PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI

Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Yeungnam Med Sci > Volume 37(1); 2020 > Article
-
Review article
Drug-induced liver injury -
Jeong Ill Suh

-
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine 2020;37(1):2-12.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00297
Published online: August 27, 2019
Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dongguk Unversity, Gyeongju, Korea
- Corresponding author: Jeong Ill Suh, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dongguk University, 87 Dongdae-ro, Gyeongju 38067, Korea Tel: +82-54-770-8207, Fax: +82-54-770-8378, E-mail: sujungil@dongguk.ac.kr
Copyright © 2020 Yeungnam University College of Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 14,417 Views
- 360 Download
- 17 Crossref
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Guidelines for drug-induced liver injury
- Online information resource on drug-induced liver injury
- Definition of drug-induced liver injury and categorization according to R-ratio
- Spectrum of drug-induced liver injury
- Incidence of drug-induced liver injury
- Diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury
- Mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury
- Individual differences in drug-induced liver injury
- Drug-induced liver injury in patients with pre-existing liver disease
- Predictive model of progression to acute liver failure
- Herbal and dietary supplement hepatotoxicity
- Treatment of drug-induced liver injury
- Drug-induced liver injury and the fourth industrial revolution
- Conclusion
- Notes
- References
Abstract
- Drug-induced liver injury (DILI), including herbal and dietary supplement hepatotoxicity, is often passed lightly; however, it can lead to the requirement of a liver transplant or may even cause death because of liver failure. Recently, the American College of Gastroenterology, Chinese Society of Hepatology and European Association for the Study of the Liver guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of DILI have been established, and they will be helpful for guiding clinical treatment decisions. Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method scoring is the most commonly used method to diagnose DILI; however, it has some limitations, such as poor validity and reproducibility. Recently, studies on new biomarkers have been actively carried out, which will help diagnose DILI and predict the prognosis of DILI. It is expected that the development of new therapies such as autophagy inducers and various other technologies of the fourth industrial revolution will be applicable to DILI research.
- In a narrow sense, drug-induced liver injury (DILI) deals with liver injury caused only by drugs. Herb-induced liver injury can be described as hepatotoxicity caused by herbal medicines other than drugs, but it is named herbal and dietary supplement (HDS) hepatotoxicity as a comprehensive concept that includes herbal medicine, health food, and folk remedies. In general, DILI is a liver injury caused by over-the-counter drugs, herbal medicines, health foods, folk remedies, and environmental hormones, as well as by a wide range of prescription drugs including HDS.
- Although DILI is a concern in several clinical fields, it is often overlooked. DILI can progress into a chronic liver injury that lasts more than six months and can reach hepatic failure, which requires liver transplantation, or death [1-4].
- Further, DILI not only hurts the health of the patient, but also has very serious personal, social, and national problems, including the financial burden of payment for treatment, loss of insurance finances, distrust of prescription doctors, medical disputes surrounding compensation issues, and the withdrawal of drugs developed by investing enormous amounts of time and money from the market [5,6].
- Therefore, basic knowledge and recent research trends about DILI are introduced.
Introduction
- In 2014, the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) first established the ACG guideline, a diagnostic and treatment guideline for the idiosyncratic DILI [7]. It presents an evidence-based approach for the diagnosis and management of DILI with special emphasis on DILI caused by HDS and DILI occurring in individuals with underlying liver disease. In 2017, the Chinese Society of Hepatology (CSH) established the CSH guideline, a diagnosis and treatment guideline for DILI that covers 16 evidence-based recommendations on diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of DILI [8]. Recently, the 2019 European Association for the Study of the Liver guideline presenting the available evidence on risk factors, diagnosis, management, and risk minimization strategies for DILI was also established [9].
Guidelines for drug-induced liver injury
- The liver disease research branch of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney disease, in collaboration with the National Library of Medicine and Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN), has developed an online resource for information on DILI resulting from prescription and over-the-counter drugs as well as from complementary and alternative medicines such as HDS. The web-based resource called “LiverTox,” provides up-to-date, accurate, and easy-to-access information about the diagnosis, cause, prevalence, pattern, and management of DILI (http://livertox.nih.gov). China also provides a web-based resource called “Hepatox” on DILI (http://hepatox.org); however, it is not very helpful as it is only in Mandarin.
Online information resource on drug-induced liver injury
- DILI is defined as a liver injury caused by various drugs, herbs, or other xenobiotics leading to abnormalities in liver function. Terms such as hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and liver necrosis should be used only to support liver biopsy findings; the term liver injury should be used if biochemical abnormalities are present and a liver biopsy has not been conducted. Clinical chemistry criteria for DILI is defined as elevation of the alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or the aspartate aminotransferase (AST) >5×upper limit of normal (ULN) without symptoms, or rise of alkaline phosphate (ALP) >2×ULN or rise of bilirubin >2×ULN with any rise of AST and ALT, or rise of AST or ALT <5 ULN with symptoms [10,11].
- If liver injury recovers within 6 months, it is called acute liver injury (ALI), and if it persists for more than 6 months, it is said to be a chronic liver injury. ALI accounts for most cases of DILI and it is divided into hepatocellular, cholestatic, and mixed types based on the R-ratio. The R-ratio is calculated by dividing ALT by ALP, using multiples of ULN for both values. R-ratios of >5 define hepatocellular; <2, cholestatic; and between 2 and 5, a mixed pattern of enzymes [12].
Definition of drug-induced liver injury and categorization according to R-ratio
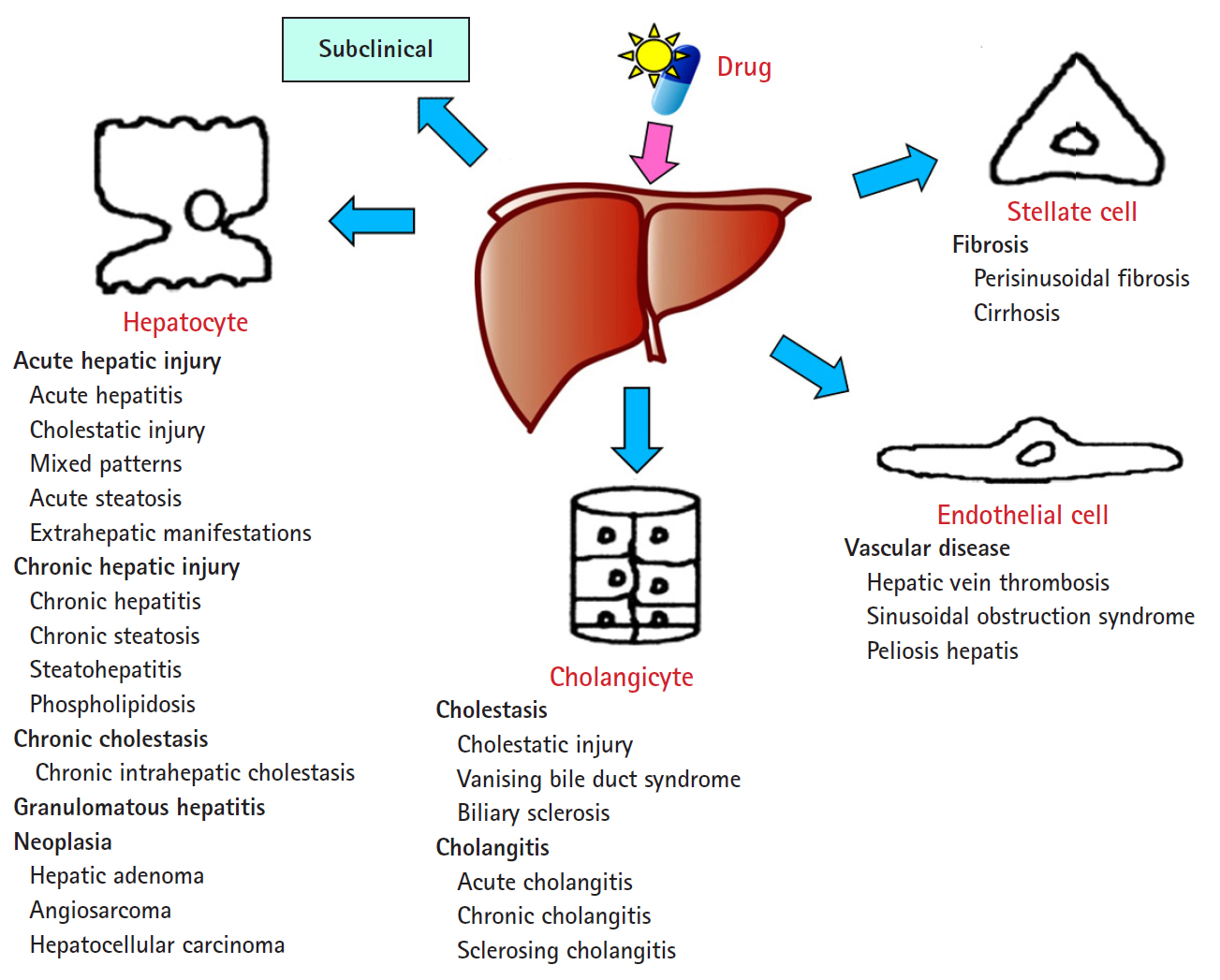
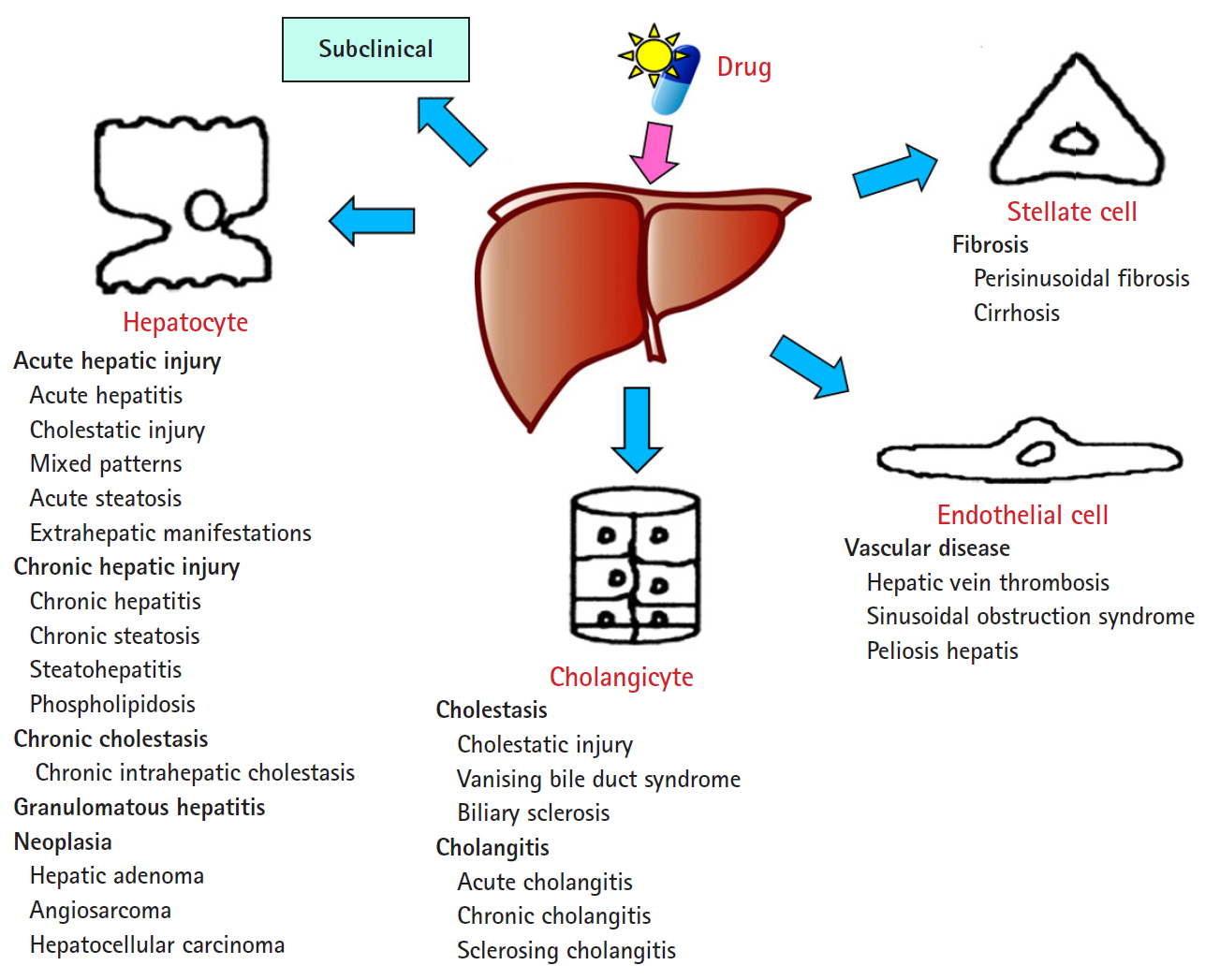
- The DILI spectrum is variable and broad; in most cases, hepatocytes are damaged, but cholangiocytes, stellate cells, and sinusoidal endothelial cells can also be damaged, and several other types of cells can also be damaged simultaneously. DILI can manifest itself as almost any kind of liver disease, from acute hepatitis to chronic hepatitis, fatty liver or steatohepatitis, vascular damage, liver cirrhosis, and even hepatic tumors (Fig. 1) [13,14].
Spectrum of drug-induced liver injury
- It is reported that the annual incidence of DILI is between 10 and 15 per 10,000 to 100,000 persons [15,16]. However, the actual incidence is estimated to be higher because diagnosis is not easy, and it is often disregarded unintentionally and is therefore not reported in the literature. A prospective study on DILI conducted in Korea estimated that 12 out of every 100,000 persons are admitted to university hospitals per year (data for 2005–2007) [17].
Incidence of drug-induced liver injury
- 1. History taking
- The most important factor for the diagnosis of DILI is careful history taking because DILI is a diagnosis of exclusion. The history of drug administration and the onset and progression of liver biochemical abnormalities must be accurate.
- 2. Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method
- The Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) is a diagnostic tool that makes a probabilistic decision using a scorecard divided into 7 categories. The total scores ranges from less than 0 to 14, and the final score is interpreted as follows: highly probable (>8), probable (6–8), possible (3–5), unlikely (1–2), or excluded (<0) (Table 1) [18]. Currently, scores are conveniently calculated using the website (http://www.pmidcalc.org/?sid=8229110&newtest=Y). Further, RUCAM can be easily used in clinical fields; however, in the case of liver transplantation for hepatic failure and HDS hepatotoxicity caused by Chinese medicine, health food, and folk remedies, the RUCAM scores may be low. In addition, the reproducibility of scoring is low [19].
- 3. Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network expert opinion
- DILIN is a network of US experts who have been conducting DILI-related research since 2004 [20]. The probability of DILI is divided into 5 categories: definite (95% or more), high likely (75%–95%), probable (50%–74%), possibly (25%–49%), and unlikely (25% or less) (Table 2) [21]. Three DILIN experts take a decision based on data recorded for more than 6 months. There is a limitation where only DILIN experts can make decisions; however, there is a high reproducibility advantage over the RUCAM scoring.
- 4. Liver biopsy
- Although there are no characteristic pathological indicators for DILI, sometimes characteristic pathological findings based on the drug may appear, and this can help identify other liver diseases and the severity of liver injury. According to the ACG guideline, a liver biopsy should be considered if autoimmune hepatitis remains a competing etiology and if immunosuppressive therapy is contemplated. Moreover, a liver biopsy may be considered if the liver biochemistries continues to increase or the liver function deteriorates despite the interruption of a suspected drug; if the peak ALT level has not dropped by >50% at 30–60 days after onset in cases of hepatocellular DILI; if the peak ALP level has not dropped by >50% at 180 days in the cases of cholestatic DILI despite stopping the suspected offending agent; in cases of DILI where continued use or re-exposure to the implicated agent is expected; or if liver biochemistry abnormalities persist beyond 180 days in the evaluation for the presence of chronic liver diseases and chronic DILI [7].
- 5. Biomarkers
- Recently, there has been a growing interest in finding biomarkers that predict the occurrence of DILI, accurately diagnose it, and predict a poor prognosis. Biomarker candidates such as glutamate dehydrogenase, high-mobility group box 1, and keratin-18 have been found [22], and DILI studies using micro-ribonucleic acid, high throughput proteomics, genomics, and metabolomics have been attempted [23,24].
Diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury
- Traditionally, DILI has been reported to be caused by intrinsic and idiosyncratic reactions, and sometimes, both may occur together. Intrinsic liver injury is dose dependent and predictable. On the other hand, idiosyncratic liver injury is divided into immunoallergic and metabolic idiosyncratic reactions regardless of dose, and it is unpredictable.
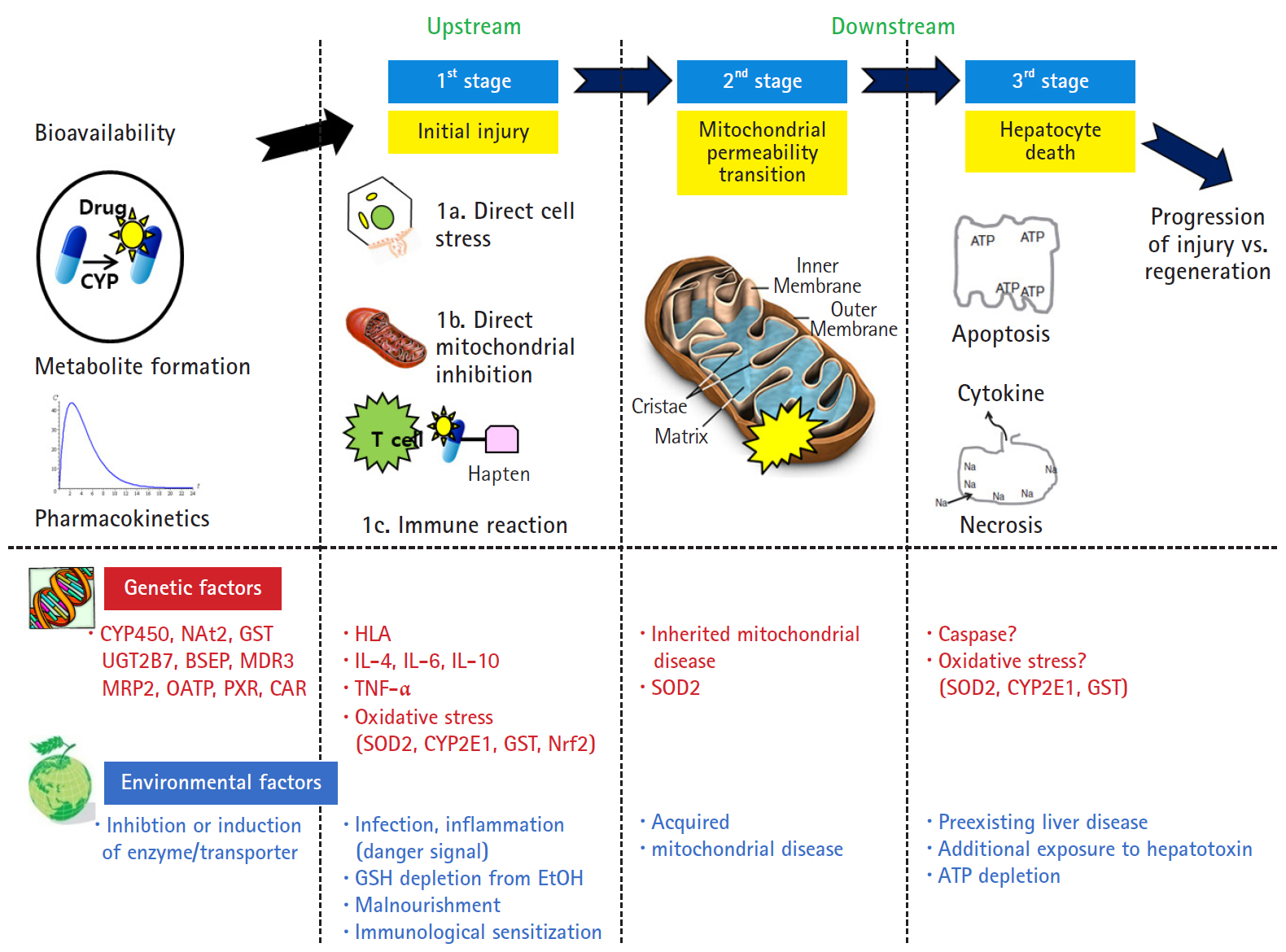
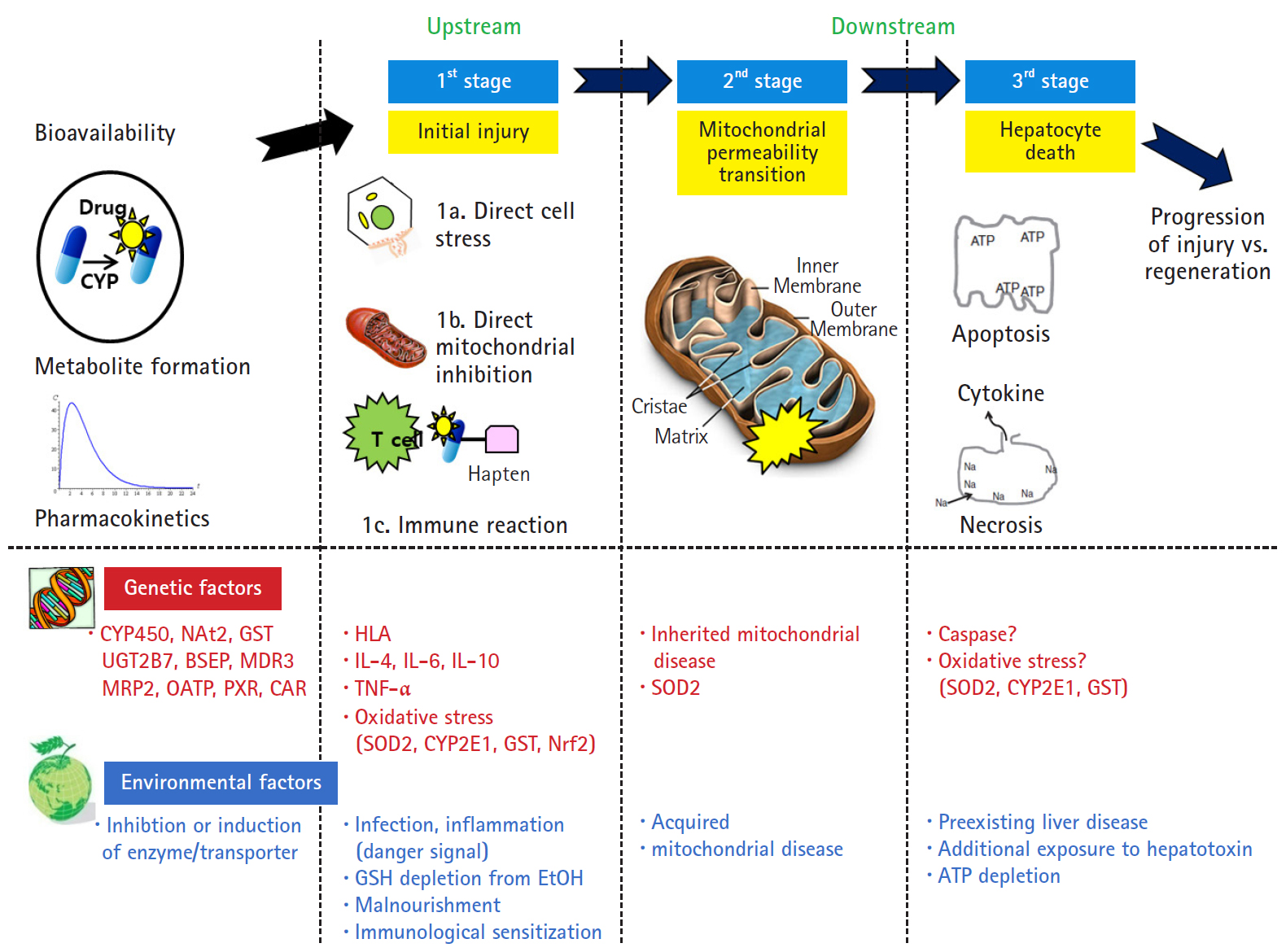
- However, Lammert et al. [25] reported the relationship between the daily dose of oral medications and idiosyncratic DILI. Higher daily doses (>50 mg/day) were associated with serious hepatic events such as liver failure, liver transplantation, and death, but there was no association with lower daily doses (<10 mg). Thus, dosage also appears to play a role in idiosyncratic liver injury. The traditional mechanism identified only the upstream of the mechanism of intrinsic and idiosyncratic reactions that cause liver injury. The current concepts of mechanisms in DILI focused not only on the upstream but also on the downstream. In other words, the hepatocyte injury mechanism is divided into 3 stages: hepatocyte injury (first stage), mitochondria permeability transition (second stage) belonging to downstream, and hepatocyte death (last stage) (Fig. 2) [26]. The initial hepatocyte injury caused by the drug does not uniformly progress to the third stage, but the injured hepatocyte may be recovered with the defense and regeneration ability of the patient. In addition, various environmental and genetic factors are involved in each stage, and the degree of individual liver injury is different.
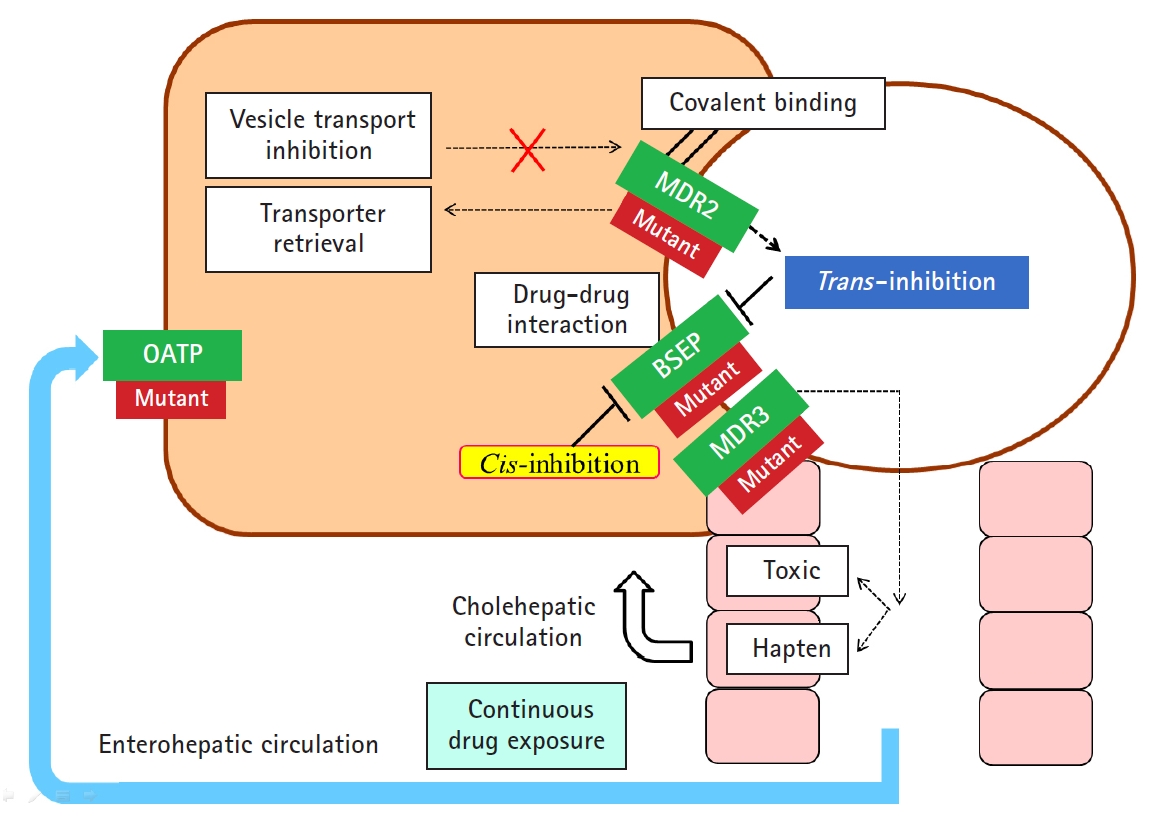
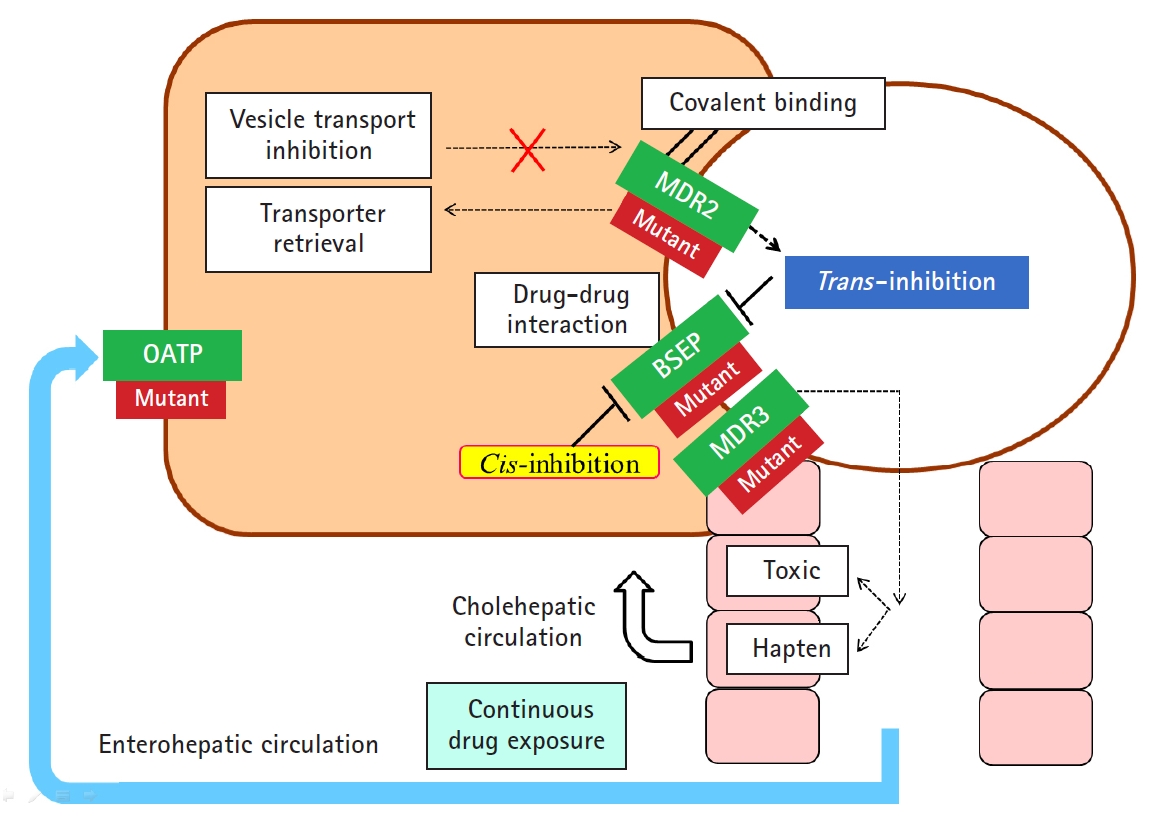
- In addition to hepatocellular injury caused by drugs, drug-induced cholestasis is also important (Fig. 3). There are 3 triggering factors that induce cholestasis, including effects on drug transporters, various hepatocellular changes, and altered bile canaliculi dynamics [27]. The function of membrane drug transporters involved is inhibited, resulting in cholestasis. In addition, the drug metabolite that exits through the canalicular membrane damages the cholangiocyte, causing cholestasis. Liver injury may be exacerbated as the accumulation of drugs in the liver via enterohepatic circulation or cholehepatic shunt.
- In addition, liver injury may be further exacerbated by transmitting hepatic injury and inflammatory signals to neighboring cells through other gap junctions, and the liver injury may be targeted to non-parenchymal cells other than hepatocytes and cholangiocytes [28].
Mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury
- Some people suffer liver injuries and others do not because every individual has different susceptibility to drugs. The risk factors for DILI can be divided into genetic factors and environmental factors [29,30]. Genetic factors include mutations in the cytochromes P450 enzyme, the expression of transport proteins and nuclear receptors, and changes in the levels of immune components. Environmental factors include old age, female gender, drug combination, previous drug adverse reactions, nutritional status, pregnancy, alcohol consumption, inflammation, and existing diseases (Table 3). The important fact is that the different risk factors are involved in different three-step model concepts that describe the changed liver injury mechanism. Changes in gut microbiota affect the drug metabolism and immune system, and it is interesting that it is one of the risk factors of DILI [31].
Individual differences in drug-induced liver injury
- There is much debate over whether DILI occurs more frequently in patients with pre-existing liver diseases than in normal people. There are several exceptions, but they are not more frequent. However, it is known that DILI is more critical and has a higher mortality rate in patients with pre-existing liver diseases [32,33].
Drug-induced liver injury in patients with pre-existing liver disease
- DILI is usually reversible and considered benign; however, it sometimes progresses to hepatic failure, requiring liver transplantation or causing death. According to Hyman Zimmerman's Hy's law, the hepatocellular type of DILI is known to have a mortality rate of over 10% if accompanied by jaundice [34,35]. Hy's law is known to have a high specificity (0.92) but a low sensitivity (0.68) for the prediction of acute liver failure (ALF) [36].
- A new index predicting ALF in DILI has been recently proposed by Robles-Diaz et al. [37], which integrates Hy's law with the new R-ratio (nR) and demonstrates a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 63%. The nR is calculated as (the highest AST or ALT/ULN)/(ALP/ULN); AST is substituted for ALT, if the AST yields a greater R-ratio.
- Recently, a drug-induced liver toxicity ALF score (DrILTox ALF Score) was developed to predict the progression of liver failure in DILI [36]. Scoring is based on platelet counts and total bilirubin (TB) [DrILTox ALF Score=−0.00691292×platelet count+0.19091500×TB (per mg/dL)]. Although the specificity (0.76) was slightly lower, the sensitivity (0.91) was higher than those of Hy’s law criteria. The risk of liver failure becomes higher as the platelet count decreases and TB increases.
Predictive model of progression to acute liver failure
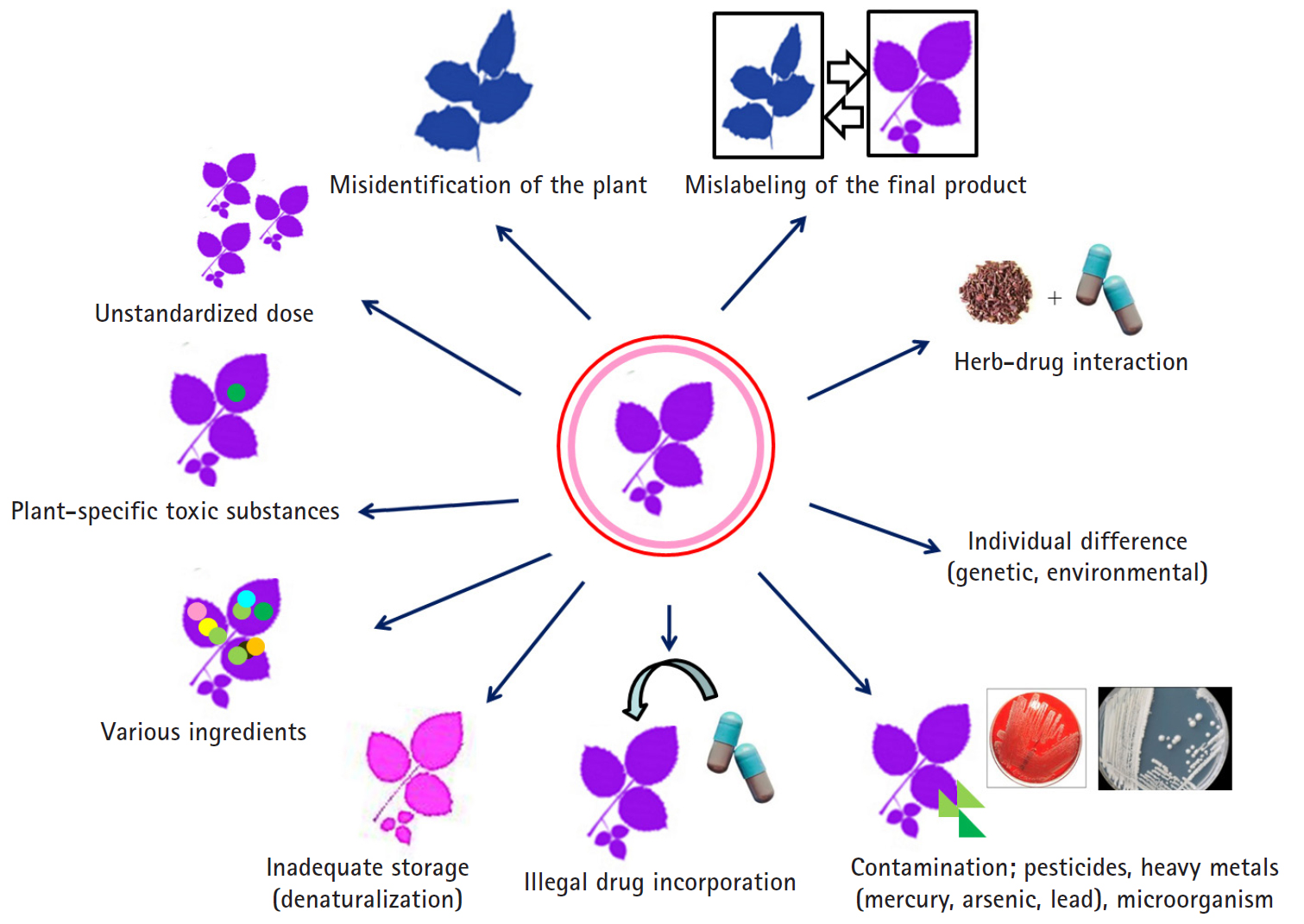
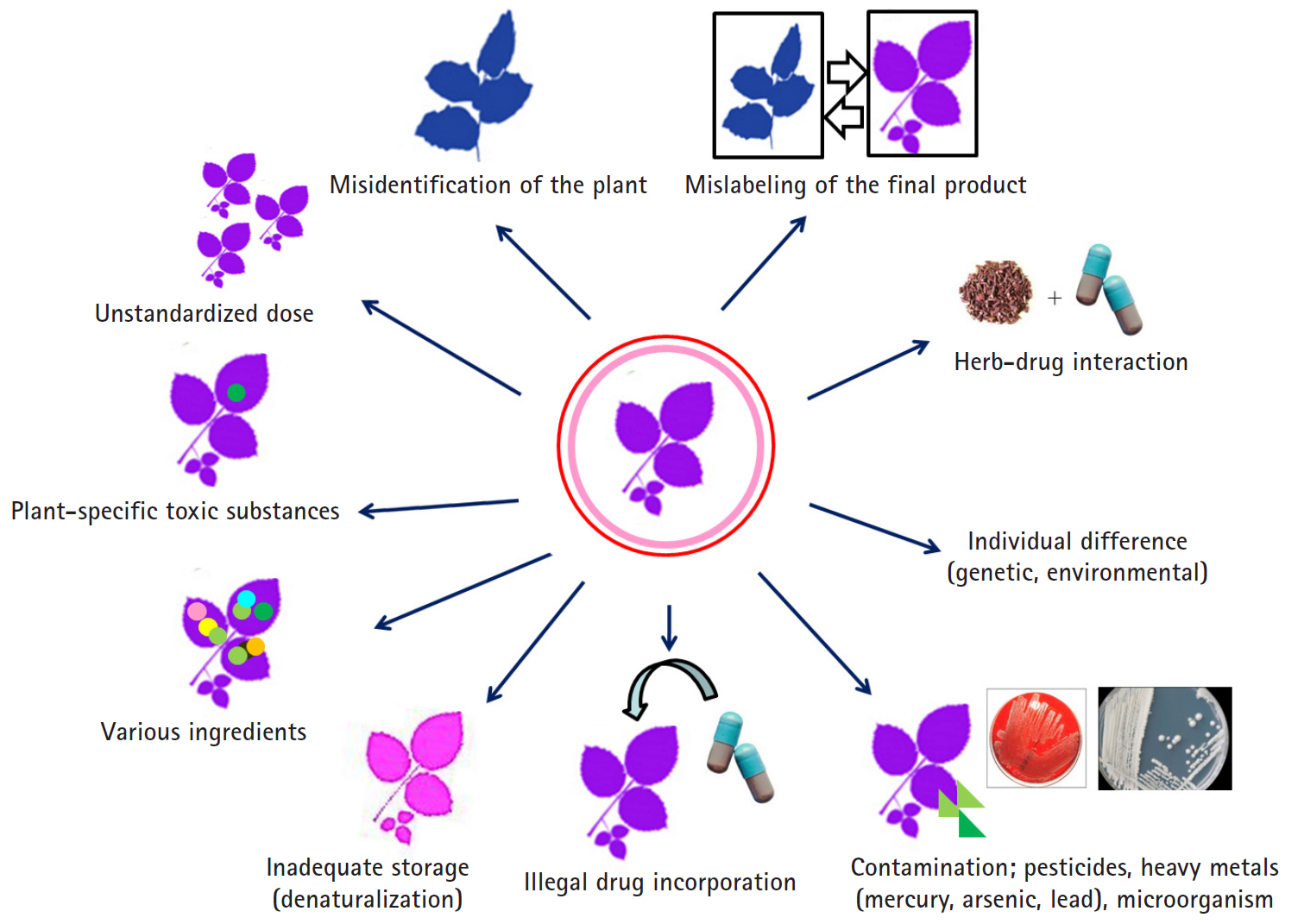
- HDS include herbs or other plant materials, vitamins, and minerals. The incidence of HDS hepatotoxicity is increasing compared to that in the past [38]. In general, it is estimated that HDS hepatotoxicity is actually more likely to occur because it is not easy to diagnose, it is often missed if the symptoms are overlooked, and often, the cases are not reported in the literature in addition to inadequate treatment for the patient. It is difficult to detect the toxic substances contained in the herb itself, unlike the commercial medicines whose causative substances are clearly defined, and it is difficult to prove causal relationships between the herb-specific components and the liver injury. Since the herb is a mixture of various substances, it is difficult to know which ingredient causes the liver injury. It can be contaminated with microorganisms or fungi during distribution or storage, or the liver injury may be caused by herb denaturation. It should be noted that there may also be liver injury caused by impurities, heavy metal contamination, or illegal incorporation of drugs into the herb (Fig. 4).
- Similar to that for the liver injury caused by commercial drugs, RUCAM scoring is applied to diagnose HDS hepatotoxicity. However, it is necessary to adjust the RUCAM for HDS hepatotoxicity [39,40] because there are few reports of HDS hepatotoxicity, and thus, the results tend to be lower than the actual RUCAM scores; further, the time between the termination of herb administration and symptom development is often long as low concentrations of plants are often taken over a long period of time.
- Interestingly, Suh et al. [41] showed that psychological factors that present vulnerability to the temptation to use alternative medicines such as herbs and plant preparations are important for understanding toxic liver injury. Therefore, the treatment of toxic liver injury itself is important. However, to prevent toxic liver injury and recurrence, it is necessary to implement an active strategy to understand and improve anxiety and depression faced by the patient.
Herbal and dietary supplement hepatotoxicity
- Stopping the suspected drugs is key to treatment. Other treatments involve the administration of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and steroids, and liver transplantation are considered when hepatic failure occurs.
- 1. Stopping the suspected drug
- Follow-ups are necessary after stopping not only the suspected drug but also herbal medicines, plant preparations, and health food. Depending on when the drug is discontinued, the severity of the liver injury can vary; therefore, the drug should be stopped as early as possible. Since such liver injuries are reversible to normal state, it is necessary to repeat liver function tests after stopping the medication. In some cases, even if the drug is discontinued, it may not immediately improve the liver condition and the liver injury may continue; therefore, careful follow-ups must be performed. It is very difficult to assess if the drug should be continued if there is a rise in hepatic enzymes in the liver function test during the course of the treatment. Further, if the suspected causative drug is important for the control of the underlying disease, the balance between the risk of progression of the underlying disease after drug withdrawal and the risk of exacerbation of liver damage due to the continued administration of potentially related drugs should be considered. According to the “stop rule” for new drugs developed by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [42], the guidelines are based on AST, ALT, and TB, and the medication being administered should be immediately stopped when any of the following results are obtained: (1) ALT or AST >8×ULN; (2) ALT or AST remains >5×ULN over 2 weeks; (3) ALT or AST >3×ULN & TB >2×ULN or international normalized ratio (INR) >1.5; (4) ALT or AST >3×ULN with symptoms (e.g., fatigue, nausea and vomiting, right upper quadrant pain, fever, and rash) or eosinophilia. Therefore, it is acceptable to follow the FDA “stop rule” in clinical practice.
- 2. Specific treatment
- Although no specific therapies are available for DILI, NAC (IV infusion, 50–150 mg/kg/day) may be administered for at least 3 days in patients with early or sub-ALF [43-45]; it is not recommended for children with severe DILI as it can lead to ALF. Several studies have shown that steroids can prove effective; however, there have been some debates on the efficacy of corticosteroid in treating patients with DILI [46,47]. In the case of immunoallergic or autoimmune hepatitis-like DILI, the administration of glucocorticoid may be considered.
- 3. Re-administration of suspected drugs
- Although there is controversy regarding the unconditional re-administration of all suspected drugs that cause DILI, care should be taken because re-administration of immunoallergic reacting drugs may cause more serious liver damage than before.
- 4. Liver transplantation
- Liver transplantation should be considered if the liver function deteriorates and is concomitant with coagulopathy and encephalopathy [48]. Survival is less than 20% if liver transplantation is not performed in drug-induced ALF caused by a hypersensitivity reaction. The recommendations of Kings’ College on indications for liver transplantation due to drug-induced liver failure as follows: In case of acetaminophen-induced liver failure, liver transplantation is required when the arterial blood pH is <7.3, regardless of encephalopathy grade, or if grade III or IV encephalopathy and an INR >6.5 and a serum creatinine >3.4 mg/dL. Liver transplantation is required for liver failure caused by non-acetaminophen drugs as follows: patients with prothrombin time (PT) >100 s (INR >6.5) (with or without encephalopathy, regardless of grade) or who satisfy any 3 of the following criteria: (1) age <10 or >40 years of age; (2) etiology: non-A/non-B hepatitis, drug-induced; (3) duration of jaundice to hepatic encephalopathy >7 days; (4) PT >50 s (INR >3.5); or (5) serum bilirubin level >17 mg/dL (>300 μmol/dL) [49,50].
- 5. New treatments for drug-induced liver injury
- Many studies have been actively pursued to develop therapeutic agents aimed at nuclear receptors in DILI [51,52]. The activation of constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) and pregnane X receptor (PXR) exacerbates hepatotoxicity by acetaminophen [53,54]. Thus, compounds that inhibit CAR and PXR may be beneficial for the treatment of hepatic damage induced by acetaminophen. Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) plays an important role in the regulation of bile acid synthesis and metabolism. Thus, FXR agonists such as obeticholic acid have been considered as promising targets for the treatment of cholestatic disorders involving drug-induced cholestasis.
- Autophagy refers to the activity in which a cell obtains energy by dissolving its protein or removing unnecessary cell components when it becomes nutrient deficient. Recently, studies on autophagy have been actively conducted in various areas such as cancer, diabetes, infectious diseases, and Crohn's disease. For DILI, a new therapeutic approach is being attempted to reduce the liver injury by controlling autophagy [55]. Acetaminophen overdose results in hepatic necrosis caused by mitochondrial damage. The activation of autophagy degrades the damaged cytoplasmic proteins, which allows cells to survive without cell necrosis. While liver injury is prevented by the administration of rapamycin (autophagy inducer), 3-methyladenine, or chloroquine (autophagy inhibitor), they have been shown to decrease liver injury. Further, it is expected that several new treatments, including autophagy induction, will be developed and applied to the treatment of DILI in clinical practice.
Treatment of drug-induced liver injury
- DILI has also been actively researched by applying various new technologies of the fourth industrial revolution. Recently, organ-on-a-chip (OOC) such as liver, lung, heart, nerve, and skin have been developed [56,57]. OOC is a technique that imitates the mechanical and physiological cellular responses as well as the functions and characteristics of the organs by culturing cells that constitute a living OOC on which electronic circuits are placed. The OOC is worth using as a model for drug development and toxicity assessment. A liver-on-a-chip can be used to evaluate the toxicity of a drug without animal testing [58]. In addition, it is reported that deep learning using artificial intelligence can predict the occurrence of DILI [59]. It is expected that research using various technologies of the fourth industrial revolution will help predict the side effects and drug–drug interactions in advance through “In-Silico,” a computer virtual test using biological big data [60,61].
Drug-induced liver injury and the fourth industrial revolution
- DILI is a problem that can be encountered in clinical settings, and clinicians should therefore have appropriate knowledge and diagnosis and treatment skills. We hope that various biomarkers to accurately diagnose and predict the prognosis of DILI will be developed and used conveniently, and various new technologies of the fourth industrial revolution will be developed and applied to DILI.
Conclusion
CYP, cytochrome P450; NAT2, N-acetyltransferase 2; GST, glutathione S-transferase; UGT2B7, glycosyltransferase 2B7; BSEP, bile salt export pump; MRP2, multidrug resistance-associated protein 2; MDR3, multidrug resistance protein 3; OATP, organic-anion-transporting polypeptide; PXR, pregnane X receptor; CAR, constitutive androstane receptor; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; POLG, polymerase gamma; MnSOD, manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase.
- 1. Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Davern T, Serrano J, et al. Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1924–34.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Hayashi PH, Bjornsson ES. Long-term outcomes after drug-induced liver injury. Curr Hepatol Rep 2018;17:292–9.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Zhu Y, Niu M, Chen J, Zou ZS, Ma ZJ, Liu SH, et al. Hepatobiliary and pancreatic: comparison between Chinese herbal medicine and Western medicine-induced liver injury of 1985 patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;31:1476–82.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Lee WJ, Kim HW, Lee HY, Son CG. Systematic review on herb-induced liver injury in Korea. Food Chem Toxicol 2015;84:47–54.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Wysowski DK, Swartz L. Adverse drug event surveillance and drug withdrawals in the United States, 1969-2002: the importance of reporting suspected reactions. Arch Intern Med 2005;165:1363–9.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Holt MP, Ju C. Mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury. AAPS J 2006;8:E48–54.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Chalasani NP, Hayashi PH, Bonkovsky HL, Navarro VJ, Lee WM, Fontana RJ, et al. ACG clinical guideline: the diagnosis and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:950–66.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Yu YC, Mao YM, Chen CW, Chen JJ, Chen J, Cong WM, et al. CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol Int 2017;11:221–41.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: drug-induced liver injury. J Hepatol 2019;70:1222–61.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Fontana RJ, Seeff LB, Andrade RJ, Björnsson E, Day CP, Serrano J, et al. Standardization of nomenclature and causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury: summary of a clinical research workshop. Hepatology 2010;52:730–42.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Devarbhavi H. An update on drug-induced liver injury. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2012;2:247–59.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Bénichou C. Criteria of drug-induced liver disorders. Report of an international consensus meeting. J Hepatol 1990;11:272–6.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Visentin M, Lenggenhager D, Gai Z, Kullak-Ublick GA. Drug-induced bile duct injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2018;1864:1498–506.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Wang T, Zhao X, Shao C, Ye L, Guo J, Peng N, et al. A proposed pathologic sub-classification of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol Int 2019;13:339–51.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Ahmad J, Odin JA. Epidemiology and genetic risk factors of drug hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis 2017;21:55–72.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Bell LN, Chalasani N. Epidemiology of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis 2009;29:337–47.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Suk KT, Kim DJ, Kim CH, Park SH, Yoon JH, Kim YS, et al. A prospective nationwide study of drug-induced liver injury in Korea. Am J Gastroenterol 2012;107:1380–7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Danan G, Benichou C. Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs--I. A novel method based on the conclusions of international consensus meetings: application to drug-induced liver injuries. J Clin Epidemiol 1993;46:1323–30.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Hayashi PH. Overview of causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken) 2017;9:29–33.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Hoofnagle JH. Drug-induced liver injury network (DILIN). Hepatology 2004;40:773.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Hayashi PH. Drug-induced liver injury network causality assessment: criteria and experience in the United States. Int J Mol Sci 2016;17:201.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Antoine DJ, Williams DP, Kipar A, Jenkins RE, Regan SL, Sathish JG, et al. High-mobility group box-1 protein and keratin-18, circulating serum proteins informative of acetaminophen-induced necrosis and apoptosis in vivo. Toxicol Sci 2009;112:521–31.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. McGill MR, Jaeschke H. Biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury. Adv Pharmacol 2019;85:221–39.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Neuman MG. Biomarkers of drug-induced liver toxicity. Ther Drug Monit 2019;41:227–34.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Lammert C, Einarsson S, Saha C, Niklasson A, Bjornsson E, Chalasani N. Relationship between daily dose of oral medications and idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury: search for signals. Hepatology 2008;47:2003–9.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Russmann S, Kullak-Ublick GA, Grattagliano I. Current concepts of mechanisms in drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Curr Med Chem 2009;16:3041–53.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Gijbels E, Vinken M. Mechanisms of drug-induced cholestasis. Methods Mol Biol 2019;1981:1–14.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Patel SJ, Milwid JM, King KR, Bohr S, Iracheta-Vellve A, Li M, et al. Gap junction inhibition prevents drug-induced liver toxicity and fulminant hepatic failure. Nat Biotechnol 2012;30:179–83.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Chalasani N, Björnsson E. Risk factors for idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Gastroenterology 2010;138:2246–59.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Björnsson ES. Epidemiology and risk factors for idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis 2014;34:115–22.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Li H, He J, Jia W. The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2016;12:31–40.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Teschke R, Danan G. Diagnosis and management of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) in patients with pre-existing liver disease. Drug Saf 2016;39:729–44.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 33. Chalasani N, Regev A. Drug-induced liver injury in patients with preexisting chronic liver disease in drug development: how to identify and manage? Gastroenterology 2016;151:1046–51.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 1999.
- 35. Reuben A. Hy's law. Hepatology 2004;39:574–8.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Lo Re V 3rd, Haynes K, Forde KA, Goldberg DS, Lewis JD, Carbonari DM, et al. Risk of acute liver failure in patients with drug-induced liver injury: evaluation of Hy's law and a new prognostic model. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;13:2360–8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Robles-Diaz M, Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N, Stephens C, Medina-Cáliz I, González-Jimenez A, et al. Use of Hy's law and a new composite algorithm to predict acute liver failure in patients with drug-induced liver injury. Gastroenterology 2014;147:109–18.ArticlePubMed
- 38. de Boer YS, Sherker AH. Herbal and dietary supplement-induced liver injury. Clin Liver Dis 2017;21:135–49.ArticlePubMed
- 39. García-Cortés M, Stephens C, Lucena MI, Fernández-Castañer A, Andrade RJ. Causality assessment methods in drug induced liver injury: strengths and weaknesses. J Hepatol 2011;55:683–91.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Teschke R, Wolff A, Frenzel C, Schwarzenboeck A, Schulze J, Eickhoff A. Drug and herb induced liver injury: Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences scale for causality assessment. World J Hepatol 2014;6:17–32.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Suh JI, Sakong JK, Lee K, Lee YK, Park JB, Kim DJ, et al. Anxiety and depression propensities in patients with acute toxic liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19:9069–76.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Ford R, Schwartz L, Dancey J, Dodd LE, Eisenhauer EA, Gwyther S, et al. Lessons learned from independent central review. Eur J Cancer 2009;45:268–74.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Lee WM, Hynan LS, Rossaro L, Fontana RJ, Stravitz RT, Larson AM, et al. Intravenous N-acetylcysteine improves transplant-free survival in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 2009;137:856–64.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Bateman DN, Dear JW, Thanacoody HK, Thomas SH, Eddleston M, Sandilands EA, et al. Reduction of adverse effects from intravenous acetylcysteine treatment for paracetamol poisoning: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2014;383:697–704.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Singh S, Hynan LS, Lee WM; Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Improvements in hepatic serological biomarkers are associated with clinical benefit of intravenous N-acetylcysteine in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure. Dig Dis Sci 2013;58:1397–402.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 46. Hu PF, Xie WF. Corticosteroid therapy in drug-induced liver injury: pros and cons. J Dig Dis 2019;20:122–6.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Hu PF, Wang PQ, Chen H, Hu XF, Xie QP, Shi J, et al. Beneficial effect of corticosteroids for patients with severe drug-induced liver injury. J Dig Dis 2016;17:618–27.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Reuben A, Koch DG, Lee WM; Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Drug-induced acute liver failure: results of a U.S. multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology 2010;52:2065–76.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Mindikoglu AL, Magder LS, Regev A. Outcome of liver transplantation for drug-induced acute liver failure in the United States: analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing database. Liver Transpl 2009;15:719–29.ArticlePubMed
- 50. O'Grady JG, Alexander GJ, Hayllar KM, Williams R. Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 1989;97:439–45.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Rudraiah S, Zhang X, Wang L. Nuclear receptors as therapeutic targets in liver disease: are we there yet? Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2016;56:605–26.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 52. Suh JI. Role of PXR and CAR in cholestasis. Korean J Hepatol 2006;12:5–15.PubMed
- 53. Zhang J, Huang W, Chua SS, Wei P, Moore DD. Modulation of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by the xenobiotic receptor CAR. Science 2002;298:422–4.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Cheng J, Ma X, Krausz KW, Idle JR, Gonzalez FJ. Rifampicin-activated human pregnane X receptor and CYP3A4 induction enhance acetaminophen-induced toxicity. Drug Metab Dispos 2009;37:1611–21.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Ni HM, Jaeschke H, Ding WX. Targeting autophagy for drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Autophagy 2012;8:709–10.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 56. Huh D, Torisawa YS, Hamilton GA, Kim HJ, Ingber DE. Microengineered physiological biomimicry: organs-on-chips. Lab Chip 2012;12:2156–64.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Kimura H, Sakai Y, Fujii T. Organ/body-on-a-chip based on microfluidic technology for drug discovery. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 2018;33:43–8.ArticlePubMed
- 58. Beckwitt CH, Clark AM, Wheeler S, Taylor DL, Stolz DB, Griffith L, et al. Liver 'organ on a chip'. Exp Cell Res 2018;363:15–25.ArticlePubMed
- 59. Xu Y, Dai Z, Chen F, Gao S, Pei J, Lai L. Deep learning for drug-induced liver injury. J Chem Inf Model 2015;55:2085–93.ArticlePubMed
- 60. Fraser K, Bruckner DM, Dordick JS. Advancing predictive hepatotoxicity at the intersection of experimental, in silico, and artificial intelligence technologies. Chem Res Toxicol 2018;31:412–30.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Suh JI. Establishment of tertiary hospital including southeast clinical research center in the era of the 4th industrial revolution. In: Choi YJ, editor. The 58th annual meeting and international symposium of Korean Society of Life Science; 2017 Aug 3-4; Gyeongju, Korea. Busan: Korean Society of Life Science; 2017. p. 71.
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Liver Injury in Favipiravir-Treated COVID-19 Patients: Retrospective Single-Center Cohort Study
Amal Oweid Almutairi, Mahmoud Zaki El-Readi, Mohammad Althubiti, Yosra Zakariyya Alhindi, Nahla Ayoub, Abdullah R. Alzahrani, Saeed S. Al-Ghamdi, Safaa Yehia Eid
Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease.2023; 8(2): 129. CrossRef - Hepatotoxic Components Effect of Chebulae Fructus and Associated Molecular Mechanism by Integrated Transcriptome and Molecular Docking
Liwen Ai, Fan Yang, Wanjun Hu, Liyang Guo, Weixue Liu, Xuexue Xue, Lulu Li, Zunlai Sheng
Molecules.2023; 28(8): 3427. CrossRef - Systematic Review of Safety of Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators in Healthy Adults: Implications for Recreational Users
Jonathan D. Vignali, Kevin C. Pak, Holly R. Beverley, Jesse P. DeLuca, John W. Downs, Adrian T. Kress, Brett W. Sadowski, Daniel J. Selig
Journal of Xenobiotics.2023; 13(2): 218. CrossRef - Antitubercular drugs induced liver injury: an updated insight into molecular mechanisms
Devaraj Ezhilarasan
Drug Metabolism Reviews.2023; 55(3): 239. CrossRef - Advances in Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury Issues: New Clinical and Mechanistic Analysis Due to Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method Use
Rolf Teschke, Gaby Danan
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 10855. CrossRef - Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning in early detection of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and drug-induced toxicity
Siyun Yang, Supratik Kar
Artificial Intelligence Chemistry.2023; 1(2): 100011. CrossRef - Rifampicin-induced ER stress and excessive cytoplasmic vacuolization instigate hepatotoxicity via alternate programmed cell death paraptosis in vitro and in vivo
KM Kainat, Mohammad Imran Ansari, Nuzhat Bano, Pankaj Ramji Jagdale, Anjaneya Ayanur, Mahadeo Kumar, Pradeep Kumar Sharma
Life Sciences.2023; 333: 122164. CrossRef - Establishment of a Stable Acute Drug-Induced Liver Injury Mouse Model by Sodium Cyclamate
Quan Zhou, Zhongtian Peng, Xialing Huang
Journal of Inflammation Research.2022; Volume 15: 1599. CrossRef - Mitochondrial toxicants in Xian-Ling-Gu-Bao induce liver injury by regulating the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway: an in vitro study
Shujuan Piao, Hongwei Lin, Xia Tao, Wansheng Chen
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Kratom-Induced Liver Injury: A Case Series and Clinical Implications
Mahesh Botejue, Gurjot Walia, Omar Shahin, Jyotsna Sharma, Rasiq Zackria
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Colestasis inducida por anabólicos: reporte de caso y revisión de la literatura
Diana Lizeth Cabrera-Rojas, Juliana Soto-Cardona, Jorge Luis Toro-Molina, Juan Camilo Pérez-Cadavid, Juan Ignacio Marín-Zuluaga
Hepatología.2021; : 273. CrossRef - Hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters in Wilson’s disease patients with liver failure
Sylwia Szeląg-Pieniek, Stefan Oswald, Mariola Post, Joanna Łapczuk-Romańska, Marek Droździk, Mateusz Kurzawski
Pharmacological Reports.2021; 73(5): 1427. CrossRef - Prediction of Drug-Induced Liver Toxicity Using SVM and Optimal Descriptor Sets
Keerthana Jaganathan, Hilal Tayara, Kil To Chong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(15): 8073. CrossRef - Five Constituents Contributed to the Psoraleae Fructus-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis
Zhaojuan Guo, Pin Li, Chunguo Wang, Qianjun Kang, Can Tu, Bingqian Jiang, Jingxuan Zhang, Weiling Wang, Ting Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Liver Function Test Results after Korean Medicine Treatment in Patients of a Korean Medicine Hospital: A Retrospective Chart Review
Min Young Yim, Han Byeol Park, Jae Soo Kim, Hyun Jong Lee, Sung Chul Lim, Yun Kyu Lee
Korean Journal of Acupuncture.2021; 38(4): 275. CrossRef - Herb-induced Liver Injury in Asia and Current Role of RUCAM for Causality Assessment in 11,160 Published Cases
Rolf Teschke, Yun Zhu, Jing Jing
Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.2020; 8(2): 200. CrossRef - Embarazo y lesión hepática inducida por medicamentos. Reporte de un caso y revisión de la literatura
Christian Labrador-López, Martín Garzón-Olarte, Rodrigo Daza-Fernández, Julián Martínez-Marín, Jorge Lizarazo-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos Molano-Villa, Juan Carlos Marulanda-Gómez, Mario Rey-Tovar
Hepatología.2020; : 157. CrossRef

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite