandemic on Italian dental professionals: a cross-sectional survey
Gaetano PAOLONE, Claudia MAZZITELLI, Sara FORMIGA, Francesco KAITSAS, Lorenzo BRESCHI, Annalisa MAZZONI, Giulia TETE, Elisabetta POLIZZI, Enrico GHERLONE, Giuseppe CANTATORE
Minerva Dental and Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Should dentists mandatorily wear ear protection device to prevent occupational noise-induced hearing loss? A randomized case–control study
KishanM Mohan, Aditi Chopra, Vasudeva Guddattu, Shruti Singh, Kumari Upasana
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2022; 12(5): 513. CrossRef - Noise levels encountered in university dental clinics during different specialty treatments
MohammadAbdul Baseer, Abdulrahman Al Saffan, ShahadMousa AlMasoud, WedTalal Dahy, HadeelWaleed Aldali, AlaaM Walid Bachat, RamaM Walid Bachat, OsamahMohammed AlMugeiren
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(8): 2987. CrossRef
- Comprehensive Profiling through a Cross-sectional Assessment on the Awareness about Eye Protection Safety among Dental Professionals in Saudi Arabia
- Telmisartan increases hepatic glucose production via protein kinase C ζ-dependent insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation in HepG2 cells and mouse liver
- Kae Won Cho, Du-Hyong Cho
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):26-35. Published online December 20, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00059

- 8,467 View
- 149 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background
Dysregulation of hepatic glucose production (HGP) contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Telmisartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker (ARB), has various ancillary effects in addition to common blood pressure-lowering effects. The effects and mechanism of telmisartan on HGP have not been fully elucidated and, therefore, we investigated these phenomena in hyperglycemic HepG2 cells and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice.
Methods
Glucose production and glucose uptake were measured in HepG2 cells. Expression levels of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase α (G6Pase-α), and phosphorylation levels of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) and protein kinase C ζ (PKCζ) were assessed by western blot analysis. Animal studies were performed using HFD-fed mice.
Results
Telmisartan dose-dependently increased HGP, and PEPCK expression was minimally increased at a 40 μM concentration without a change in G6Pase-α expression. In contrast, telmisartan increased phosphorylation of IRS-1 at Ser302 (p-IRS-1-Ser302) and decreased p-IRS-1-Tyr632 dose-dependently. Telmisartan dose-dependently increased p-PKCζ-Thr410 which is known to reduce insulin action by inducing IRS-1 serine phosphorylation. Ectopic expression of dominant-negative PKCζ significantly attenuated telmisartan-induced HGP and p-IRS-1-Ser302 and -inhibited p-IRS-1-Tyr632. Among ARBs, including losartan and fimasartan, only telmisartan changed IRS-1 phosphorylation and pretreatment with GW9662, a specific and irreversible peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) antagonist, did not alter this effect. Finally, in the livers from HFD-fed mice, telmisartan increased p-IRS-1-Ser302 and decreased p-IRS-1-Tyr632, which was accompanied by an increase in p-PKCζ-Thr410.
Conclusion
These results suggest that telmisartan increases HGP by inducing p-PKCζ-Thr410 that increases p-IRS-1-Ser302 and decreases p-IRS-1-Tyr632 in a PPARγ-independent manner. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HM-chromanone attenuates TNF-α-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance by controlling JNK activation and NF-κB pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Jea Eun Park, Eunji Kang, Ji Sook Han
European Journal of Pharmacology.2022; 921: 174884. CrossRef - Label-free study of intracellular glycogen level in metformin and resveratrol-treated insulin-resistant HepG2 by live-cell FTIR spectroscopy
Anchisa Poonprasartporn, K.L. Andrew Chan
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2022; 212: 114416. CrossRef - Improved lipogenesis gene expression in liver is associated with elevated plasma angiotensin 1-7 after AT1 receptor blockade in insulin-resistant OLETF rats
Jose A. Godoy-Lugo, Dora A. Mendez, Ruben Rodriguez, Akira Nishiyama, Daisuke Nakano, Jose G. Soñanez-Organis, Rudy M. Ortiz
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2022; 555: 111729. CrossRef
- HM-chromanone attenuates TNF-α-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance by controlling JNK activation and NF-κB pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- Non–coplanar whole brain radiotherapy is an effective modality for parotid sparing
- Jaehyeon Park, Jae Won Park, Ji Woon Yea
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):36-42. Published online January 3, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00087

- 7,092 View
- 132 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and feasibility of non–coplanar whole brain radiotherapy (NC–WBRT) for parotid sparing.
Methods
Fifteen cases, previously treated with WBRT were selected. NC–WBRT plans were generated. The beam arrangement for the non–coplanar plans consisted of superior anterior, right, and left beams. After generation of the non–coplanar plans a field–in–field technique was applied to the bilateral parallel opposed beams in order to reduce maximum dose and increase dose homogeneity. The NC–WBRT plans were subsequently compared with the previously generated bilateral WBRT (B–WBRT) plans. A field–in–field technique was also used with the B–WBRT plans according to our departmental protocol. As per our institutional practice a total dose of 30 Gy in 10 fractions of WBRT was administered 5 days a week.
Results
The mean dose to the parotid gland for the two different plans were 16.2 Gy with B–WBRT and 13.7 Gy with NC–WBRT (p<0.05). In the NC–WBRT plan, the V5Gy, V10Gy, V15Gy, V20Gy, and V25Gy of the parotid were significantly lower (p<0.05) than those of the B–WBRT plan. The Dmax of the lens was also lower by 10% with NC–WBRT.
Conclusion
The use of NC–WBRT plans could be a simple and effective method to reduce irradiated volumes and improve the dose–volume parameters of the parotid gland. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- DiffRecon: Diffusion-based CT reconstruction with cross-modal deformable fusion for DR-guided non-coplanar radiotherapy
Jiawei Sun, Nannan Cao, Hui Bi, Liugang Gao, Kai Xie, Tao Lin, Jianfeng Sui, Xinye Ni
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2024; 179: 108868. CrossRef - Technical note: Feasibility of gating for dynamic trajectory radiotherapy – Mechanical accuracy and dosimetric performance
Hannes A. Loebner, Daniel Frauchiger, Silvan Mueller, Gian Guyer, Paul‐Henry Mackeprang, Marco F. M. Stampanoni, Michael K. Fix, Peter Manser, Jenny Bertholet
Medical Physics.2023; 50(10): 6535. CrossRef - Impact of the gradient in gantry‐table rotation on dynamic trajectory radiotherapy plan quality
Hannes A. Loebner, Silvan Mueller, Werner Volken, Philipp Wallimann, Daniel M. Aebersold, Marco F. M. Stampanoni, Michael K. Fix, Peter Manser
Medical Physics.2023; 50(11): 7104. CrossRef - Retrospective analysis of portal dosimetry pre-treatment quality assurance of intracranial SRS/SRT VMAT treatment plans
Ernest Osei, Sarah Graves, Johnson Darko
Journal of Radiotherapy in Practice.2022; 21(4): 540. CrossRef - Application of piecewise VMAT technique to whole-brain radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost for multiple metastases
Yuan Xu, Yingjie Xu, Kuo Men, Jianping Xiao, Jianrong Dai
Radiation Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Setup uncertainties and appropriate setup margins in the head-tilted supine position of whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT)
Jae Won Park, Ji Woon Yea, Jaehyeon Park, Se An Oh, Ngie Min Ung
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0271077. CrossRef - Examination of the best head tilt angle to reduce the parotid gland dose maintaining a safe level of lens dose in whole‐brain radiotherapy using the four‐field box technique
Hidetoshi Shimizu, Koji Sasaki, Takahiro Aoyama, Hiroyuki Tachibana, Hiroshi Tanaka, Yutaro Koide, Tohru Iwata, Tomoki Kitagawa, Takeshi Kodaira
Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics.2021; 22(2): 49. CrossRef - Noncoplanar Versus Coplanar Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) for Protection of the Lip and Buccal Mucosa
Zheng Lao, Fan Bi, Wenhui Fan, Xuanli Xu, Wenyong Tu, Huifeng Shi
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2021; 20: 153303382110195. CrossRef - Whole brain radiotherapy using four-field box technique with tilting baseplate for parotid gland sparing
Jaehyeon Park, Ji Woon Yea
Radiation Oncology Journal.2019; 37(1): 22. CrossRef
- DiffRecon: Diffusion-based CT reconstruction with cross-modal deformable fusion for DR-guided non-coplanar radiotherapy
- Comparison of the removal torque and a histomorphometric evaluation of the RBM treated implants with the RBM followed by laser treated implants: an experimental study in rabbits
- Eun Young Park, Hae Ok Sohn, Eun-Kyong Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):43-49. Published online January 11, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00094

- 4,971 View
- 92 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
In the osseointegration of dental implants, the implant surface properties have been reported to be some of the most important critical factors. The effect of implant’s surfaces created by resorbable blast media (RBM) followed by laser ablation on bone tissue reactions was examined using the removal torque test and histomorphometric analysis.
Methods
Two types of dental implants, RBM-laser implants (experimental group) and RBM implants (control group) (CSM implant system, Daegu, Korea; L=6 mm, diameter=3.75 mm) were placed into the right and left distal femoral metaphysis of 17 adult rabbits. Six weeks after placement, removal torque was measured and histomorphometric analysis was performed.
Results
The mean removal torque was 24.0±10.2 Ncm and 46.6±16.4 Ncm for the control and test specimens, respectively. The experimental RBM-laser implants had significantly higher removal torque values than the control RBM implants (p=0.013). The mean values of total and cortical bone to implant contact (BIC) were respectively 46.3±10.8% and 65.3±12.5% for the experimental group, and 41.9±18.5% and 57.6±10.6% for the control group. The experimental RBM-laser implants showed a higher degree of total and cortical BIC compared with RBM implants, but there was no statistical significance (p=0.482, 0.225).
Conclusion
The removal torque and BIC of the test group were higher than those of the control group. In this study, the surface treatment created by RBM treatment followed by laser ablation appears to have a potential in improving bone tissue reactions of dental implants. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Determining primary stability for adhesively stabilized dental implants
Ole Zoffmann Andersen, Benjamin Bellón, Maryam Lamkaouchi, Marzia Brunelli, Qiuju Wei, Philip Procter, Benjamin E. Pippenger
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3741. CrossRef
- Determining primary stability for adhesively stabilized dental implants
Case reports
- Awareness during general anesthesia despite simultaneous bispectral index and end-tidal anesthetic gas concentration monitoring
- Jungwon Lee, Chorong Park, Saeyoung Kim
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):50-53. Published online December 14, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00010

- 5,800 View
- 134 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Awareness during general anesthesia occurs in approximately 0.1–0.2% of cases; nevertheless, particular attention is required because it can lead to critical complications including insomnia, depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder. To prevent these complications, bispectral index (BIS) and end-tidal anesthetic gas (ETAG) concentration monitoring are commonly used to examine patient consciousness during surgery. In the present case, an 80-year-old man was scheduled for total gastrectomy. Anesthesia was maintained using desflurane 4.0–5.0% vol, oxygen, and nitrous oxide. The authors simultaneously monitored BIS, which was maintained between 37 and 43, and ETAG, which was maintained between 0.9 and 1.2 minimum alveolar concentration (MAC). After the operation, however, the authors were surprised to learn that the patient complained of awareness during anesthesia. Although BIS and ETAG concentration monitoring are useful in preventing awareness during anesthesia, they cannot be completely trusted. Even though BIS was maintained at approximately 40 and ETAG at 0.7–1.3 MAC, awareness during anesthesia occurred.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Depth of anaesthesia monitoring: updated evidence. Comment on Br J Anaesth 2023; 131: 196–9
Paul S. Myles
British Journal of Anaesthesia.2023; 131(5): e145. CrossRef - Impact of bispectral index monitoring on critical incidents rate in high-risk patients: a randomised controlled trial
N. V. Trembach
Kuban Scientific Medical Bulletin.2022; 29(1): 48. CrossRef - A Crossover Comparison of the Sensitivity and the Specificity between BIS and AEP in Predicting Unconsciousness in General Anesthesia
Haitao Yang, Guan Wang, Jinxia Gao, Jie Liu, Liang Zhao
Scientific Programming.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef
- Depth of anaesthesia monitoring: updated evidence. Comment on Br J Anaesth 2023; 131: 196–9
- Estrogen-secreting adrenocortical carcinoma
- You Jeong, Sung Chul Cho, Hee Joon Cho, Ji Soo Song, Joon Seog Kong, Jong Wook Park, Yun Hyi Ku
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):54-58. Published online December 20, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00017

- 6,282 View
- 94 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare type of endocrine malignancy with an annual incidence of approximately 1–2 cases per million. The majority of these tumors secrete cortisol, and a few secrete aldosterone or androgen. Estrogen-secreting adrenocortical carcinomas are extremely rare, irrespective of the secretion status of other adrenocortical hormones. Here, we report the case of a 53-year-old man with a cortisol and estrogen-secreting adrenocortical carcinoma. The patient presented with gynecomastia and abdominal discomfort. Radiological assessment revealed a tumor measuring 21×15.3×12 cm localized to the retroperitoneum. A hormonal evaluation revealed increased levels of estradiol, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, and cortisol. The patient underwent a right adrenalectomy, and the pathological examination revealed an adrenocortical carcinoma with a Weiss’ score of 6. After surgery, he was treated with adjuvant radiotherapy. Twenty-one months after treatment, the patient remains alive with no evidence of recurrence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gynecomastia in a Man With Adrenal Mass
Jasmine Saini, Patrick Navin, Michael Rivera, Irina Bancos
JCEM Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adrenocortical Carcinoma: Updates of Clinical and Pathological Features after Renewed World Health Organisation Classification and Pathology Staging
Alfred King-yin Lam
Biomedicines.2021; 9(2): 175. CrossRef
- Gynecomastia in a Man With Adrenal Mass
- Isolated tubal torsion in the third trimester of pregnancy managed with simultaneous salpingectomy and cesarean section
- Seong Nam Park
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):59-62. Published online December 14, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00024
- 6,723 View
- 92 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
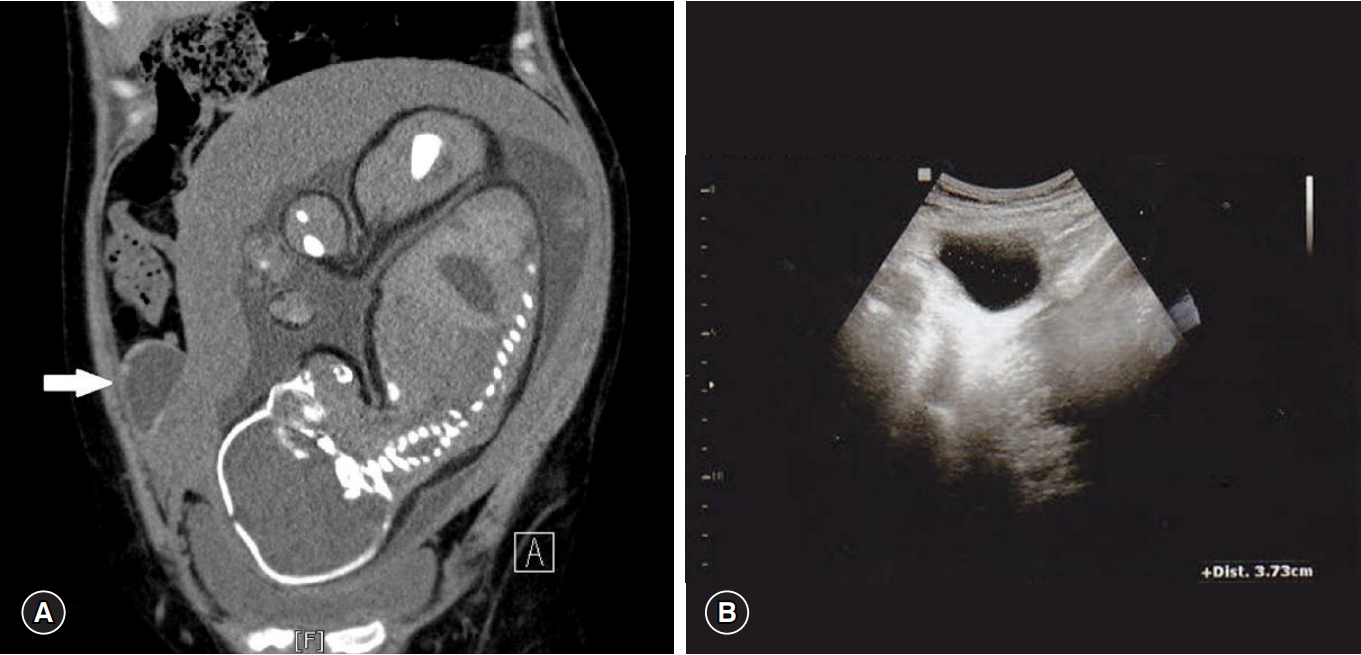
PDF - Isolated tubal torsion is an uncommon cause of acute abdomen in pregnancy. Tubal torsion may occur in the absence of adnexal disease. Diagnosing tubal torsion is especially difficult in pregnancy because no precise preoperative radiological and biochemical investigations have been conducted. Most patients are diagnosed during surgery. Here, we present a case of isolated tubal torsion in a pregnant woman at 35 weeks and 6 days of gestation that was managed with salpingectomy and cesarean section simultaneously.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emergency Surgery for Adnexal Torsion in Late Preterm Pregnancy Causing Term Vaginal Delivery: A Case Report and Literature Review
Kentaro Taniguchi, Yuji Tanaka, Tsukuru Amano, Shunichiro Tsuji, Takashi Murakami
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Adnexal torsion in pregnancy: A systematic review of case reports and case series
Hamidreza Didar, Hanieh Najafiarab, Amirreza Keyvanfar, Bahareh Hajikhani, Elena Ghotbi, Seyyedeh Neda Kazemi
The American Journal of Emergency Medicine.2023; 65: 43. CrossRef - Isolated Tubal Torsion in a Term Pregnancy: Case Report and Systematic Review of Literature of the Last 10 Years
Ferdinando Antonio Gulino, Carla Ettore, Gianfranco Morreale, Stefano Siringo, Emanuele Russo, Marco D'Asta, Francesco Cannone, Giuseppe Ettore
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Laparoscopic surgery for fallopian tube torsion due to benign tumour in the third trimester of pregnancy: a case report and literature review
Jae Yoon Jo, In Ae Cho, Jeong Kyu Shin, Soon Ae Lee, Won Jun Choi
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2022; 42(7): 2566. CrossRef
- Emergency Surgery for Adnexal Torsion in Late Preterm Pregnancy Causing Term Vaginal Delivery: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Superficial malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor from recurrent neurofibroma in the abdominal wall of a patient without neurofibromatosis type 1
- Chang Yeon Jung, Jung Min Bae, Joon Hyuk Choi, Ki Hoon Jung
- Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(1):63-66. Published online December 20, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00031
- 6,772 View
- 101 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
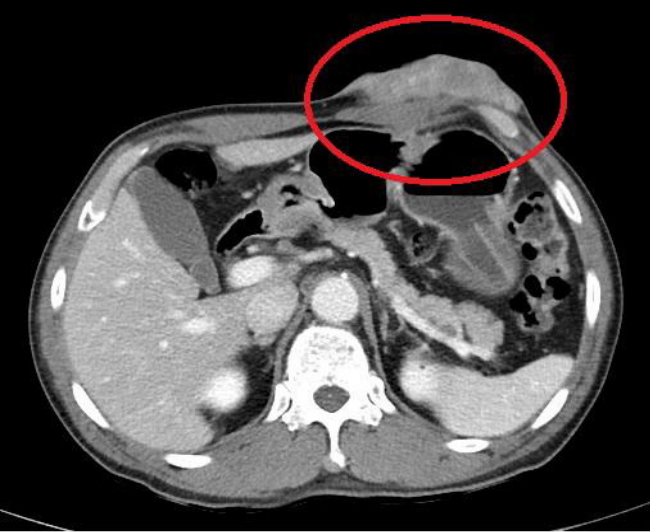
PDF - Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is rare, accounting for 5–10% of all soft tissue sarcomas. MPNST is characteristically aggressive and has a poor prognosis. Fifty percent of patients with MPNST have neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). NF-associated MPNST (NF-MPNST) occurs more often at younger ages than sporadic MPNST (sMPNST), but the survival difference is controversial. Superficial MPNST from a recurrent neurofibroma is extremely rare and only a limited number of cases have been reported in the literature. Herein, we report an unusual case of superficial MPNST from a recurrent neurofibroma in a patient without NF1.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sporadic neurofibroma of transverse colon in a patient without neurofibromatosis type 1: A case report
Toru Imagami, Saburo Sugita, Takaya Nagasaki, Masahiro Kimura, Keisuke Ito, Shingo Inaguma
International Journal of Surgery Case Reports.2020; 71: 19. CrossRef
- Sporadic neurofibroma of transverse colon in a patient without neurofibromatosis type 1: A case report

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine


 First
First Prev
Prev



