PubMed Central, CAS, DOAJ, KCI

Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Yeungnam Med Sci > Volume 35(2); 2018 > Article
-
Review Article
Potential health effects of emerging environmental contaminants perfluoroalkyl compounds -
Youn Ju Lee

-
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine 2018;35(2):156-164.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2018.35.2.156
Published online: December 31, 2018
Department of Pharmacology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- Corresponding Author: Youn Ju Lee, Department of Pharmacology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, 33, Duryugongwon-ro 17-gil, Nam-gu, Daegu 42472, Korea Tel: +82-53-650-4337, Fax: +82-53-650-4488 E-mail: whrytn4337@cu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2018 Yeungnam University College of Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 7,794 Views
- 102 Download
- 7 Crossref
Abstract
- Environmental contaminants are one of the important causal factors for development of various human diseases. In particular, the perinatal period is highly vulnerable to environmental toxicants and resultant dysregulation of fetal development can cause detrimental health outcomes potentially affecting life-long health. Perfluoroalkyl compounds (PFCs), emerging environmental pollutants, are man-made organic molecules, which are widely used in diverse industries and consumer products. PFCs are non-degradable and bioaccumulate in the environment. Importantly, PFCs can be found in cord blood and breast milk as well as in the general population. Due to their physicochemical properties and potential toxicity, many studies have evaluated the health effects of PFCs. This review summarizes the epidemiological and experimental studies addressing the association of PFCs with neurotoxicity and immunotoxicity. While the relationships between PFC levels and changes in neural and immune health are not yet conclusive, accumulative studies provide evidence for positive associations between PFC levels and the incidence of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and reduced immune response to vaccination both in children and adults. In conclusion, PFCs have the potential to affect human health linked with neurological disorders and immunosuppressive responses. However, our understanding of the molecular mechanism of the effects of PFCs on human health is still in its infancy. Therefore, along with efforts to develop methods to reduce exposure to PFCs, studies on the mode of action of these chemicals are required in the near future.
- Environmental pollutants have long been considered one of the critical etiologies of the development of various pathologies such as cardiovascular, respiratory, metabolic, immunologic, and neurodegenerative diseases [1-3]. Recently, multiple accumulative studies have addressed the relationship between exposure to environmental toxicants and health outcomes.
- Perfluoroalkyl compounds (PFCs) are a group of synthetic chemicals, which have been widely used since the 1950s for diverse industrial and consumer products such as carpets, clothes, non-stick cookware, food packaging and fire-foaming due to their water- and oil-repelling properties [4]. Since PFCs are extremely stable and are not biodegradable, these chemicals accumulate in the ecosystem and are biomagnified via the food web [5-7]. As ubiquitous contaminants, PFCs can be detected in serum from the general population as well as industry workers, to a relatively high level compared to other environmental contaminants [8]. More importantly, they are found in umbilical cord blood and breast milk [9,10], suggesting a lifelong exposure to PFCs may start from fetal development. This has raised particular concerns over the potential deleterious effects of PFCs because the perinatal period is especially vulnerable to environmental toxins, which can induce developmental defects and chronic diseases. The most extensively distributed and studied PFCs are perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS), perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), hence most studies on potential health effects are based around these. Due to its bioaccumulative and potentially toxic properties, PFOS was added as persistent organic pollutants as an Annex B substance under the Stockholm Convention in 2009, meaning there should be ‘restriction in its use’ (United Nations Environment Programme 2009). Generally, the serum concentration of PFCs has been shown to be higher in developed countries. However, it is noteworthy that the serum concentration of PFOA in Korean women was about 88 ppb, which is much higher than that in the US general population (4.7-5.7 ppb) [11].
- With the establishment of regulation on their use, there have been extensive studies focusing on a wide range of health outcomes of PFCs. In fact, sufficient evidence has now been reported for the association between PFCs and neurotoxicity and immunosuppression.
- This review aims to provide a brief introduction of PFCs and a summary of the literature comparing epidemiological and experimental evidence for the impacts of PFCs on health outcomes including neurological disorders and immune health.
INTRODUCTION
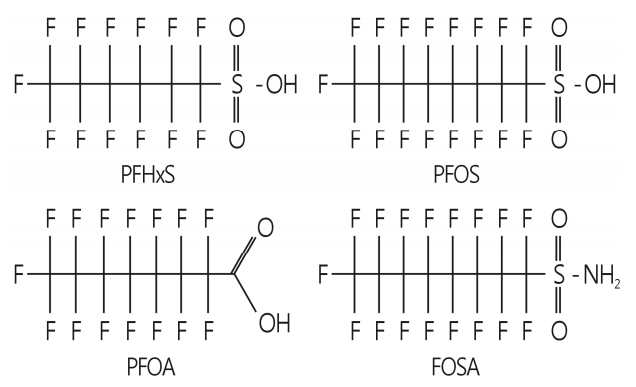
- PFCs are aliphatic substances containing one or more carbon (C) atoms on which all hydrogen (H) atoms are replace by fluorine (F), having the CnF2n+1- moiety attached to various functional groups (Fig. 1). The major functional groups include carboxylic acid (-COOH), sulfonic acid (SO3H) and sulfonamides (-SO2NH2). Examples of the major PFCs are listed in Table 1.
- As mentioned above, the C-H covalent bond is extremely stable and resistant to chemical and thermal degradation. In addition to their water-proof and oil-proof properties, their high stability made these chemicals highly useful for application in various industrial and consumer products [4]. PFCs are present in all environmental matrices, wildlife and human body even after their use was phased out. The first study demonstrating global contamination by PFCs was a report focused on the occurrence of PFOS, PFOA and other PFCs in wildlife [12]. Hansen et al. [13] have also reported the presence of PFOS, PFOA, and other PFCs in human blood samples obtained from several biological suppliers. Human exposure to PFCs occurs through diverse routes such as food, drinking water, breast milk, and dust [14].
- Many studies have shown that long-chain PFCs, i.e., CnF2n+1COOH where n≥7 and CnF2n+1-SO3H where n≥6, which include PFOA and PFOS, are more bioaccumulative and have longer elimination half-lives than short-chain PFCs [15-18]. Therefore, PFOA and PFOS have received particular attention from the global regulatory community and scientific groups. The global concern over the potential environmental and health impact of long-chain PFCs has led to the phase-out of production of PFOA and PFOS by their major manufacturer (the 3M Company) in 2000, and has facilitated regulatory initiatives to reduce the environmental release of these PFCs in many countries. PFHxS, the six carbon congener (C6) is generally considered to be less toxic than PFOS (C8) and has therefore replaced PFOS in many industrial applications. Although the biological effects of PFHxS are less studied than those of other PFCs, PFHxS is one of three major PFCs found in human blood and has physicochemical properties similar to PFOS [19]. Importantly, the serum level of PFHxS in children has been reported to be higher than in adults [20-22].
Classification and physicochemical properties of PFCs
- The global attention to PFCs has led to multiple epidemiological and experimental studies to elucidate their toxicological impacts, in addition to the regulations and agreements between related organizations to restrict their use. The Mid-Ohio Valley C8 Cohort Study during 2005-2013 conducted epidemiological investigations on exposure and health outcomes in communities of the Mid-Ohio Valley, an area which has been contaminated with PFOA(or C8) from the Washington Works plant in Parkersburg, West Virginia since the 1950s. The conclusions of the study are published in multiple scientific papers which report probable links between exposure and various health conditions, such as high cholesterol, thyroid disease, ulcerative colitis, pregnancy hypertension, and cancers (testicular and kidney) [23-26]. In 2013, the southwest of the Veneto Region, Italy, was known to be affected by massive PFC contamination of tap water, as well as ground and surface water. Comprehensive studies on biomonitoring and risk assessment have been conducted as a result, and studies on continuous biomonitoring and long-term health outcomes are still ongoing [27]. Very recently, it has been announced that PFCs, in particular PFHxS, are detected at a high concentration in the tap water of the Daegu and Busan regions in Korea. This is due to contamination of the Nakdong River, a major source of drinking water in these regions. Epidemiological studies involving the populations of these areas are therefore warranted in the near future.
- 1. Neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative impacts
- Neurodevelopment involves complex and dynamic processes. The perinatal period, which involves the brain growth spurt (BGS), is exquisitely vulnerable to environmental stimuli and the impairment of neurodevelopment during this period can induce serious neurological disorders affecting life-long health. Considering the reports that PFCs are found in cord blood and breast milk [9,10], the potential of PFCs to induce neurotoxicity have drawn both scientific and public concerns. To examine the association between PFCs and neurological outcomes, a large number of studies have been conducted using human and animal subjects.
- Studies examining neurodevelopmental markers have generally reported no association with PFCs [28-35], however some studies have presented positive associations. Fei et al. [28] found that the PFOS level measured in maternal blood samples in early pregnancy was inversely correlated with the ability of the child to sit without support at 18 months of age. However, no association was found between maternal PFOA and PFOS levels and behavioral and motor coordination at 7 years of age in the same cohort [36]. In a cohort in Cincinnati, increased PFOS in maternal blood was positively associated with executive function deficits at 5-8 years of age [37]. Furthermore, Harris et al. [38] reported an inverse association between prenatal and childhood exposure to PFCs and childhood visual motor abilities.
- Many different cohort studies have reported a positive association between prenatal exposure to PFCs and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or related behavioral problems. In the Taiwan Birth Panel Study and the Taiwan Early-Life Cohort, the level of perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), but not PFOA and PFOS in umbilical cord blood was associated with ADHD at 7 years of age [39]. Similarly, positive associations have been reported between serum PFOS and PFHxS and ADHD in children [35], maternal PFOA and increased hyperactivity and behavioral problems [40], and maternal PFOA and ADHD[41]. In contrast, Ode et al. [42] reported no association between prenatal exposure to PFCs and ADHD in a Swedish cohort.
- As well as potentially causing neurodevelopmental defects in children, early exposure to environmental toxicants could be a critical causal factor for increased risk of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases in later life [43-45]. Very recently, an epidemiological study conducted in Italy has reported a higher level of mortality by Alzheimer’s disease in areas contaminated with PFCs in drinking water compared with uncontaminated areas [46].
- In addition to epidemiological studies, experimental animal studies have provided additional evidence of the life-long effects of PFC-induced neurological damages. For example, neonatal exposure to PFOS and PFOA resulted in alteration of the expression of critical neuroproteins in the developing brain and neurobehavioral defects manifested as changes in spontaneous behavior and habitation in adult mice [47,48]. Similar results were observed with neonatal exposure to PFHxS [49,50]. Although the molecular mechanisms responsible for the neurotoxic effects caused by PFCs are not completely understood, apoptosis of neuronal cells during the BGS period is considered as a critical causal factor for the disturbance of neurobehavioral function, which can manifest either in childhood or in adulthood [51]. We have recently reported that PFOS induced apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells via reactive oxygen species-dependent protein kinase C and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2)-dependent pathways [52,53]. Similarly, PFHxS increased neuronal cell apoptosis via N-methyl-D-aspartate-mediated ERK1/2 and AMP-activated protein kinase pathways [54-56]. A summary of epidemiological and laboratory experimental studies related to the neurological impact of PFCs are presented in Table 2.
- Despite several epidemiological studies reporting the positive association of PFCs with neurological disorders such as ADHD and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as experimental animal studies reporting the underlying mechanism for the neurotoxicity of PFCs, the evidence for the association of PFCs with neurodevelopmental defects are still inconsistent. Therefore, further studies are needed for solid conclusions on this causal relationship.
- 2. Immunoregulatory impacts
- The perinatal period is a critical time for immune system development and exposure to environmental pollutants during this period can adversely affect immune functions including antibody production and increase the development of allergic phenotypes [57-61]. Dysregulation of immune responses may increase the risk of infectious diseases, hypersensitivity disorders, and even death. Therefore, elucidation of a possible relationship between exposure to environmental contaminants and immunological diseases is paramount.
- Several animal studies have provided evidence for immunotoxic effects of PFCs. In adult B6C3F1 mice exposed for 28 days to PFOS at serum concentrations reported in general population and occupationally exposed humans, the immune response, possibly involving B-cell dependent immunoglobulin M(IgM) production, was suppressed [62]. Furthermore, a study by Guruge et al. [63] reported that gavage exposure of female B6C3F1 mice to PFOS (0.025 and 0.05mg/kg body weight/day) for 21 days increased mortality after infection with influenza A virus in a dose-dependent manner. Recently, a growing number of epidemiological studies have also demonstrated an association of prenatal and postnatal exposure to PFCs with immunotoxicity. In a birth cohort of the National Hospital in the Faroe Islands, the serum levels of PFOS and PFOA at age 5 were negatively associated with diphtheria antibody concentration at age 7 [64]. Consistent results were observed at age 13 in the same cohort group [65]. In accordance with the immunosuppressive effects of PFCs, prenatal exposure has been inversely correlated with the level of rubella antibody and positively correlated with the incidence of the common cold at age 3, as measured in the Norwegian Mother and Child cohort [66]. In a hospital-based cohort of Hokkaido, Japan, prenatal exposure to PFOS and PFHxS increased the incidence of infectious diseases including otitis media, pneumonia, respiratory syncytial virus infection and varicella up to 4 years of age [67]. Timmermann et al. [68] reported that the serum levels of PFHxS, PFOA, PFOS, PFNA and perfluorodecanoic acid at 5 years of age were associated with increased risk of asthma or allergic diseases in the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR)-unvaccinated group but not in the MMR-vaccinated group. In this study, prenatal exposure to PFCs showed no association with asthma or allergic diseases. The immunosuppressive effect of PFCs has also been observed in adult individuals. Kielsen et al. [69] reported that the serum PFC level in adults was negatively associated with the rate of increase in antibody responses following booster vaccination with diphtheria and tetanus. Although there are few studies on the association of PFC exposure with allergic responses, Buser and Scinicariello [70] reported a positive correlation between serum levels of PFCs including PFOA, PFOS and PFHxS and self-reported food allergies in adolescents. We recently examined the effects of PFOS on the activation of mast cells, a specialized cell type involved in IgE-antigen mediated allergic responses. PFOS significantly increased activation of mast cells as measured by degranulation, production of the eicosanoids PGD2 and LTC4, and calcium influx [71].
- Although there are fewer studies on immunomodulatory effects than those on other health outcomes elicited by PFCs, recent epidemiological studies have provided some solid evidence for immunosuppressive effects on pediatric vaccination and other immune-related responses in both childhood and adulthood. A summary of epidemiological and laboratory experimental studies relating to the immunomodulatory effects of PFCs are presented in Table 3.
The potential health impacts of PFCs
- This review summarizes the neurotoxicological and immunotoxicological impacts of PFCs from peer-reviewed studies. During the last decade, these has been an impressive increase in studies examining the association of PFCs with health risk potential. Although this review does not cover all aspects of health outcomes caused by PFCs, neurological and immunological disorders are the most concerning potential health outcomes resulting from exposure to diverse environmental toxicants including PFCs. The epidemiological and toxicological studies provide evidence for positive association of PFCs, mostly PFOA, PFOS, and PFHxS with ADHD. One study also suggests the possible relationship between exposure to PFCs and Alzheimer’s disease. Several animal and in vitro studies provide evidence supporting the neurotoxic effects of PFCs and have presented molecular mechanisms responsible for neuronal cell apoptosis. To date, there have been limited studies on the effects of PFCs on immunological responses. However, several epidemiological studies have reported that serum levels of PFCs are inversely related with the immune response to vaccination both in childhood and adulthood. In addition, immunosuppressive effects of PFCs have been consistently observed in animal studies. Although positive associations with asthma and other allergic diseases have been reported, more studies are needed to lead a concrete conclusion.
- Since PFOS, PFOA, and PFHxS are the PFCs most highly detected in humans, these are the focus of most current studies on the health effects of PFCs. Considering the longer chain PFCs have longer elimination half-lives, more investigations are needed to gain toxicological information on the longer-chain PFCs and to identify the underlying mechanisms of action of novel PFCs. In addition, many studies have discussed their health outcomes as individual compounds, whereas PFCs can be mixed with diverse contaminants in the environment. The composition of these contaminant mixtures can change over time and also vary depending on location. The chemicals within such mixtures may share a common pathway or may have disparate pathways in terms of their mechanisms of action, potentially leading to potentiated effects or unexpected outcomes. Therefore, in addition to studies on the action of PFCs as individual chemicals, more research on their impact as complex mixtures is needed for practical application in the future.
CONCLUSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2014R1A1A2056565), Republic of Korea.
| Study group | Sample | PFCs | Effects | Summary | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danish National Birth Cohort | Maternal serum | PFOS | Start of sit without support at age 18 mon | Negative association between PFOS and start of sit without support | Fei et al. [28] |
| A cohort in Cincinnati | Maternal serum | PFOS | Executive function deficits at age 5-8 yr | Positive association between PFOS and executive function deficits | Vuong et al. [37] |
| Boston-area birth cohort | Maternal and childhood serum | PFCs | Visual motor abilities | Negative association between serum PFCs and visual motor abilities | Harris et al. [38] |
| Taiwan Birth Panel Study and the Taiwan Early-Life Cohort | Cord blood | PFNA | ADHD at age 7 yr | Positive association between cord blood PFNA and ADHD | Lien et al. [39] |
| Mid-Ohio Valley C8 cohort | Serum at age 5-18 yr | PFOS, PFHxS | Parental ADHD | Positive association between serum PFCs and parental report of ADHD | Stein and Savitz [35] |
| INUENDO cohort | Serum of child | PFOA | Hyperactivity and behavioral problems | Positive association between serum PFOA and hyperactivity and behavioral problems | Hoyer et al. [40] |
| Danish National Birth Cohort | Maternal serum | PFOA | ADHD | Positive association between serum PFOA and ADHD | Liew et al. [41] |
| A cohort in Italy including Veneto Region | Drinking water | PFCs | Mortality caused by Alzheimer、disease | Positive association between level of PFCs in drinking water and mortality caused by Alzheimer’s disease | Mastrantonio et al. [46] |
| Mice | Serum | PFOS, PFOA | Spontaneous behavior and habitation in adult | Positive association between serum PFOS and PFOA and spontaneous behavior and habitation in adult | Johansson et al. [48] |
| Mice | Serum | PFOS, PFOA | Neuroprotein expression in developing brain | Positive association between serum PFOS and PFOA and alteration of neuroprotein expression | Johansson et al. [47] |
| Mice | Serum | PFHxS | Cognitive disturbance in adult | Positive association between serum PFHxS and cognitive disturbance in adult | Viberg et al. [50] |
| Mice | Serum | PFHxS | Neuroprotein expression in developing brain | Positive association between serum PFHxS and alteration of neuroprotein expression | Lee and Viberg [49] |
| Cerebellar granule cell | PFOS | Apoptosis | PFOS increases apoptosis via ROS-PKC pathway | Lee et al. [52] | |
| Cerebellar granule cell | PFOS | Apoptosis | PFOS increases apoptosis via ERK1/2 pathway | Lee et al. [53] | |
| Cerebellar granule cell | PFHxS | Apoptosis | PFHxS increases apoptosis via ERK1/2 pathway | Lee et al. [54] | |
| PC12 cells | PFHxS | Apoptosis | PFHxS increases apoptosis via NMDA-ERK1/2 pathway | Lee et al. [55] | |
| PC12 cells | PFHxS | Apoptosis | PFHxS increases apoptosis via AMPK pathway | Lee et al. [56] |
PFC, perfluoroalkyl compounds; PFOS, perfluorooctane sulfonic acid; PFNA, perfluorononanoic acid; ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; PFHxS, perfluorohexane sulfonic acid; PFOA, perfluorooctanoic acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PKC, protein kinase C; ERK1/2, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase.
| Study model | Sample | PFCs | Effects | Summary | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth cohort of the National Hospital in the Faroe Islands | Serum at age 5 yr | PFOS, PFOA | Diphtheria antibody at age 7 yr | Negative association between PFOS and PFOA and antibody production | Grandjean et al. [64] |
| Birth cohort of the National Hospital in the Faroe Islands | Serum at age 5 yr | PFOS, PFOA | Diphtheria antibody at age 13 yr | Negative association between PFOS and PFOA and antibody production | Grandjean et al. [65] |
| Norwegian Mother and Child cohort | Maternal serum | PFCs | Rubella antibody at age 3 yr | Negative association between maternal serum PFCs and antibody concentration | Granum et al. [66] |
| Hospital-based cohort of Hokkaido | Maternal serum | PFOS, PFHxS | Otitis media, pneumonia, respiratory Syncytial virus infection and varicella | Positive association between maternal serum PFOS and PFHxS infectious diseases | Goudarzi et al. [67] |
| A cohort of Faroese children | Serum at age 5 yr | PFHxS, PFOA, PFOS, PFNA, PFDA | Asthma or allergic diseases | Positive association between serum PFCs and increased risk of asthma or allergic diseases | Timmermann et al. [68] |
| 12 healthy adult volunteers | Serum of adult | PFCs | Booster vaccination with diphtheria and tetanus | Negative association between serum PFCs and rate of increase in antibody responses | Kielsen et al. [69] |
| NHANES in U.S. | Serum at age 12-19 yr | PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS | Food allergy | Positive association between serum PFCs and self-reported food allergy | Buser and Scinicariello [70] |
| Adult B6C3F1 mice | Serum | PFOS | IgM production | Negative association between serum PFOS and B-cell mediated IgM production | Peden-Adams et al. [62] |
| Female B6C3F1 mice | Serum | PFOS | Mortality after influenza A infection | Positive association between serum PFOS and mortality after influenza A infection | Guruge et al. [63] |
- 1. Lei M, Zhang L, Lei J, Zong L, Li J, Wu Z, et al. Overview of emerging contaminants and associated human health effects. Biomed Res Int 2015;2015:404796.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Pereira LC, de Souza AO, Franco Bernardes MF, Pazin M, Tasso MJ, Pereira PH, et al. A perspective on the potential risks of emerging contaminants to human and environmental health. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2015;22:13800–23.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Vrijheid M, Casas M, Gascon M, Valvi D, Nieuwenhuijsen M. Environmental pollutants and child health - a review of recent concerns. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2016;219:331–42.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Giesy JP, Kannan K. Perfluorochemical surfactants in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 2002;36:146.A-52A.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Lau C, Thibodeaux JR, Hanson RG, Narotsky MG, Rogers JM, Lindstrom AB, et al. Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid exposure during pregnancy in the mouse. Toxicol Sci 2006;90:510–8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Morikawa A, Kamei N, Harada K, Inoue K, Yoshinaga T, Saito N, et al. The bioconcentration factor of perfluorooctane sulfonate is significantly larger than that of perfluorooctanoate in wild turtles (Trachemys scripta elegans and Chinemys reevesii): an Ai river ecological study in Japan. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2006;65:14–21.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Harada KH, Yang HR, Moon CS, Hung NN, Hitomi T, Inoue K, et al. Levels of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in female serum samples from Japan in 2008, Korea in 1994-2008 and Vietnam in 2007-2008. Chemosphere 2010;79:314–9.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Kato K, Wong LY, Jia LT, Kuklenyik Z, Calafat AM. Trends in exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the U.S. Population: 1999-2008. Environ Sci Technol 2011;45:8037–45.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Kärrman A, Ericson I, van Bavel B, Darnerud PO, Aune M, Glynn A, et al. Exposure of perfluorinated chemicals through lactation: levels of matched human milk and serum and a temporal trend, 1996-2004, in Sweden. Environ Health Perspect 2007;115:226–30.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Lee YJ, Kim MK, Bae J, Yang JH. Concentrations of perfluoroalkyl compounds in maternal and umbilical cord sera and birth outcomes in Korea. Chemosphere 2013;90:1603–9.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Kannan K, Corsolini S, Falandysz J, Fillmann G, Kumar KS, Loganathan BG, et al. Perfluorooctanesulfonate and related fluorochemicals in human blood from several countries. Environ Sci Technol 2004;38:4489–95.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Giesy JP, Kannan K. Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ Sci Technol 2001;35:1339–42.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Hansen KJ, Clemen LA, Ellefson ME, Johnson HO. Compound-specific, quantitative characterization of organic fluorochemicals in biological matrices. Environ Sci Technol 2001;35:766–70.ArticlePubMed
- 14. D’Hollander W, de Voogt P, De Coen W, Bervoets L. Perfluorinated substances in human food and other sources of human exposure. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 2010;208:179–215.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Martin JW, Mabury SA, Solomon KR, Muir DC. Dietary accumulation of perfluorinated acids in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 2003;22:189–95.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Martin JW, Mabury SA, Solomon KR, Muir DC. Bioconcentration and tissue distribution of perfluorinated acids in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 2003;22:196–204.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Conder JM, Hoke RA, De Wolf W, Russell MH, Buck RC. Are PFCAs bioaccumulative? A critical review and comparison with regulatory criteria and persistent lipophilic compounds. Environ Sci Technol 2008;42:995–1003.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Olsen GW, Chang SC, Noker PE, Gorman GS, Ehresman DJ, Lieder PH, et al. A comparison of the pharmacokinetics of perfluorobutanesulfonate (PFBS) in rats, monkeys, and humans. Toxicology 2009;256:65–74.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Olsen GW, Huang HY, Helzlsouer KJ, Hansen KJ, Butenhoff JL, Mandel JH. Historical comparison of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorooctanoate, and other fluorochemicals in human blood. Environ Health Perspect 2005;113:539–45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Calafat AM, Wong LY, Kuklenyik Z, Reidy JA, Needham LL. Polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the U.S. population: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003-2004 and comparisons with NHANES 1999-2000. Environ Health Perspect 2007;115:1596–602.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Olsen GW, Church TR, Hansen KJ, Burris JM, Butenhoff JL, Mandel JH, et al. Quantitative evaluation of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and other fluorochemicals in the serum of children. J Child Health 2004;2:53–76.Article
- 22. Toms LM, Calafat AM, Kato K, Thompson J, Harden F, Hobson P, et al, Mueller JF. Polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in pooled blood serum from infants, children, and adults in Australia. Environ Sci Technol 2009;43:4194–9.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Darrow LA, Groth AC, Winquist A, Shin HM, Bartell SM, Steenland K. Modeled perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) exposure and liver function in a Mid-Ohio Valley Community. Environ Health Perspect 2016;124:1227–33.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Dhingra R, Lally C, Darrow LA, Klein M, Winquist A, Steenland K. Perfluorooctanoic acid and chronic kidney disease: Longitudinal analysis of a Mid-Ohio Valley community. Environ Res 2016;145:85–92.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Steenland K, Zhao L, Winquist A, Parks C. Ulcerative colitis and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in a highly exposed population of community residents and workers in the mid-Ohio valley. Environ Health Perspect 2013;121:900–5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Winquist A, Lally C, Shin HM, Steenland K. Design, methods, and population for a study of PFOA health effects among highly exposed mid-Ohio valley community residents and workers. Environ Health Perspect 2013;121:893–9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. WHO Regional Office for Europe. Keeping our water clean: the case of water contamination in the Veneto Region, Italy [Internet] Copenhagen: WHO Regional Office for Europe; 2017 [cited 2018 October 31]. http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0019/341074/pfas-report-20170606-h1330-print-isbn.pdf?ua=1.
- 28. Fei C, McLaughlin JK, Lipworth L, Olsen J. Prenatal exposure to perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and maternally reported developmental milestones in infancy. Environ Health Perspect 2008;116:1391–5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Donauer S, Chen A, Xu Y, Calafat AM, Sjodin A, Yolton K. Prenatal exposure to polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polyfluoroalkyl chemicals and infant neurobehavior. J Pediatr 2015;166:736–42.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Chen MH, Ha EH, Liao HF, Jeng SF, Su YN, Wen TW, et al. Perfluorinated compound levels in cord blood and neurodevelopment at 2 years of age. Epidemiology 2013;24:800–8.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Forns J, Iszatt N, White RA, Mandal S, Sabaredzovic A, Lamoree M, et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances measured in breast milk and child neuropsychological development in a Norwegian birth cohort study. Environ Int 2015;83:176–82.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Goudarzi H, Nakajima S, Ikeno T, Sasaki S, Kobayashi S, Miyashita C, et al. Prenatal exposure to perfluorinated chemicals and neurodevelopment in early infancy: the Hokkaido Study. Sci Total Environ 2016;541:1002–10.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Stein CR, Savitz DA, Bellinger DC. Perfluorooctanoate and neuropsychological outcomes in children. Epidemiology 2013;24:590–9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Wang Y, Rogan WJ, Chen HY, Chen PC, Su PH, Chen HY, et al. Prenatal exposure to perfluroalkyl substances and children’s IQ: The Taiwan maternal and infant cohort study. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2015;218:639–44.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Stein CR, Savitz DA. Serum perfluorinated compound concentration and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children 5-18 years of age. Environ Health Perspect 2011;119:1466–71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Fei C, Olsen J. Prenatal exposure to perfluorinated chemicals and behavioral or coordination problems at age 7 years. Environ Health Perspect 2011;119:573–8.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Vuong AM, Yolton K, Webster GM, Sjödin A, Calafat AM, Braun JM, et al. Prenatal polybrominated diphenyl ether and perfluoroalkyl substance exposures and executive function in school-age children. Environ Res 2016;147:556–64.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Harris MH, Oken E, Rifas-Shiman SL, Calafat AM, Ye X, Bellinger DC, et al. Prenatal and childhood exposure to perand polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and child cognition. Environ Int 2018;115:358–69.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Lien GW, Huang CC, Shiu JS, Chen MH, Hsieh WS, Guo YL, et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances in cord blood and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in seven-year-old children. Chemosphere 2016;156:118–27.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Høyer BB, Ramlau-Hansen CH, Obel C, Pedersen HS, Hernik A, Ogniev V, et al. Pregnancy serum concentrations of perfluorinated alkyl substances and offspring behaviour and motor development at age 5-9 years--a prospective study. Environ Health 2015;14:2.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 41. Liew Z, Ritz B, von Ehrenstein OS, Bech BH, Nohr EA, Fei C, et al. Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and childhood autism in association with prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances: a nested case-control study in the Danish National Birth Cohort. Environ Health Perspect 2015;123:367–73.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Ode A, Källén K, Gustafsson P, Rylander L, Jönsson BA, Olofsson P, et al. Fetal exposure to perfluorinated compounds and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in childhood. PLoS One 2014;9:e95891.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Bolin CM, Basha R, Cox D, Zawia NH, Maloney B, Lahiri DK, et al. Exposure to lead and the developmental origin of oxidative DNA damage in the aging brain. FASEB J 2006;20:788–90.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Wu J, Basha MR, Brock B, Cox DP, Cardozo-Pelaez F, McPherson CA, et al. Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-like pathology in aged monkeys after infantile exposure to environmental metal lead (Pb): evidence for a developmental origin and environmental link for AD. J Neurosci 2008;28:3–9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Fox DA, Grandjean P, de Groot D, Paule MG. Developmental origins of adult diseases and neurotoxicity: epidemiological and experimental studies. Neurotoxicology 2012;33:810–6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 46. Mastrantonio M, Bai E, Uccelli R, Cordiano V, Screpanti A, Crosignani P. Drinking water contamination from perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): an ecological mortality study in the Veneto Region, Italy. Eur J Public Health 2018;28:180–5.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 47. Johansson N, Eriksson P, Viberg H. Neonatal exposure to PFOS and PFOA in mice results in changes in proteins which are important for neuronal growth and synaptogenesis in the developing brain. Toxicol Sci 2009;108:412–8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 48. Johansson N, Fredriksson A, Eriksson P. Neonatal exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) causes neurobehavioural defects in adult mice. Neurotoxicology 2008;29:160–9.ArticlePubMed
- 49. Lee I, Viberg H. A single neonatal exposure to perfluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS) affects the levels of important neuroproteins in the developing mouse brain. Neurotoxicology 2013;37:190–6.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Viberg H, Lee I, Eriksson P. Adult dose-dependent behavioral and cognitive disturbances after a single neonatal PFHxS dose. Toxicology 2013;304:185–91.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Olney JW. New insights and new issues in developmental neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicology 2002;23:659–68.ArticlePubMed
- 52. Lee HG, Lee YJ, Yang JH. Perfluorooctane sulfonate induces apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells via a ROS-dependent protein kinase C signaling pathway. Neurotoxicology 2012;33:314–20.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Lee YJ, Lee HG, Yang JH. Perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells is mediated by ERK 1/2 pathway. Chemosphere 2013;90:1597–602.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Lee YJ, Choi SY, Yang JH. PFHxS induces apoptosis of neuronal cells via ERK1/2-mediated pathway. Chemosphere 2014;94:121–7.ArticlePubMed
- 55. Lee YJ, Choi SY, Yang JH. NMDA receptor-mediated ERK 1/2 pathway is involved in PFHxS-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells. Sci Total Environ 2014;491-2:227–34.Article
- 56. Lee YJ, Choi SY, Yang JH. AMP-activated protein kinase is involved in perfluorohexanesulfonate-induced apoptosis of neuronal cells. Chemosphere 2016;149:1–7.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Dunlop J, Matsui E, Sharma HP. Allergic rhinitis: environmental determinants. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2016;36:367–77.ArticlePubMed
- 58. Yang SN, Hsieh CC, Kuo HF, Lee MS, Huang MY, Kuo CH, et al. The effects of environmental toxins on allergic inflammation. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 2014;6:478–84.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 59. Takano H, Inoue KI. Environmental pollution and allergies. J Toxicol Pathol 2017;30:193–9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Holladay SD, Smialowicz RJ. Development of the murine and human immune system: differential effects of immunotoxicants depend on time of exposure. Environ Health Perspect 2000;108(Suppl 3):463–73.Article
- 61. Martino D, Prescott S. Epigenetics and prenatal influences on asthma and allergic airways disease. Chest 2011;139:640–7.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Peden-Adams MM, Keller JM, Eudaly JG, Berger J, Gilkeson GS, Keil DE. Suppression of humoral immunity in mice following exposure to perfluorooctane sulfonate. Toxicol Sci 2008;104:144–54.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 63. Guruge KS, Hikono H, Shimada N, Murakami K, Hasegawa J, Yeung LW, et al. Effect of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on influenza A virus-induced mortality in female B6C3F1 mice. J Toxicol Sci 2009;34:687–91.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Grandjean P, Andersen EW, Budtz-Jørgensen E, Nielsen F, Mølbak K, Weihe P, et al. Serum vaccine antibody concentrations in children exposed to perfluorinated compounds. JAMA 2012;307:391–7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Grandjean P, Heilmann C, Weihe P, Nielsen F, Mogensen UB, Budtz-Jørgensen E. Serum vaccine antibody concentrations in adolescents exposed to perfluorinated compounds. Environ Health Perspect 2017;125:077018.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 66. Granum B, Haug LS, Namork E, Stølevik SB, Thomsen C, Aaberge IS, et al. Pre-natal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances may be associated with altered vaccine antibody levels and immune-related health outcomes in early childhood. J Immunotoxicol 2013;10:373–9.ArticlePubMed
- 67. Goudarzi H, Miyashita C, Okada E, Kashino I, Chen CJ, Ito S, et al. Prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl acids and prevalence of infectious diseases up to 4 years of age. Environ Int 2017;104:132–8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Timmermann CA, Budtz-Jørgensen E, Jensen TK, Osuna CE, Petersen MS, Steuerwald U, et al. Association between perfluoroalkyl substance exposure and asthma and allergic disease in children as modified by MMR vaccination. J Immunotoxicol 2017;14:39–49.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 69. Kielsen K, Shamim Z, Ryder LP, Nielsen F, Grandjean P, Budtz-Jørgensen E, et al. Antibody response to booster vaccination with tetanus and diphtheria in adults exposed to perfluorinated alkylates. J Immunotoxicol 2016;13:270–3.ArticlePubMed
- 70. Buser MC, Scinicariello F. Perfluoroalkyl substances and food allergies in adolescents. Environ Int 2016;88:74–9.ArticlePubMed
- 71. Lee YJ, Park SJ, Yang JH. Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) activates mast cell-mediated allergic reaction. Organohalogen Compd 2017;79:718–21.
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Modifiable contributing factors to COVID-19: A comprehensive review
Ronald Neil Kostoff, Michael Brandon Briggs, Darja Kanduc, Saikat Dewanjee, Ramesh Kandimalla, Yehuda Shoenfeld, Alan L. Porter, Aristidis Tsatsakis
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2023; 171: 113511. CrossRef - Effect of prenatal perfluoroheptanoic acid exposure on spermatogenesis in offspring mice
Yijie Zhou, Weilian Sun, Qiuqin Tang, Yiwen Lu, Mei Li, Jing Wang, Xiumei Han, Di Wu, Wei Wu
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2023; 260: 115072. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Contaminants of Concern in Uganda: Occurrence, Sources, Potential Risks, and Removal Strategies
Gabson Baguma, Gadson Bamanya, Allan Gonzaga, Wycliffe Ampaire, Patrick Onen
Pollutants.2023; 3(4): 544. CrossRef - Association between maternal serum concentration of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) at delivery and acute infectious diseases in infancy
Zixia Wang, Rong Shi, Guodong Ding, Qian Yao, Chengyu Pan, Yu Gao, Ying Tian
Chemosphere.2022; 289: 133235. CrossRef - The Association between ADHD and Environmental Chemicals—A Scoping Review
Sonja Moore, Laura Paalanen, Lisa Melymuk, Andromachi Katsonouri, Marike Kolossa-Gehring, Hanna Tolonen
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(5): 2849. CrossRef - The Occurrence and Distributions of Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in groundwater after a PFAS leakage incident in 2018
Zhi Yuan Yong, Ki Yong Kim, Jeong-Eun Oh
Environmental Pollution.2020; : 115395. CrossRef - Dysregulated lipid and fatty acid metabolism link perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and impaired glucose metabolism in young adults
Zhanghua Chen, Tingyu Yang, Douglas I. Walker, Duncan C. Thomas, Chenyu Qiu, Leda Chatzi, Tanya L. Alderete, Jeniffer S. Kim, David V. Conti, Carrie V. Breton, Donghai Liang, Elizabeth R. Hauser, Dean P. Jones, Frank D. Gilliland
Environment International.2020; 145: 106091. CrossRef

 E-Submission
E-Submission Yeungnam University College of Medicine
Yeungnam University College of Medicine PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite