Indexed in: ESCI, Scopus, PubMed,
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI
FREE article processing charge

Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Yeungnam Med Sci > Volume 37(1); 2020 > Article
-
Review article
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young: update and perspectives on diagnosis and treatment -
Kyung Mi Jang

-
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine 2020;37(1):13-21.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00409
Published online: January 9, 2020
Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- Corresponding author: Kyung Mi Jang Department of Pediatrics, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, 170 Hyeonchung-ro, Nam-gu, Daegu 42415, Korea Tel: +82-53-620-3532, Fax: +82-53-629-2252 E-mail: fortune001j@gmail.com
• Received: November 1, 2019 • Revised: December 8, 2019 • Accepted: December 16, 2019
Copyright © 2020 Yeungnam University College of Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 13,048 Views
- 359 Download
- 20 Crossref
- Abstract
- Introduction
- MODY2 (GCK-MODY)
- MODY3 (HNF1A-MODY)
- MODY1 (HNF4A-MODY)
- MODY5 (HNF1B-MODY)
- MODY4 (IPF1-MODY)
- MODY6 (NEUROD1-MODY)
- MODY7 (KLF11-MODY)
- MODY8 (CEL-MODY)
- MODY9 (PAX4-MODY)
- MODY10 (INS-MODY)
- MODY11 (BLK-MODY)
- MODY12 (ABCC8-MODY)
- MODY13 (KCNJ11-MODY)
- MODY14 (APPL1-MODY)
- Ways to avoid misdiagnosing patients with MODY
- Conclusion
- Notes
- References
Abstract
- Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a clinically heterogeneous group of monogenic disorders characterized by ß-cell dysfunction. MODY accounts for between 2% and 5% of all diabetes cases, and distinguishing it from type 1 or type 2 diabetes is a diagnostic challenge. Recently, MODY-causing mutations have been identified in 14 different genes. Sanger DNA sequencing is the gold standard for identifying the mutations in MODY-related genes, and may facilitate the diagnosis. Despite the lower frequency among diabetes mellitus cases, a correct genetic diagnosis of MODY is important for optimizing treatment strategies. There is a discrepancy in the disease-causing locus between the Asian and Caucasian patients with MODY. Furthermore, the prevalence of the disease in Asian populations remains to be studied. In this review, the current understanding of MODY is summarized and the Asian studies of MODY are discussed in detail.
- Monogenic diabetes is caused by mutations in one of the genes that control insulin levels [1,2]. Forms of monogenic diabetes include neonatal diabetes, maternally inherited diabetes with deafness and genetic syndromes, such as Bardet-Biedl syndrome, and Wolfram syndrome; however, maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) and neonatal diabetes are the most common. MODY was first described in 1974 by Tattersall [3] as a mild familial diabetes with dominant mode of inheritance. MODY is a clinically heterogeneous group of monogenic diabetes mellitus characterized by ß-cell dysfunction. The diagnostic criteria reported in 2008 include onset before 25 years of age in at least one of the family members, ß-cell dysfunction without autoantibodies, and family history of autosomal dominant diabetes for at least two generations [4]. In the 1990s, molecular methods for the diagnosis of MODY were introduced, after which the mutations associated with the disease were identified. To date, MODY-associated mutations have been reported in 14 different genes (Table 1) [5-10]. MODY is the most common type of monogenic diabetes and comprises between 2% to 5% of all diabetes cases in Europe [11,12]. Among these genes, mutations in HNF1A, GCK, HNF4A, and HNF1B are the underlying cause in more than 95% cases of MODY; the other mutations are rare in the Caucasian population [12-14]. There is a discrepancy in the disease-causing locus between the Caucasian and Asian patients with MODY. Moreover, the exact prevalence of the disease in the Asian population has not been reported. This review summarizes the current understanding of MODY and discusses the Asian studies of the disease.
Introduction
- Glucokinase (GCK) is a major enzyme in glucose metabolism, which catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6 phosphate, and thus, controls glucose-mediated insulin secretion. Until 2009, more than 600 mutations in GCK had been identified in over 1,400 families [15]. The inactivating heterozygous mutations in GCK elevate the glucose threshold for insulin secretion resulting in mild fasting hyperglycemia (5.6–8.0 mmol/L, glycosylated hemoglobin range of 5.6%–7.3%) [16]. Mutations in GCK are some of the most common causes of MODY, and affect 32% of the total number of patients with MODY in the United Kingdom [17]. Patients with GCK-MODY are usually asymptomatic; hence, the majority are diagnosed through routine examination, such as urine glucose screening at school or during pregnancy. Mutations in GCK were found in 40%–50% of incidental hyperglycemia cases in children; therefore, the prevalence of GCK-MODY is high in countries where the school glucose screening test is performed [18,19]. However, only 2.5% of 40 studies of MODY and early onset type 2 diabetes in Korea reported GCK mutations [20]. This implies that there might be a discrepancy between the Caucasian and Asian patients. The clinical manifestations of GCK-MODY may be mild and non-progressive as long-term complications rarely develop despite chronic mild hyperglycemia. Therefore, patients with this mutation usually do not require treatment, except during pregnancy [21].
MODY2 (GCK-MODY)
- Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α (HNF1A) is a transcription factor expressed in various organs, such as the pancreas, kidney, liver, and intestine. HNF1A knockout mice develop diabetes due to impaired glucose-induced insulin secretion [22,23]. Prevalence of this mutation is the highest in Europe, North America, and Asia [17,20,24]. Over 400 different HNF1A mutations have been identified in approximately 1,200 families; among these, a mutation in exon 4 of the gene (P291fsinsC) is the most frequently observed [25,26]. These mutations alter the expression of proteins related to glucose transport, such as glucose transporters, as well as that of key enzymes involved in mitochondrial glucose metabolism. In HNF1A-knockout mice, reduced ß-cell proliferation and increased apoptosis leads to a progressive decline in ß-cell function [27]. HNF1A mutations have high penetrance, with almost 63% of their carriers developing diabetes by the age of 25, and almost 96% by the age of 55 [28]. Since HNF1A is also expressed in tissues other than the pancreas, patients with HNF1A-MODY can display extra-pancreatic manifestations such as glycosuria, which can develop even before the onset of diabetes because of a low renal threshold for glucose [29]. Hyperglycemia induced by heterozygous HNF1A mutations might be deteriorating and progressive, and the risk of developing long-term complications in HNF1A-MODY is similar to that in type 1 and type 2 diabetes [30]. Therefore, rigorous glucose control is needed in these patients.
- Patients with HNF1A-MODY show marked sensitivity to the oral hypoglycemic agent sulfonylurea, which elicits a five-fold greater response than metformin although the two agents show similar efficacy in type 2 diabetes [31]. Consequently, many patients with HNF1A-MODY achieve better glycemic control with sulfonylurea than with insulin treatment [32,33]. Therefore, low-dose sulfonylurea should be considered the first-line treatment for HNF1A-MODY, although some patients might need additional insulin therapy as the diabetes progresses [34].
MODY3 (HNF1A-MODY)
- HNF4A is a transcription factor primarily expressed in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the kidney and pancreas. HNF4A regulates the transcription of genes involved in glucose transport and metabolism [35]. Mutations in the HNF4A gene are uncommon and account for only approximately 3%–5% of all MODY cases; more than 100 HNF4A mutations have been identified in 173 families [25,36]. Patients with heterozygous HNF4A mutations display progressive ß-cell dysfunction similar to that observed in patients with HNF1A mutations. Fetal heterozygous HNF4A mutation results in diazoxide-responsive form of neonatal hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia and subsequent macrosomia [31]. Therefore, close monitoring of the baby of an affected mother is recommended. The hyperinsulinemia usually resolves during infancy and the insulin production gradually decreases leading to the development of diabetes in adolescence [24]. Unlike HNF1A-MODY, HNF4A-MODY is not associated with glycosuria. Instead, low levels of apolipoproteins (apoAII, apoCIII, and apoB) can be a clue to diagnosing this subtype [37]. HNF4A-MODY is characterized by sensitivity to sulfonylureas similar to that of HNF1A-MODY; therefore, low-dose sulfonylurea is recommended as the first-line treatment [31].
MODY1 (HNF4A-MODY)
- HNF1B is a transcription factor associated with early organogenesis of the pancreas, kidney, liver, lungs, gut, and genito-urinary tract [38]. Patients with HNF1B mutations develop abnormalities in all these organs; however, renal manifestations, such as renal cysts, renal dysplasia, renal tract malformations, and familial hypoplastic glomerulocystic kidney disease, are the most common [39,40]. The association of renal cysts and diabetes mellitus with mutations in the HNF1B gene is termed the renal cysts and diabetes syndrome. Renal dysfunction is usually developed by the age of 45, and approximately 50% of the patients progress to end-stage renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy without diabetic renal disease [41]. Therefore, carriers of HNF1B mutations should be monitored for the development of diabetes and non-diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes associated with MODY5 develops in adolescence or early adulthood and presents with hepatic insulin resistance before progressing to insulin-dependent status due to pancreatic hypoplasia. HNF1B mutations can reduce the birth weight by up to 900 g [42,43]. In contrast to patients with MODY3, those with MODY5 progress to insulin-dependent status and do not respond to sulfonylurea; therefore, they usually require early insulin therapy. Patients with HNF1B mutations manifest highly variable phenotypes, which might even differ between family members carrying the same mutation. Hence, patients with HNF1B-MODY should seek endocrinology, as well as nephrology, urology, and gynecology consultation.
MODY5 (HNF1B-MODY)
- Insulin promoter factor 1 (IPF1) is a transcription factor that regulates ß-cell development and insulin expression in pancreatic islets, and has roles similar to those of the HNF family of transcription factors [44,45]. IPF1-MODY was first discovered in 1997 and is a very rare subtype of MODY [46]. Heterozygous mutation in the IPF1 gene causes ß-cell dysfunction and MODY, while homozygous mutation in the IPF1 gene results in neonatal diabetes [47].
MODY4 (IPF1-MODY)
- NEUROD1 encodes neurogenic differentiation 1, a basic helix-loop transcription factor involved in the development of endocrine cell lineage as well as neuronal development. Although heterozygous mutations in NEUROD1 result in MODY, homozygous mutations cause a novel syndrome of permanent neonatal diabetes and neurological abnormalities [48].
MODY6 (NEUROD1-MODY)
- The Krüppel-like factor (KLF) 11 gene is located on chromosome 2 and encodes a zinc-finger transcription factor. Mutations in KLF11 cause ß-cell dysfunction by modulating the expression of free radical scavengers. Two rare variants of KLF11 that impair its transcriptional activity (Ala347Ser and Thr220Met) were identified in families with early-onset type 2 diabetes [49].
MODY7 (KLF11-MODY)
- The CEL gene encodes the bile salt-stimulated lipase, a major component of the pancreatic juice that is secreted by the pancreas into the digestive tract. The enzyme aids in the digestion of cholesterol and lipid-soluble vitamins, ester hydrolysis, and absorption of dietary fat from the intestine. In 2006, a heterozygous mutation in the CEL gene was identified in two families [50]. Exocrine pancreatic dysfunction (defined by fecal elastase deficiency) and ß-cell failure were found in a patient with single-base deletion in CEL. To date, heterozygous mutations in CEL have only been identified in three families [51].
MODY8 (CEL-MODY)
- PAX4 is a homeodomain transcription factor that plays a central role in ß-cell development and function [52]. Two variants of PAX4 (R164W and IVS7-1G>A) were identified in two Thai probands [53].
MODY9 (PAX4-MODY)
- Dominant misfolding mutations in the INS gene are a common cause of isolated permanent neonatal diabetes; however, the age at which the disease develops can vary [54]. These mutations cause a severe folding defect, unfolded protein response, and ß-cell apoptosis.
MODY10 (INS-MODY)
- B-lymphocyte kinase (BLK) is a nonreceptor tyrosine-kinase from the Src family of proto-oncogenes. It is expressed in ß-cells where it promotes insulin synthesis and secretion by up-regulating the transcription factors PDX1 and NKX6.1 [55]. These transcription factors enhance pancreatic ß-cell mass. Decreased BLK activity reduces the insulin content and renders the ß-cells less responsive to glucose, leading to decreased insulin secretion and, eventually, diabetes.
MODY11 (BLK-MODY)
- The ABCC8 gene encodes the sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) subunit of the pancreatic ß-cell ATP-sensitive potassium channel (KATP), which directly regulates insulin release. Recessive loss-of-function mutations in ABCC8 lead to the development of congenital hypoglycemic hyperinsulinism (CHI) [56], while dominantly inherited ABCC8 mutations may cause CHI with predisposition to insulin deficiency and diabetes later in life. Heterozygous activating mutations in ABCC8 cause MODY without a history of diabetes or hyperinsulinism in the neonatal period, and produce clinical manifestations similar to those of HNF1A/4A MODY [57]. Patients with mutations in ABCC8 respond to high-dose sulfonylurea therapy.
MODY12 (ABCC8-MODY)
- KCNJ11 encodes the Kir6.2 subunit of the hetero-octameric KATP channel, which is highly expressed in pancreatic ß-cells. Homozygous or heterozygous mutations in this gene lead to the development of either transient or permanent neonatal diabetes within the first 6 months of life. Heterozygous KCNJ11 mutations were identified in 6 out of 96 families with early-onset type 2 diabetes [58]. Some of these carriers stopped the insulin therapy and switched to sulfonylurea.
MODY13 (KCNJ11-MODY)
- APPL1 (adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain, and leucine zipper containing 1) is the most recently identified MODY-related gene (first reported in 2015). APPL1 is an anchor protein with multiple functional domains that interact with other proteins, including the key components of the insulin-signaling pathway. Two loss-of-function mutations in the APPL1 gene have been identified in 60 families through whole-exome sequencing [9].
MODY14 (APPL1-MODY)
- The diagnostic criteria for MODY are as follows: (1) presence of overt diabetes in at least three consecutive generations, with autosomal dominant mode of inheritance, (2) at least one family member diagnosed with diabetes before the age of 25, (3) absence of ß-cell autoantibodies, and (4) relatively preserved endogenous insulin secretion with a serum C-peptide level of >0.6 ng/mL. These diagnostic criteria can help discriminate MODY from type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Nevertheless, distinguishing MODY from type 1 or type 2 diabetes at presentation is often challenging [24,59,60].
- Various algorithms have been developed to identify diabetic patients who should undergo genetic testing for MODY. Shields et al. [61] proposed a clinical prediction model to distinguish MODY from type 1 and type 2 diabetes. According to the model, patients with MODY have lower HbA1c levels than those with type 1 diabetes. Further, compared to type 1 diabetics, patients with MODY tend to have an older age at diagnosis and higher probability of being female and having a parent with diabetes. Compared to type 2 diabetics, patients with MODY tend to have a lower body mass index, lower HbA1c level, younger age at diagnosis, higher probability of being female and having a parent with diabetes, and lower probability of prior treatment with oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin. Although this model calculates a standardized probability of being diagnosed with MODY, it is important to bear in mind that the clinical manifestations of MODY may vary.
- Sanger DNA sequencing, which is the gold standard for identifying mutations in MODY-related genes, might improve the chances of a correct diagnosis. However, genetic testing for MODY is expensive and may only be offered in specialist centers. Therefore, considerable efforts have been made to identify non-genetic biomarkers to facilitate the differential diagnosis of MODY. Persistent postprandial C-peptide level, which is measured in a spot urine sample, can discriminate HNF1/4A-MODY from type 1 diabetes [62]. Moreover, compared to type 2 diabetics, patients with HNF1A-MODY tend to have a lower level of high-sensitive C-reactive protein [63]. A proposed diagnostic algorithm for the identification of diabetic patients who might benefit from MODY genetic testing is presented in Fig. 1.
Ways to avoid misdiagnosing patients with MODY
- The genetic etiology and pathophysiology of MODY have been widely researched. The biosynthesis and secretion of insulin from pancreatic beta cells are changed at various stages depending on the specific gene mutations (Fig. 2). In a recent study from Korea, 109 patients with clinically suspected MODY underwent targeted panel sequencing. The diagnosis was confirmed in 23 patients (21.1%) [64]. The diagnostic rate was similar to that in a large study on monogenic diabetes performed in the United Kingdom (27%) [14]. In the latter study, molecular genetic testing confirmed a diagnosis of GCK-MODY, i.e. the most common subtype of MODY, in 50% of the patients. This result was in agreement with that of studies in the Caucasian population [65,66]. In contrast, in a China-based study, HNF1A-MODY and GCK-MODY comprised only 9% and 1% of the total tested cases, respectively [67]. These results were similar to those obtained in Japanese studies [68-70]. A possible explanation for these discrepancies is that a large proportion of the MODY cases in China have defects in unknown MODY genes [67]. The studies from Korea, Japan, and China suggest that East Asia has a high prevalence of a not yet identified form of diabetes, i.e., ‘MODY X’ [64,67-72]. Next generation sequencing is one of the most powerful tools to discover unknown genetic defects [71,73], and attempts to identify new causative gene variants in MODY using whole-exome sequencing have been undertaken in Korea [72].
- MODY is estimated to be the cause of 2%–5% of diabetes cases in Europe [11,12]. Owing to the increase in molecular genetic testing, the frequency of its detection has increased worldwide. Correct molecular diagnosis can help to ensure that patients with MODY receive optimal treatment. Metabolic profiling can also be an important diagnostic tool in patients with MODY.
Conclusion
Fig. 1.Clinical algorithm to aid the diagnosis of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. MODY, maturity-onset diabetes of the young; BMI, body mass index.
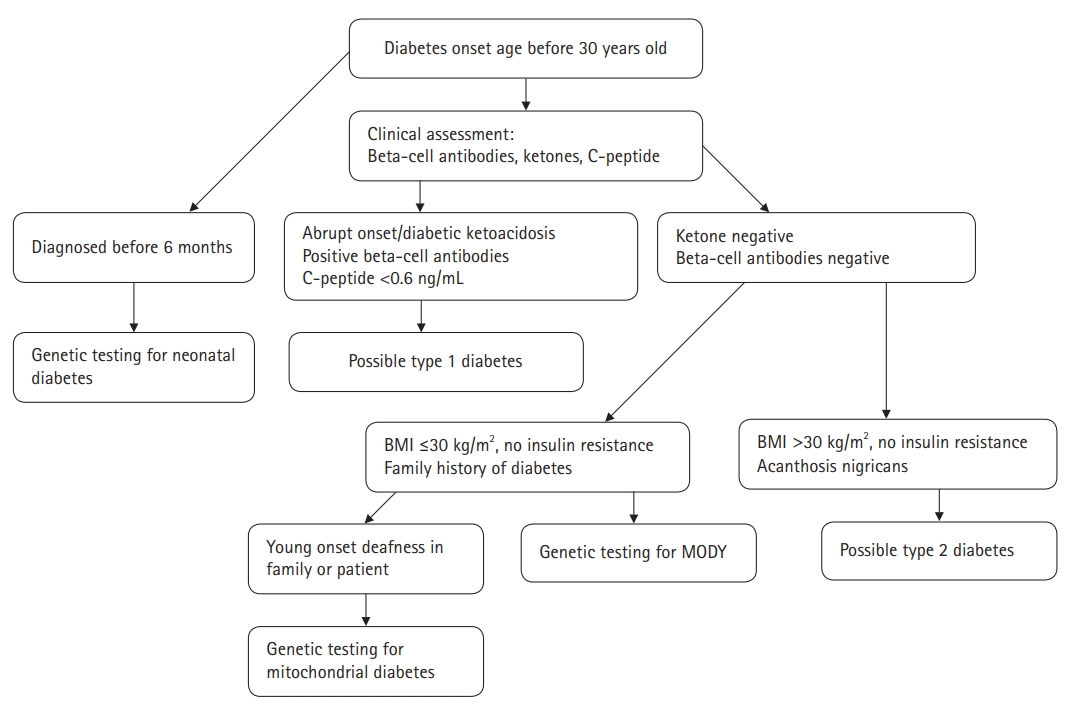

Fig. 2.Schematic representation of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Location of the causative genes and affected proteins in the pancreatic beta cells in maturity-onset diabetes of the young.


Table 1.Genes related to MODY and clinical characteristics of each MODY subtype
- 1. Yang Y, Chan L. Monogenic diabetes: what it teaches us on the common forms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 2016;37:190–222.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Steck AK, Winter WE. Review on monogenic diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2011;18:252–8.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Tattersall RB. Mild familial diabetes with dominant inheritance. Q J Med 1974;43:339–57.PubMed
- 4. Ellard S, Bellanne-Chantelot C, Hattersley AT; European Molecular Genetics Quality Network (EMQN) MODY group. Best practice guidelines for the molecular genetic diagnosis of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Diabetologia 2008;51:546–53.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. Froguel P, Vaxillaire M, Sun F, Velho G, Zouali H, Butel MO, et al. Close linkage of glucokinase locus on chromosome 7p to early-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature 1992;356:162–4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Yamagata K, Furuta H, Oda N, Kaisaki PJ, Menzel S, Cox NJ, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY1). Nature 1996;384:458–60.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Horikawa Y, Iwasaki N, Hara M, Furuta H, Hinokio Y, Cockburn BN, et al. Mutation in hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta gene (TCF2) associated with MODY. Nat Genet 1997;17:384–5.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Kim SH. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young: what do clinicians need to know? Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:468–77.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Prudente S, Jungtrakoon P, Marucci A, Ludovico O, Buranasupkajorn P, Mazza T, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in appl1 in familial diabetes mellitus. Am J Hum Genet 2015;97:177–85.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Urakami T. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): current perspectives on diagnosis and treatment. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2019;12:1047–56.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Henzen C. Monogenic diabetes mellitus due to defects in insulin secretion. Swiss Med Wkly 2012;142:w13690.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Shepherd M, Shields B, Hammersley S, Hudson M, McDonald TJ, Colclough K, et al. Systematic population screening, using biomarkers and genetic testing, identifies 2.5% of the U.K. pediatric diabetes population with monogenic diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016;39:1879–88.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Fajans SS, Bell GI, Polonsky KS. Molecular mechanisms and clinical pathophysiology of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. N Engl J Med 2001;345:971–80.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Shields BM, Hicks S, Shepherd MH, Colclough K, Hattersley AT, Ellard S. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): how many cases are we missing? Diabetologia 2010;53:2504–8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Osbak KK, Colclough K, Saint-Martin C, Beer NL, Bellanne-Chantelot C, Ellard S, et al. Update on mutations in glucokinase (GCK), which cause maturity-onset diabetes of the young, permanent neonatal diabetes, and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Hum Mutat 2009;30:1512–26.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Steele AM, Wensley KJ, Ellard S, Murphy R, Shepherd M, Colclough K, et al. Use of HbA1c in the identification of patients with hyperglycaemia caused by a glucokinase mutation: observational case control studies. PLoS One 2013;8:e65326.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Kavvoura FK, Owen KR. Maturity onset diabetes of the young: clinical characteristics, diagnosis and management. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 2012-2013;10:234–42.PDF
- 18. Estalella I, Rica I, Perez de Nanclares G, Bilbao JR, Vazquez JA, San Pedro JI, et al. Mutations in GCK and HNF-1alpha explain the majority of cases with clinical diagnosis of MODY in Spain. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2007;67:538–46.PubMed
- 19. Codner E, Rocha A, Deng L, Martinez-Aguayo A, Godoy C, Mericq V, et al. Mild fasting hyperglycemia in children: high rate of glucokinase mutations and some risk of developing type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Diabetes 2009;10:382–8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Hwang JS, Shin CH, Yang SW, Jung SY, Huh N. Genetic and clinical characteristics of Korean maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2006;74:75–81.ArticlePubMed
- 21. McDonald TJ, Ellard S. Maturity onset diabetes of the young: identification and diagnosis. Ann Clin Biochem 2013;50:403–15.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Pontoglio M, Sreenan S, Roe M, Pugh W, Ostrega D, Doyen A, et al. Defective insulin secretion in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha-deficient mice. J Clin Invest 1998;101:2215–22.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Boileau P, Wolfrum C, Shih DQ, Yang TA, Wolkoff AW, Stoffel M, et al. Decreased glibenclamide uptake in hepatocytes of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha-deficient mice: a mechanism for hypersensitivity to sulfonylurea therapy in patients with maturity-onset diabetes of the young, type 3 (MODY3). Diabetes 2002;51(Suppl 3):S343–8.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Hattersley AT, Greeley SA, Polak M, Rubio-Cabezas O, Njolstad PR, Mlynarski W, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: the diagnosis and management of monogenic diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes 2018;19(Suppl 27):47–63.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Colclough K, Bellanne-Chantelot C, Saint-Martin C, Flanagan SE, Ellard S. Mutations in the genes encoding the transcription factors hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha and 4 alpha in maturity-onset diabetes of the young and hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Hum Mutat 2013;34:669–85.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Ellard S, Colclough K. Mutations in the genes encoding the transcription factors hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (HNF1A) and 4 alpha (HNF4A) in maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Hum Mutat 2006;27:854–69.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Yamagata K, Nammo T, Moriwaki M, Ihara A, Iizuka K, Yang Q, et al. Overexpression of dominant-negative mutant hepatocyte nuclear fctor-1 alpha in pancreatic beta-cells causes abnormal islet architecture with decreased expression of E-cadherin, reduced beta-cell proliferation, and diabetes. Diabetes 2002;51:114–23.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Shepherd M, Ellis I, Ahmad AM, Todd PJ, Bowen-Jones D, Mannion G, et al. Predictive genetic testing in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY). Diabet Med 2001;18:417–21.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Pontoglio M, Prie D, Cheret C, Doyen A, Leroy C, Froguel P, et al. HNF1alpha controls renal glucose reabsorption in mouse and man. EMBO Rep 2000;1:359–65.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Steele AM, Shields BM, Shepherd M, Ellard S, Hattersley AT, Pearson ER. Increased all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in monogenic diabetes as a result of mutations in the HNF1A gene. Diabet Med 2010;27:157–61.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Pearson ER, Pruhova S, Tack CJ, Johansen A, Castleden HA, Lumb PJ, et al. Molecular genetics and phenotypic characteristics of MODY caused by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha mutations in a large European collection. Diabetologia 2005;48:878–85.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Pearson ER, Liddell WG, Shepherd M, Corrall RJ, Hattersley AT. Sensitivity to sulphonylureas in patients with hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene mutations: evidence for pharmacogenetics in diabetes. Diabet Med 2000;17:543–5.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Shepherd M, Pearson ER, Houghton J, Salt G, Ellard S, Hattersley AT. No deterioration in glycemic control in HNF-1alpha maturity-onset diabetes of the young following transfer from long-term insulin to sulphonylureas. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3191–2.Article
- 34. Shepherd M, Shields B, Ellard S, Rubio-Cabezas O, Hattersley AT. A genetic diagnosis of HNF1A diabetes alters treatment and improves glycaemic control in the majority of insulin-treated patients. Diabet Med 2009;26:437–41.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Stoffel M, Duncan SA. The maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY1) transcription factor HNF4alpha regulates expression of genes required for glucose transport and metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997;94:13209–14.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Frayling TM, Evans JC, Bulman MP, Pearson E, Allen L, Owen K, et al. beta-cell genes and diabetes: molecular and clinical characterization of mutations in transcription factors. Diabetes 2001;50(Suppl 1):S94–100.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Lehto M, Bitzen PO, Isomaa B, Wipemo C, Wessman Y, Forsblom C, et al. Mutation in the HNF-4alpha gene affects insulin secretion and triglyceride metabolism. Diabetes 1999;48:423–5.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Barbacci E, Reber M, Ott MO, Breillat C, Huetz F, Cereghini S. Variant hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 is required for visceral endoderm specification. Development 1999;126:4795–805.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 39. Bingham C, Ellard S, Allen L, Bulman M, Shepherd M, Frayling T, et al. Abnormal nephron development associated with a frameshift mutation in the transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta. Kidney Int 2000;57:898–907.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Edghill EL, Oram RA, Owens M, Stals KL, Harries LW, Hattersley AT, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta gene deletions: a common cause of renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2008;23:627–35.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Bingham C, Bulman MP, Ellard S, Allen LI, Lipkin GW, Hoff WG, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta gene are associated with familial hypoplastic glomerulocystic kidney disease. Am J Hum Genet 2001;68:219–24.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Bellanne-Chantelot C, Chauveau D, Gautier JF, Dubois-Laforgue D, Clauin S, Beaufils S, et al. Clinical spectrum associated with hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta mutations. Ann Intern Med 2004;140:510–7.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Edghill EL, Bingham C, Slingerland AS, Minton JA, Noordam C, Ellard S, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 beta mutations cause neonatal diabetes and intrauterine growth retardation: support for a critical role of HNF-1beta in human pancreatic development. Diabet Med 2006;23:1301–6.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Cerf ME. Transcription factors regulating beta-cell function. Eur J Endocrinol 2006;155:671–9.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Gragnoli C, Stanojevic V, Gorini A, von Preussenthal GM, Thomas MK, Habener JF. IPF-1/MODY4 gene missense mutation in an Italian family with type 2 and gestational diabetes. Metabolism 2005;54:983–8.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Stoffers DA, Zinkin NT, Stanojevic V, Clarke WL, Habener JF. Pancreatic agenesis attributable to a single nucleotide deletion in the human IPF1 gene coding sequence. Nat Genet 1997;15:106–10.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 47. Nicolino M, Claiborn KC, Senee V, Boland A, Stoffers DA, Julier C. A novel hypomorphic PDX1 mutation responsible for permanent neonatal diabetes with subclinical exocrine deficiency. Diabetes 2010;59:733–40.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Rubio-Cabezas O, Minton JA, Kantor I, Williams D, Ellard S, Hattersley AT. Homozygous mutations in NEUROD1 are responsible for a novel syndrome of permanent neonatal diabetes and neurological abnormalities. Diabetes 2010;59:2326–31.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Neve B, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Ashkenazi-Katalan V, Dina C, Hamid YH, Joly E, et al. Role of transcription factor KLF11 and its diabetes-associated gene variants in pancreatic beta cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:4807–12.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 50. Raeder H, Johansson S, Holm PI, Haldorsen IS, Mas E, Sbarra V, et al. Mutations in the CEL VNTR cause a syndrome of diabetes and pancreatic exocrine dysfunction. Nat Genet 2006;38:54–62.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 51. Torsvik J, Johansson S, Johansen A, Ek J, Minton J, Raeder H, et al. Mutations in the VNTR of the carboxyl-ester lipase gene (CEL) are a rare cause of monogenic diabetes. Hum Genet 2010;127:55–64.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 52. Jonsson J, Carlsson L, Edlund T, Edlund H. Insulin-promoter-factor 1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature 1994;371:606–9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 53. Plengvidhya N, Kooptiwut S, Songtawee N, Doi A, Furuta H, Nishi M, et al. PAX4 mutations in Thais with maturity onset diabetes of the young. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:2821–6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 54. Edghill EL, Flanagan SE, Patch AM, Boustred C, Parrish A, Shields B, et al. Insulin mutation screening in 1,044 patients with diabetes: mutations in the INS gene are a common cause of neonatal diabetes but a rare cause of diabetes diagnosed in childhood or adulthood. Diabetes 2008;57:1034–42.ArticlePubMed
- 55. Borowiec M, Liew CW, Thompson R, Boonyasrisawat W, Hu J, Mlynarski WM, et al. Mutations at the BLK locus linked to maturity onset diabetes of the young and beta-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:14460–5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 56. Kapoor RR, Flanagan SE, James C, Shield J, Ellard S, Hussain K. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. Arch Dis Child 2009;94:450–7.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Bowman P, Flanagan SE, Edghill EL, Damhuis A, Shepherd MH, Paisey R, et al. Heterozygous ABCC8 mutations are a cause of MODY. Diabetologia 2012;55:123–7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 58. Liu L, Nagashima K, Yasuda T, Liu Y, Hu HR, He G, et al. Mutations in KCNJ11 are associated with the development of autosomal dominant, early-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2013;56:2609–18.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 59. Thanabalasingham G, Pal A, Selwood MP, Dudley C, Fisher K, Bingley PJ, et al. Systematic assessment of etiology in adults with a clinical diagnosis of young-onset type 2 diabetes is a successful strategy for identifying maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Diabetes Care 2012;35:1206–12.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Vaxillaire M, Froguel P. Monogenic diabetes in the young, pharmacogenetics and relevance to multifactorial forms of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 2008;29:254–64.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 61. Shields BM, McDonald TJ, Ellard S, Campbell MJ, Hyde C, Hattersley AT. The development and validation of a clinical prediction model to determine the probability of MODY in patients with young-onset diabetes. Diabetologia 2012;55:1265–72.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 62. Besser RE, Shepherd MH, McDonald TJ, Shields BM, Knight BA, Ellard S, et al. Urinary C-peptide creatinine ratio is a practical outpatient tool for identifying hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-{alpha}/hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-{alpha} maturity-onset diabetes of the young from long-duration type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011;34:286–91.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Reiner AP, Barber MJ, Guan Y, Ridker PM, Lange LA, Chasman DI, et al. Polymorphisms of the HNF1A gene encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha are associated with C-reactive protein. Am J Hum Genet 2008;82:1193–201.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Park SS, Jang SS, Ahn CH, Kim JH, Jung HS, Cho YM, et al. Identifying pathogenic variants of monogenic diabetes using targeted panel sequencing in an east Asian population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019;jc.2018-02397.ArticlePDF
- 65. Hattersley AT, Patel KA. Precision diabetes: learning from monogenic diabetes. Diabetologia 2017;60:769–77.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 66. Bansal V, Gassenhuber J, Phillips T, Oliveira G, Harbaugh R, Villarasa N, et al. Spectrum of mutations in monogenic diabetes genes identified from high-throughput DNA sequencing of 6888 individuals. BMC Med 2017;15:213.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 67. Xu JY, Dan QH, Chan V, Wat NM, Tam S, Tiu SC, et al. Genetic and clinical characteristics of maturity-onset diabetes of the young in Chinese patients. Eur J Hum Genet 2005;13:422–7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 68. Iwasaki N, Oda N, Ogata M, Hara M, Hinokio Y, Oda Y, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha/MODY3 gene in Japanese subjects with early- and late-onset NIDDM. Diabetes 1997;46:1504–8.ArticlePubMed
- 69. Nishigori H, Yamada S, Kohama T, Utsugi T, Shimizu H, Takeuchi T, et al. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha gene (MODY3) are not a major cause of early-onset non-insulin-dependent (type 2) diabetes mellitus in Japanese. J Hum Genet 1998;43:107–10.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 70. Tonooka N, Tomura H, Takahashi Y, Onigata K, Kikuchi N, Horikawa Y, et al. High frequency of mutations in the HNF-1alpha gene in non-obese patients with diabetes of youth in Japanese and identification of a case of digenic inheritance. Diabetologia 2002;45:1709–12.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 71. Tanaka D, Nagashima K, Sasaki M, Funakoshi S, Kondo Y, Yasuda K, et al. Exome sequencing identifies a new candidate mutation for susceptibility to diabetes in a family with highly aggregated type 2 diabetes. Mol Genet Metab 2013;109:112–7.ArticlePubMed
- 72. Shim YJ, Kim JE, Hwang SK, Choi BS, Choi BH, Cho EM, et al. Identification of candidate gene variants in Korean MODY families by whole-exome sequencing. Horm Res Paediatr 2015;83:242–51.ArticlePubMed
- 73. Johansson S, Irgens H, Chudasama KK, Molnes J, Aerts J, Roque FS, et al. Exome sequencing and genetic testing for MODY. PLoS One 2012;7:e38050.ArticlePubMedPMC
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 7 (MODY7) and mutation in the Krüppel-like transcription factor 11 (KLF11) gene
Y Wang, X Ye, X Chen, H Zang, Q Shen, L Chen
QJM: An International Journal of Medicine.2024; 117(3): 219. CrossRef - Novel gene mutation in maturity-onset diabetes of the young: A case report
Na Zhang, Hui Zhao, Cui Li, Feng-Zhi Zhang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(5): 1099. CrossRef - Cardio-cerebrovascular Outcomes in MODY, Type 1 Diabetes, and Type 2 Diabetes: A Prospective Cohort Study
Hui-Xuan Wu, Tian-Yao Chu, Junaid Iqbal, Hong-Li Jiang, Long Li, Yan-Xuan Wu, Hou-De Zhou
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(11): 2970. CrossRef - Genetic and Clinical Characterization of Patients with HNF1B-Related MODY in Croatia
Maja Baretić, Domagoj Caban, Jadranka Sertić
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(7): 1063. CrossRef - Quantitative profiling and diagnostic potential of one-carbon and central metabolism pools in MODY2 and T1DM
Jieying Liu, Ziyan Xie, Junling Fu, Miao Yu, Tong Wang, Cuijuan Qi, Peng Liu, Xiangyi Hui, Dongmei Wang, Lu Ding, Qian Zhang, Ting Xie, Xinhua Xiao
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - When do we need to suspect maturity onset diabetes of the young in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Özlem Üstay, Tugçe Apaydın, Onur Elbasan, Hamza Polat, Gizem Günhan, Ceyda Dinçer, Lamia Şeker, Esra Arslan Ateş, Ayşegül Yabacı, Ahmet lter Güney, Dilek Gogas Yavuz
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Meta-analysis of HNF1A-MODY3 variants among human population
Rachna Behl, Nishtha Malhotra, Vinay Joshi, Shruti Poojary, Sanniya Middha, Shalini Gupta, Arinola B. Olaonipekun, Ikechukwu Okoye, Bhushan Wagh, Dibyendu Biswas, Chukwuemelie Aginah, Bhavya Saini, Chinaza Nwanya, Sopuluchukwu Ugwu, Modupe M. Anthony, Xua
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(1): 1037. CrossRef - Unusual manifestations of young woman with MODY5 based on 17q12 recurrent deletion syndrome
Ying Cheng, Da-Peng Zhong, Li Ren, Hang Yang, Chen-Fu Tian
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Monogenic Forms of Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Mody-Diabetes
K. A. Aitbaev, I. T. Murkamilov, Zh. A. Murkamilova, V. V. Fomin, I. O Kudaibergenova, F. A. Yusupov
The Russian Archives of Internal Medicine.2022; 12(6): 430. CrossRef - Monogenic diabetes: recent updates on diagnosis and precision treatment: A narrative review
Kyung Mi Jang
Precision and Future Medicine.2022; 6(4): 209. CrossRef - Modeling Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young in Pluripotent Stem Cells: Challenges and Achievements
Carmel Braverman-Gross, Nissim Benvenisty
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Gençlerin Erişkin Başlangıçlı Diyabeti (MODY) Sorumlu HNF4A, GCK ve HNF1 Gen Varyasyonlarının Dünya Genelinde Coğrafik Dağılımı
Deniz KANCA DEMİRCİ, Nurdan GÜL, İlhan SATMAN, Oguz OZTURK, Hülya YILMAZ AYDOĞAN
Haliç Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Dergisi.2021; 4(1): 41. CrossRef - ABCC8 variants in MODY12: Review of the literature and report of a case with severe complications
Marijke Timmers, Eveline Dirinck, Patrick Lauwers, Wim Wuyts, Christophe De Block
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Monogenic Childhood Diabetes: Dissecting Clinical Heterogeneity by Next-Generation Sequencing in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young
Deniz Kanca Demirci, Feyza Darendeliler, Sukran Poyrazoglu, Asli Derya Kardelen Al, Nurdan Gul, Yildiz Tutuncu, Gizem Gulfidan, Kazim Yalcin Arga, Canan Cacina, Oguz Ozturk, Hulya Yilmaz Aydogan, Ilhan Satman
OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology.2021; 25(7): 431. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Hungarian MODY Patients—Part II: Glucokinase MODY Is the Most Prevalent Subtype Responsible for about 70% of Confirmed Cases
Zsolt Gaál, Zsuzsanna Szűcs, Irén Kántor, Andrea Luczay, Péter Tóth-Heyn, Orsolya Benn, Enikő Felszeghy, Zsuzsanna Karádi, László Madar, István Balogh
Life.2021; 11(8): 771. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Hungarian MODY Patients—Part I: Gene Panel Sequencing Reveals Pathogenic Mutations in HNF1A, HNF1B, HNF4A, ABCC8 and INS Genes
Zsolt Gaál, Zsuzsanna Szűcs, Irén Kántor, Andrea Luczay, Péter Tóth-Heyn, Orsolya Benn, Enikő Felszeghy, Zsuzsanna Karádi, László Madar, István Balogh
Life.2021; 11(8): 755. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of MODY: An Updated Mini Review
Abegail Tshivhase, Tandi Matsha, Shanel Raghubeer
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(20): 9436. CrossRef - Functional Genomics in Pancreatic β Cells: Recent Advances in Gene Deletion and Genome Editing Technologies for Diabetes Research
Ming Hu, Ines Cherkaoui, Shivani Misra, Guy A. Rutter
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on Monogenic Diabetes in Korea
Ye Seul Yang, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 627. CrossRef - The epidemiology, molecular pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY)
Ken Munene Nkonge, Dennis Karani Nkonge, Teresa Njeri Nkonge
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite



